Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) represent a dynamic integration of computational algorithms and physical processes, manifesting as a new class of engineered systems. CPS blend the digital and physical worlds, allowing seamless interactions between humans, machines, and the environment.
- Introduction: CPS full form
- Overview: CPS full form
- Interdisciplinary Foundations of CPS: CPS full form
- Importance: CPS full form
- Design: CPS full form
- Mobile cyber-physical systems: CPS full form
- Applications and Use Cases of CPS: CPS full form
- Challenges and Concerns in CPS: CPS full form
- Technologies and Components in CPS: CPS full form
- Architecture and Design Principles
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction : CPS full form


Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) constitute a pivotal advancement within the integration of physical procedures with computational talents and networked verbal exchange. CPS merge the bodily and digital worlds, allowing seamless interactions among physical additives and virtual systems to reveal, manage, and optimize complicated approaches in real-time.
At its middle, CPS harness the strength of interconnected sensors, actuators, and computational algorithms to accumulate records from bodily environments, analyze it in real-time, and autonomously modify bodily methods. This integration permits CPS to decorate performance, accuracy, and reliability throughout diverse domains, from production and transportation to healthcare and infrastructure management.
The evolution of CPS is driven by means of advancements in several foundational technologies, consisting of embedded structures, Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and conversation networks. These technologies enable CPS to display and respond to changes of their environment, predict destiny states, and optimize operations to reap favored outcomes.
However, the mixing of CPS also introduces new demanding situations, specially in cybersecurity, where the interconnected nature of CPS additives increases vulnerability to cyber threats consisting of unauthorized get admission to, information breaches, and machine disruptions. Addressing those challenges calls for strong cybersecurity measures, secure layout concepts, and ongoing vigilance to protect touchy facts and ensure the integrity and reliability of CPS operations.
Overview: CPS full form
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Integrations of computation, networking, and physical processes involving real-time interaction and control. |
| Components | Sensors, actuators, algorithms, software, and physical processes. |
| Real-Time Processing | Requires timely processing to respond to changes in the physical environment. |
| Applications | Smart grids, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, healthcare systems, smart cities, etc. |
| Challenges | Security, reliability, real-time constraints, and complexity of integration. |
| Interdisciplinary Nature | Combines expertise from computer science, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, and other fields. |
| Examples | Smart thermostats, automated manufacturing systems, robotic surgery systems, traffic management systems, and environmental monitoring systems. |
Interdisciplinary Foundations of CPS: CPS full form
Integration of Knowledge: Interdisciplinary processes combo theories, methodologies, and insights from one-of-a-kind fields to create a greater complete know-how of complicated issues. For instance, fixing environmental problems would possibly require expertise from biology, chemistry, engineering, and social sciences.
Collaboration and Communication: Effective interdisciplinary work is based on collaboration between professionals from various disciplines. Clear verbal exchange and mutual understanding are important for integrating diverse views and accomplishing common dreams.
Complex Problem Solving: Many real-international troubles are too complex to be addressed with the aid of a unmarried area. Interdisciplinary foundations assist in breaking down these problems into achievable additives and addressing them from multiple angles.
Innovative Solutions: Combining knowledge from distinct fields frequently ends in modern solutions that wouldn’t emerge inside a unmarried subject. For example, improvements in clinical generation regularly result from the integration of engineering, laptop science, and medicinal drug.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Interdisciplinary paintings requires flexibility in wondering and flexibility to exclusive methodologies. Professionals must be inclined to examine from different disciplines and adapt their methods hence.
Shared Methodologies: Interdisciplinary research frequently involves growing or adopting shared methodologies that can be implemented across disciplines. This may consist of statistics analysis strategies, modeling strategies, or experimental designs that may be used in more than one fields.
