In the world of explosives, one compound stands out for its remarkable explosive power and versatility: Royal Demolition Explosive, commonly known as RDX. This powerful explosive has played a pivotal role in both military and civilian applications, showcasing its effectiveness in various fields.
- RDX Full Form: Introduction to RDX
- RDX Full Form: Manufacturing Process of RDX
- RDX Full Form:Characteristics
- RDX Full Form: Properties
- RDX Full Form: History
- RDX Full Form: Structure
- RDX Full Form: Emerging Chemicals List
- RDX Full Form: Applications of RDX
- RDX Full Form: Advantages of RDX
- RDX Full Form: Challenges of RDX
- RDX Full Form: Comparison with Other Explosive Compounds
- RDX Full Form: Safety Measures and Regulations
- RDX Full Form: Conclusion
- RDX Full Form: FAQs
Introduction to RDX


Join us as we journey through the explosive history, development, and applications of RDX, uncovering the science behind its detonation, its contribution to modern warfare, and its role in shaping industries such as construction, mining, and more. We’ll also examine the advantages and challenges associated with RDX, highlighting its explosive power while acknowledging the need for careful handling and safety measures.
As we embark on this exploration of RDX, we’ll delve into its its historical use in wartime, its manufacturing process, and its role in shaping both military and civilian landscapes. Additionally, we’ll shed light on the ethical considerations surrounding its use, and the innovations driving its future development.
RDX Manufacturing Process
Let’s take a closer look at the steps involved in the manufacturing of RDX:
- Raw Material Acquisition:
The manufacturing process begins with the acquisition of the necessary raw materials. The primary precursor chemicals used in RDX production are hexamine and nitric acid. - Nitration Reaction:
The key step in RDX synthesis is the nitration reaction. Hexamine, a white crystalline powder, is reacted with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of sulfuric . This reaction results in the formation of a nitramine compound known as hexamethylene tetramine dinitrate (HMXDN). - Isolation of HMXDN:
The HMXDN compound is isolated and purified through processes such as filtration, washing, and crystallization. This ensures that impurities and byproducts are removed, leading to a higher purity of the desired compound. - Cyclization Reaction:
HMXDN is subjected to a cyclization reaction, also known as the “cyclonite process.” This involves heating the compound at elevated temperatures in the presence of a catalyst. This process leads to the rearrangement of molecules, resulting in the formation of RDX crystals. - Washing and Purification:
The formed RDX crystals are washed and purified to remove any remaining impurities, catalyst residues, or unreacted compounds. This step enhances the quality and stability of the final RDX product.
RDX Full Form:Characteristics
High Explosive Power: RDX has a high detonation velocity, making it one of the most powerful army explosives.
Stability: It is particularly solid at room temperature, making it safe to address below controlled situations.
Sensitivity: While solid under normal conditions, it will become touchy while combined with different substances or subjected to intense heat, surprise, or friction.
Energy Density: RDX has a high strength content consistent with unit weight, making it powerful for military programs.
Versatility: It may be used on my own or as element in diverse explosive combinations, including C-4.
Non-Hygroscopic: It does not absorb moisture, which adds to its stability and usability in a number of environmental situations.
Chemical Composition: RDX is a nitrogen-wealthy organic compound with the formula C₃H₆N₆O₆, contributing to its high explosive overall performance.
RDX Full Form: Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Cyclotrimethylene trinitramine (Hexogen) |
| Molecular Formula | C₃H₆N₆O₆ |
| Molecular Weight | 222.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.82 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 204°C (400°F) |
| Detonation Velocity | 8,750 m/s |
| Sensitivity | Sensitive to shock, heat, and friction when not handled properly |
| Explosive Power | High energy release, used in military and industrial applications |
| Stability | Stable at room temperature, can be stored for long periods |
| Uses | Used in plastic explosives (like C-4), military-grade explosives, and detonators |
RDX Full Form: History
1899 – Discovery: RDX turned into first synthesized with the aid of German chemist Georg Friedrich Henning. However, its capability as a excessive explosive become not realized until an awful lot later.
Nineteen Twenties – Early Research: Initial studies into RDX’s explosive homes commenced in the Nineteen Twenties, in general in Germany, however its use remained limited.
Thirties – Development: During the Nineteen Thirties, research and improvement of RDX intensified as part of army programs in diverse countries, specially inside the UK and the USA.
World War II – Extensive Use: RDX become broadly utilized by Allied forces for the duration of World War II in bombs, shells, and torpedoes because of its excessive explosive strength. The British codenamed it “Research Department Explosive”.
C-four and Plastic Explosives: Post-WWII, RDX became a key issue within the improvement of plastic explosives together with C-4, which changed into used appreciably in army operations.
Cold War and Beyond: During the Cold War, RDX endured to be a crucial material in navy and defense applications, forming a part of missile warheads, detonators, and demolition prices.
