Natural Language Processing (NLP) represents a transformative department of system getting to know technology, empowering computers with the exceptional functionality to decipher, manipulate, and actually recognize human language. In modern-day technology, enterprises locate themselves inundated with enormous troves of textual and vocal records stemming from a mess of conversation channels, together with however now not restricted to emails, text messages, social media streams, video content, and audio recordings.


Why is NLP important?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) holds profound significance in our virtual age for several compelling motives:
- Effective Communication with Machines: NLP bridges the distance between human language and computers. It allows us to speak with machines using natural language, making the era extra handy and consumer-pleasant. This is pivotal for the development of consumer interfaces, virtual assistants, and chatbots that decorate human-machine interactions.
- Data Insights: In our information-driven global, a significant amount of statistics is saved in unstructured textual content, together with emails, social media posts, and documents. NLP algorithms can extract precious insights, styles, and tendencies from these textual facts, aiding organizations in making knowledgeable choices, improving client studies, and staying competitive.
- Automation and Efficiency: NLP automates time-ingesting and exertions-extensive obligations, consisting of textual content summarization, translation, sentiment evaluation, and content categorization. This automation now not only saves time but also reduces the threat of errors associated with guide processing.
- Personalization: NLP is instrumental in creating personalised personal reviews. By analyzing personal choices and conduct from textual statistics, agencies can tailor content material, recommendations, and advertisements to character customers, thereby growing engagement and customer pleasure.
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP can determine the sentiment or emotional tone of a bit of textual content. This is beneficial for groups to gauge public opinion, client comments, and emblem sentiment in actual time, letting them reply hastily to both fine and bad feedback.
Companies use it for several automated tasks, such as:
• Process, analyze, and archive large documents
• Analyze customer feedback or call centre recordings
• Run chatbots for automated customer service
• Answer who-what-when-where questions
• Classify and extract text
You can also integrate NLP in customer-facing applications to communicate more effectively with customers. For example, a chatbot analyzes and sorts customer queries, responding automatically to common questions and redirecting complex queries to customer support. This automation helps reduce costs, saves agents from spending time on redundant queries, and improves customer satisfaction.
Fundamentals of NLP
Natural Language Processing (NLP) holds profound significance in our virtual age for several compelling reasons:
- Effective Communication with Machines: NLP bridges the distance between human language and computer systems. It enables us to speak with machines through the usage of natural language, making era greater accessible and person-pleasant. This is pivotal for the development of consumer interfaces, virtual assistants, and chatbots that enhance human-device interactions.
- Data Insights: In our records-driven global, an extensive quantity of facts is stored in unstructured text, inclusive of emails, social media posts, and files. NLP algorithms can extract valuable insights, patterns, and tendencies from these textual records, assisting organizations in making knowledgeable decisions, improving consumer stories, and staying competitive.
- Automation and Efficiency: NLP automates time-eating and exertions-intensive responsibilities, inclusive of textual content summarization, translation, sentiment analysis, and content material categorization. This automation now not only saves time but also reduces the danger of mistakes related to manual processing.
- Personalization: NLP is instrumental in creating personalised user reviews. By studying user options and behaviour from textual statistics, corporations can tailor content, tips, and advertisements to individual customers, thereby growing engagement and customer pride.
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP can determine the sentiment or emotional tone of a chunk of textual content. This is useful for organizations to gauge public opinion, consumer remarks, and logo sentiment in actual time, permitting them to respond hastily to each positive and negative feedback.
How does NLP work?
Natural language processing (NLP) combines computational linguistics, machine getting to know, and deep knowledge of models to manner human language.
- Computational linguistics: Computational linguistics is the technology of knowledge and constructing human language fashions with computers and software program gear. Researchers use computational linguistics strategies, including syntactic and semantic analysis, to create frameworks that help machines understand conversational human language. Tools like language translators, textual content-to-speech synthesizers, and speech popularity software are based on computational linguistics.