Importance: CPS full form
| Domain | Importance of CPS |
|---|---|
| Industry/Manufacturing | – Automation: Enhances efficiency, precision, and safety in manufacturing processes. – Predictive Maintenance: Monitors equipment health to prevent failures and reduce downtime. |
| Healthcare | – Real-time Monitoring: Allows continuous monitoring of patient health, enabling timely interventions. – Remote Surgery: Facilitates precise and controlled remote surgeries through robotic systems. |
| Transportation | – Autonomous Vehicles: Enables the development of self-driving cars and drones, improving safety and efficiency. – Traffic Management: Optimizes traffic flow and reduces congestion in smart cities. |
| Energy | – Smart Grids: Balances supply and demand, improving energy efficiency and reliability. – Renewable Integration: Manages the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. |
| Agriculture | – Precision Farming: Uses data to optimize crop yields, reduce waste, and manage resources efficiently. – Automated Irrigation: Controls water usage based on real-time soil moisture data. |
| Security/Defense | – Surveillance Systems: Enhances security through automated monitoring and threat detection. – Autonomous Defense Systems: Implements real-time decision-making in defense scenarios. |
| Smart Homes/Buildings | – Energy Management: Optimizes energy usage in homes and buildings for cost savings and environmental benefits. – Automated Control: Manages lighting, heating, and security systems for convenience and safety. |
| Environmental Monitoring | – Disaster Management: Provides early warning systems for natural disasters like earthquakes and floods. – Pollution Control: Monitors air and water quality, helping to enforce environmental regulations. |
Design: CPS full form
Automation in Industry/Manufacturing: CPS complements industrial automation by means of growing efficiency, precision, and protection in manufacturing procedures. It also allows predictive renovation by way of constantly tracking gadget health, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Real-time Healthcare Monitoring: In healthcare, CPS gives actual-time monitoring of affected person vitals, allowing for well timed interventions. It supports superior scientific tactics like remote surgical operation, wherein robot systems offer precision and manipulate from a distance.
Advancements in Transportation: CPS is essential inside the development of independent motors, along with self-riding vehicles and drones, improving transportation safety and efficiency. It additionally optimizes site visitors management systems in smart cities, decreasing congestion and improving city mobility.
Energy Efficiency in Smart Grids: CPS performs a key function in smart grids via balancing energy supply and call for, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of strength structures. It additionally enables the mixing of renewable power resources, contributing to sustainable power solutions.
Precision Agriculture: In agriculture, CPS enables precision farming techniques, optimizing crop yields, decreasing waste, and improving aid control. Automated irrigation structures use real-time soil moisture statistics to manipulate water usage efficaciously, protecting sources.
Enhanced Security and Defense: CPS enhances security thru state-of-the-art surveillance systems that automate monitoring and danger detection. In protection, independent systems utilize real-time decision-making capabilities to respond swiftly and accurately in critical conditions.
Mobile cyber-physical systems: CPS full form
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Mobile Cyber-Physical Systems (MCPS) are CPS where mobility is a key feature, integrating computation, communication, and control with mobile entities such as vehicles, drones, or robots. |
| Components | – Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, drones, robots, vehicles. – Sensors/Actuators: Embedded in mobile devices to gather data and interact with the environment. – Communication Networks: Wireless technologies (e.g., Wi-Fi, 4G/5G, Bluetooth) that enable real-time data exchange between mobile entities and centralized systems. |
| Applications | – Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars that navigate and interact with their environment in real-time. – Drones: Used for delivery, surveillance, and agricultural monitoring. – Wearable Technology: Health monitoring devices that collect and transmit physiological data. – Smartphones: Applications in navigation, augmented reality, and mobile health (mHealth). |
| Challenges | – Real-Time Communication: Ensuring low latency and reliable data exchange between mobile units and control systems. – Security: Protecting MCPS from cyber-attacks that could disrupt mobile operations or compromise data. – Energy Efficiency: Managing the power consumption of mobile devices to prolong operational time. – Interoperability: Ensuring different mobile entities and systems can work together seamlessly. |
| Benefits | – Increased Mobility: Enhanced flexibility and reach, allowing systems to operate in diverse and dynamic environments. – Scalability: Ability to scale operations by adding more mobile units as needed. – Improved Efficiency: Real-time data processing and decision-making optimize resource use and operational efficiency. |
| Use Cases | – Smart Transportation: Traffic management and coordination of autonomous vehicles. – Disaster Response: Drones and robots deployed for search and rescue missions in disaster-stricken areas. – Healthcare: Mobile health monitoring for real-time patient care. – Agriculture: Drones and robots for precision farming and crop monitoring. |
| Future Trends | – 5G and Beyond: Enhanced connectivity will further enable real-time, reliable communication for MCPS. – Edge Computing: Distributed processing closer to the data source to reduce latency. – AI Integration: Advanced AI algorithms for autonomous decision-making in mobile entities. – IoT Integration: Greater synergy between MCPS and IoT devices for a more connected ecosystem. |
Applications and Use Cases of CPS: CPS full form
Smart Cities: CPS enable city infrastructure to come to be greater green and responsive. They display and control traffic waft, optimize power usage in homes, and beautify public protection thru clever surveillance structures. Smart metropolis initiatives use CPS to enhance great of existence, reduce environmental effect, and manage assets successfully.