Modern Applications: Today, RDX remains one of the maximum important navy explosives used in a extensive variety of contemporary munitions, inclusive of plastic explosives, formed expenses, and blasting caps.
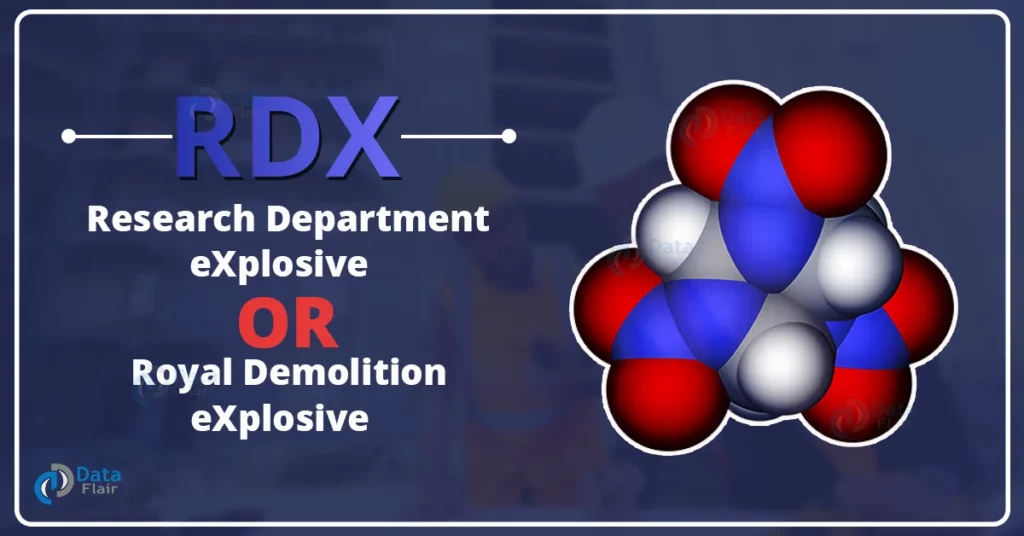
RDX Full Form: Structure
Molecular Formula: The chemical formula of RDX is C₃H₆N₆O₆, indicating it incorporates carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms.
Cyclic Nitramine: RDX is a cyclic nitramine compound, which means its structure consists of a ring shaped by means of alternating nitrogen and carbon atoms.
Three Nitramine Groups: The shape has three nitramine companies (-NO₂) attached to the nitrogen atoms inside the ring, contributing to its explosive properties.
Six-Membered Ring: The core shape of RDX is a 6-membered ring, composed of 3 carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms (C-N-C-N-C-N), which gives it stability and high power content.
Symmetry: The RDX molecule has a especially symmetrical structure, which influences its balance and controlled detonation homes.
Bonding: The sturdy C-N bonds and N-O bonds save a massive quantity of electricity, that’s launched rapidly at some point of detonation, resulting in a effective explosion.
Solid-State Crystalline Form: RDX usually exists as a white crystalline stable, and its strong shape contributes to its stability at room temperature, permitting safe handling below controlled conditions.
RDX Full Form: Emerging Chemicals List
| Chemical | Description | Applications/Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Graphene | A single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a 2D lattice. | Electronics, materials science, energy storage |
| MXenes | A family of 2D transition metal carbides, nitrides, or carbonitrides. | Energy storage, electromagnetic shielding, water purification |
| Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) | A class of fluorinated compounds used as refrigerants. | Refrigeration, air conditioning, foams |
| Perovskite Materials | A group of materials with a specific crystal structure, often used in solar cells. | Solar energy, LEDs, lasers |
| Boron Nitride Nanotubes | Tubular nanostructures made of boron and nitrogen. | Electronics, thermal management, lubricants |
| Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) | Compounds consisting of metal ions linked by organic ligands. | Gas storage, catalysis, sensors |
| Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) | Organic compounds that emit light in response to an electric current. | Displays, lighting |
Applications of RDX
- Military Ordnance: RDX is a staple ingredient in the production of military explosives and ordnance. It is used in the formulations for munitions such as grenades, artillery shells, and bombs. Its explosive power and stability make it a preferred choice for these applications, contributing to the effectiveness of modern warfare.
- Demolition and Controlled Blasting: In the construction and RDX plays a crucial role in controlled blasting operations. It helps break down rock formations, concrete structures, and other materials in a controlled manner.
- Propellants and Rocket Motors: RDX is utilized in the formulation of propellants and rocket motors due to its ability to release energy in a controlled and predictable manner.
- Explosive Welding: RDX is employed in a process known as explosive welding or explosive bonding. In this technique, controlled detonation of RDX creates a high-pressure shock wave that causes to impact and fuse together. This method is used to join dissimilar metals and alloys, enabling the creation of composite materials with unique properties.