- Machine learning: Machine mastering is a technology that trains a computer with sample records to enhance its performance. Human language has numerous functions like sarcasm, metaphors, versions in sentence shape, plus grammar and utilization exceptions that take people years to analyze. Programmers use machine-getting-to-know strategies to teach NLP packages to recognize and accurately apprehend these capabilities from the beginning.
- Deep mastering is a particular field of machine-gaining knowledge that teaches computer systems to examine and think like human beings. It involves a neural community that consists of information processing nodes based to resemble the human mind. With deep mastering, computer systems recognize, classify, and co-relate complicated patterns inside the entered information.
- NLP implementation steps: Typically, NLP implementation begins by amassing and getting ready unstructured text or speech facts from resources like cloud data warehouses, surveys, emails, or inner business manner applications.
- Tokenization breaks a sentence into individual units of words or phrases.
- Stemming and lemmatization simplify words into their root form. For example, these processes turn “starting” into “start.”
- Stop word removal ensures that words that do not add significant meaning to a sentence, such as “for” and “with,” are removed.
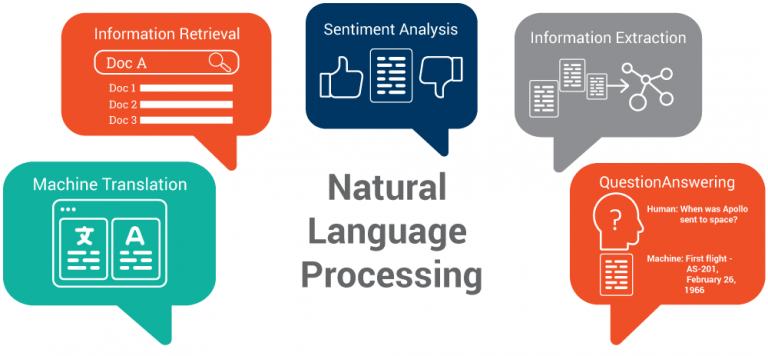
NLP Applications
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: NLP powers virtual helpers like Siri and Alexa for natural language interactions, from answering queries to setting reminders.
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP gauges public sentiment in social media, reviews, and news, aiding businesses and policymakers.
- Language Translation: NLP drives tools like Google Translate for cross-language communication.
- Text Summarization: NLP condenses lengthy documents into concise summaries for easier comprehension.
- Information Extraction: NLP extracts structured data, like names and dates, from unstructured text.
- Question Answering Systems: NLP enables systems like IBM Watson to answer questions from vast knowledge databases.
- Content Recommendation: NLP powers Netflix and Spotify to suggest content based on user preferences.
- Healthcare: NLP aids in processing medical records, patient data extraction, and even disease diagnosis.
- Legal Document Analysis: NLP accelerates legal document review, identifying critical information for professionals.
- Customer Support: NLP-driven chatbots handle routine customer inquiries, freeing human agents for complex issues.
Conclusion
In the end, Natural Language Processing (NLP) represents a transformative field at the intersection of linguistics and artificial intelligence. Its applications span a multitude of industries and domains, reshaping how we interact with generation and information.
NLP permits machines to recognize, interpret, and generate human language, providing a myriad of benefits, which include greater verbal exchange with digital assistants, sentiment evaluation for organizations and policymakers, go-language translation, textual content summarization, and dependent facts extraction. It empowers question-answering structures, helps content recommendations, streamlines healthcare facts analysis, speeds up prison report evaluate, and optimizes customer support via chatbots.
Frequently Asked Question
NLP has numerous applications, including chatbots, sentiment analysis, language translation, text summarization, information extraction, and content recommendation, among others.
Sentiment analysis uses NLP to determine the emotional tone or sentiment expressed in text, such as positive, negative, or neutral. It’s often used to gauge public opinion or customer feedback.
NLP faces challenges like handling ambiguity in language, understanding context, dealing with multiple languages, and addressing bias in data and algorithms.