Healthcare: CPS are remodeling healthcare delivery by way of permitting far off patient tracking, personalized remedy, and automated scientific methods. Wearable gadgets and sensors accumulate actual-time fitness facts, which CPS analyze to provide early disorder detection, manipulate chronic situations, and enhance patient results thru timely interventions.
Autonomous Vehicles: CPS play a crucial function in the development of self sustaining automobiles (AVs). They integrate sensors, actuators, and AI algorithms to understand the environment, make real-time choices, and navigate properly without human intervention. CPS in AVs aim to enhance street protection, optimize traffic go with the flow, and enable green transportation structures.
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: In production, CPS facilitate the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles by using creating clever factories. They allow seamless verbal exchange between machines, automate manufacturing processes, and support predictive renovation via continuous monitoring of device overall performance. CPS in production enhance productiveness, reduce downtime, and enable agile response to market demands.
Energy Grids: CPS beautify the efficiency and reliability of strength generation, distribution, and intake. Smart grids integrate CPS to monitor energy call for in actual-time, stability deliver from renewable assets, and control electricity garage structures. CPS optimize power usage, reduce wastage, and aid the integration
Challenges and Concerns in CPS: CPS full form
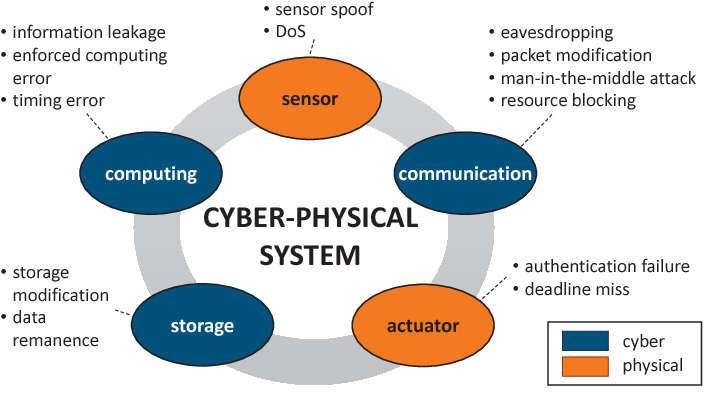
Security and Privacy: CPS are prone to cyber threats because of their interconnected nature and reliance on statistics exchange. Ensuring robust cyber – security measures, including encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection, is essential to defend towards malicious assaults and ensure facts integrity and person privateness.
Reliability and Resilience: CPS need to function reliably in dynamic and unpredictable environments. They need to face up to hardware disasters, communique disruptions, and environmental adjustments while retaining steady performance. Designing fault-tolerant systems and implementing redundancy techniques are crucial to beautify resilience and minimize downtime.
Interoperability: CPS regularly contain heterogeneous systems and devices from unique companies, which can also use diverse conversation protocols and facts formats. Achieving seamless interoperability between these components is hard however essential for effective collaboration and records exchange throughout the gadget.
Scalability: As CPS develop in complexity and scale, handling and scaling infrastructure becomes an increasing number of tough. Designing scalable architectures, optimizing useful resource allocation, and ensuring efficient records processing are essential to aid the developing demands of huge-scale CPS deployments.
Ethical and Legal Considerations: CPS raise ethical concerns related to statistics ownership, accountability for system screw ups, and the effect on human lives and society. Addressing moral implications, establishing clean regulatory frameworks, and making sure responsible deployment and use of CPS are crucial for fostering believe and acceptance.
Skills and Expertise: Developing and maintaining CPS requires interdisciplinary expertise in fields such as computer science, engineering, cybersecurity, and data analytics. There is a need for skilled professionals capable of designing, deploying, and managing complex CPS solutions to address emerging challenges and ensure successful implementation.
Technologies and Components in CPS: CPS full form
Sensors and Actuators: Sensors detect bodily parameters consisting of temperature, pressure, motion, and chemical composition, while actuators manipulate bodily tactics by means of converting electrical indicators into mechanical motion. These components shape the foundation of CPS through allowing actual-time information acquisition and bodily machine manipulation.
Embedded Systems: Embedded systems include hardware and software designed for precise functions within CPS. They include microcontrollers, programmable common sense controllers (PLCs), and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) that system facts, execute algorithms, and interface with sensors and actuators in real-time.
Communication Technologies: CPS rely on diverse conversation protocols and technology to permit facts alternate between bodily additives and computational units. These encompass stressed out technologies consisting of Ethernet and fieldbus protocols, in addition to wi-fi technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cell networks. Reliable and occasional-latency verbal exchange is vital for coordinating CPS operations.
Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computational electricity in the direction of the information source, decreasing latency and improving actual-time decision-making in CPS. Edge devices manner statistics domestically earlier than transmitting relevant data to centralized systems or cloud platforms, improving system responsiveness and scalability.
Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide scalable storage and computational for processing large volumes of facts generated through CPS. They help statistics analytics, machine learning fashions, and faraway control of CPS deployments, allowing scalability, flexibility, and accessibility of CPS packages.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies enhance CPS development, training, and maintenance processes. They enable visualizing sensor data, simulating system behavior in real-world environments, and providing immersive training experiences for operators and maintenance personnel.
Architecture and Design Principles
| Architecture and Design | Description |
|---|---|
| Hierarchical Architecture | Designing a structure with multiple levels of hierarchy, where each level focuses on specific functionalities and levels of abstraction, facilitating efficient organization, management, and optimization of the system. |
| Layered Architecture | Organizing CPS into distinct layers, each responsible for specific tasks (e.g., data acquisition, processing, application), enhancing modularity, scalability, and ease of development, maintenance, and integration. |
| Distributed Architecture | Distributing components and functionalities across the system to improve performance, fault tolerance, and scalability, allowing for parallel processing and reducing the risk of system failures. |
| Event-Driven Architecture | Structuring the system to respond to events triggered by changes in the environment or within the system itself, enabling real-time responsiveness and efficient handling of asynchronous events and data updates. |
| Modular Design | Breaking down the CPS into smaller, manageable modules or components, promoting reusability, ease of maintenance, and flexibility in design changes, upgrades, and integration of new functionalities. |
Industrial Applications of CPS
Threat Landscape: CPS face various cyber threats, such as unauthorized get entry to, records breaches, malware injection, and denial-of-provider (DoS) attacks. The interconnected nature of CPS components increases their vulnerability to cyber incidents.
Risk Assessment and Management: Conducting comprehensive risk exams is important to become aware of vulnerabilities and verify the impact of cyber threats on CPS operations. Implementing hazard control strategies allows prioritize cybersecurity investments and assets.
Secure Architecture Design: Designing CPS with security in thoughts includes implementing defense-in-depth principles, in which a couple of layers of protection controls (e.G., firewalls, get right of entry to controls, encryption) are integrated into the system structure. Secure layout mitigates vulnerabilities from the outset.
Data Security and Privacy: Protecting touchy information within CPS is crucial. Encryption strategies protect records integrity and confidentiality in the course of storage, transmission, and processing. Privacy-improving technology make certain compliance with policies and protect consumer records.
Access Control and Authentication: Implementing robust get admission to manage mechanisms guarantees that most effective authorized users and devices can engage with CPS components. Multi-element authentication (MFA) and position-based get right of entry to control (RBAC) restrict get admission to primarily based on user privileges and roles.
Intrusion Detection and Response: Continuous monitoring and real-time detection of suspicious activities are essential for early risk detection in CPS. Intrusion detection systems (IDS), anomaly detection algorithms, and safety information and event management (SIEM) tools help become aware of and respond to security incidents right away.
Conclusion
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) represent a transformative integration of computational capabilities with physical processes, revolutionizing industries and everyday life. CPS leverage technologies such as sensors, actuators, AI, and communication networks to enable real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of complex systems.
Throughout this exploration, we’ve seen how CPS enhance efficiency, productivity, and safety across various domains, including manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and smart cities. They enable predictive maintenance, autonomous decision-making, and adaptive responses to dynamic environments, thereby improving operational reliability and resource utilization.
FAQs
Q1: What are Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)?
A: Cyber-Physical Systems are integrated systems of computational algorithms and physical components that interact with and control physical processes. They merge the physical and virtual worlds through sensors, actuators, and networked communication.
Q2: What are some examples of Cyber-Physical Systems?
A: Examples include smart grids for energy management, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation systems, healthcare monitoring devices, and smart city infrastructure like traffic monitoring and control systems.
Q3: What are the key technologies that enable Cyber-Physical Systems?
A: CPS rely on technologies such as sensors and actuators, embedded systems, communication networks (wired and wireless), edge computing, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML).
Q4: How do Cyber-Physical Systems impact cybersecurity?
A: CPS introduce cybersecurity challenges due to their interconnected nature and reliance on data exchange. They require robust security measures to protect against cyber threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and system disruptions.
Q5: What are the applications of Cyber-Physical Systems in industry?
A: CPS are used in smart manufacturing (Industry 4.0), supply chain management, predictive maintenance, energy grid optimization, robotics and automation, quality control, and safety systems.