Advantages of RDX
- Explosive Power: RDX boasts a high energy content and , making it one of the most powerful explosive compounds. This energy release is critical for applications that require significant force, such as military ordnance and controlled demolitions.
- Stability: Compared to some other explosives, RDX exhibits a higher level of stability, which is crucial for storage, transportation, and handling. Its stability reduces the risk of accidental detonation and allows for controlled use.
- Precision: RDX’s controlled and predictable detonation properties contribute to precision in applications like controlled blasting and military munitions. This precision minimizes collateral damage and ensures desired outcomes.
- Reduced Sensitivity to Shock: RDX is less sensitive to shock and impact compared to other explosive compounds, enhancing its , handling, and use.
- Compatibility with Binders: RDX can be mixed with binders to create plastic explosives like C-4. These plastic explosives are malleable and can be shaped to suit specific applications, making them versatile tools in various scenarios.
Challenges Of RDX
- Sensitivity to Initiation: While RDX is less sensitive to shock, it can still be initiated under certain conditions. Careful handling and are essential to prevent accidental detonation.
- Environmental Impact: The production and use of RDX may have environmental implications, particularly in areas where explosives are employed extensively. Contaminants from explosive residues can impact soil and water quality.
- Regulatory Oversight: Due to its potential for misuse, RDX is subject to strict regulations and oversight, particularly in its distribution and acquisition. Compliance with regulations is crucial to prevent illegal or unsafe usage.
- Safety Precautions: Handling and manufacturing RDX requires adherence to rigorous safety protocols to protect workers, facilities, and the environment. Failure to follow can result in accidents and injuries.
- Dual-Use Nature: RDX’s versatile applications mean that it has both civilian and military uses. This dual-use nature raises ethical considerations and necessitates measures to prevent misuse.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Ensuring a stable supply of high-quality for RDX production can be challenging due to geopolitical factors and changes in demand.
Comparison with Other Explosive Compounds
| Characteristic | RDX | TNT |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Content | RDX generally has a higher energy content than TNT, resulting in a more potent explosive power. | While TNT is powerful, RDX surpasses it in terms of energy release upon detonation. |
| Sensitivity | RDX is less sensitive to shock and impact compared to TNT, contributing to safer handling and storage. | TNT is relatively more sensitive to shock and friction, requiring careful handling protocols. |
| Usage | RDX is commonly used in military ordnance, controlled demolition, and various applications requiring a high-energy explosive. | TNT has historical significance and is used in military and industrial applications, including mining and construction. |
| Stability | RDX offers good stability, but its sensitivity to heat can be a consideration in certain situations. | TNT is known for its stability and resistance to detonation under most conditions. |
Safety Measures and Regulations
- Personnel Training:
Individuals working with RDX should undergo comprehensive training in handling, storage, and safety protocols. This includes understanding the compound’s properties, sensitivity, and proper procedures. - Proper Handling:
RDX should be handled with care to avoid any shock, friction, or impact that could initiate detonation. Tools and equipment should be non-sparking and appropriate for the task. - Storage Guidelines:
RDX must be stored in designated storage facilities that meet . Storage areas should be well-ventilated, dry, and equipped with fire suppression systems. - Transport Regulations:
Transporting RDX requires compliance with transportation regulations set by relevant authorities. Proper packaging, labeling, and documentation are essential to ensure safe transit.
Conclusion
In the realm of explosive materials, the handling, storage, and utilization of Royal Demolition eXplosive (RDX) demand the utmost commitment to safety. As we conclude our exploration of safety measures and regulations surrounding RDX, it’s evident that responsible practices are essential to mitigate risks, protect personnel, and safeguard the environment.
Comprehensive personnel training is the cornerstone of safe RDX management. Equipping individuals with knowledge about RDX’s properties, sensitivities, and proper procedures empowers them to handle this potent compound with confidence and competence. From the moment RDX is acquired to its various applications, adherence to established safety protocols is non-negotiable.
FAQs
Q1:What is the full form of RDX?
A: RDX stands for Research Department Explosive.
Q2: When was RDX first synthesized and what was its original full form?
A: RDX was first synthesized in the late 19th century, and its full form, Research Department Explosive, was adopted in the 1920s
Q3: Does RDX have any other names or full forms?
A: Yes, RDX is also known as Cyclonite or Hexogen, but Research Department Explosive is the most commonly used full form.
Q4: How is the full form of RDX used in military terminology?
A: In military terminology, Research Department Explosive (RDX) is used to describe a powerful and versatile explosive used in various munitions and demolition charges.
Q5: Are there any other compounds with similar full forms to RDX?
A: While RDX specifically refers to Research Department Explosive, other explosives may have different full forms related to their composition or use, such as TNT (Trinitrotoluene).
 60 minutes of Duration
60 minutes of Duration