A Lathe Machine Operations is a flexible and vital device withinside the area of machining and metalworking. It operates through rotating a workpiece on its axis to carry out numerous operations including cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, or deformation with equipment which might be implemented to the workpiece to create an item with symmetry approximately that axis. This functionality to govern a workpiece whilst it rotates permits for specific manipulate and regular consequences in shaping materials.
The records of lathe machines dates lower back to historical times, with the earliest variations believed to were advanced through the Egyptians round 1300 BCE. These early lathes had been simple, which includes a two-character operation in which one grew to become the wooden workpiece with a rope whilst the alternative used a pointy device to reduce shapes. Over centuries, the layout advanced significantly.
- Components of a Lathe Machine
- Types of Lathe Machines
- Lathe Machine Accessories and Attachments
- Basic Lathe Machine Operations
- Advanced Lathe Machine Operations
- Lathe Machine Tools and Cutting Instruments
- Workholding Techniques on a Lathe Machine
- Lathe Machine Safety Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
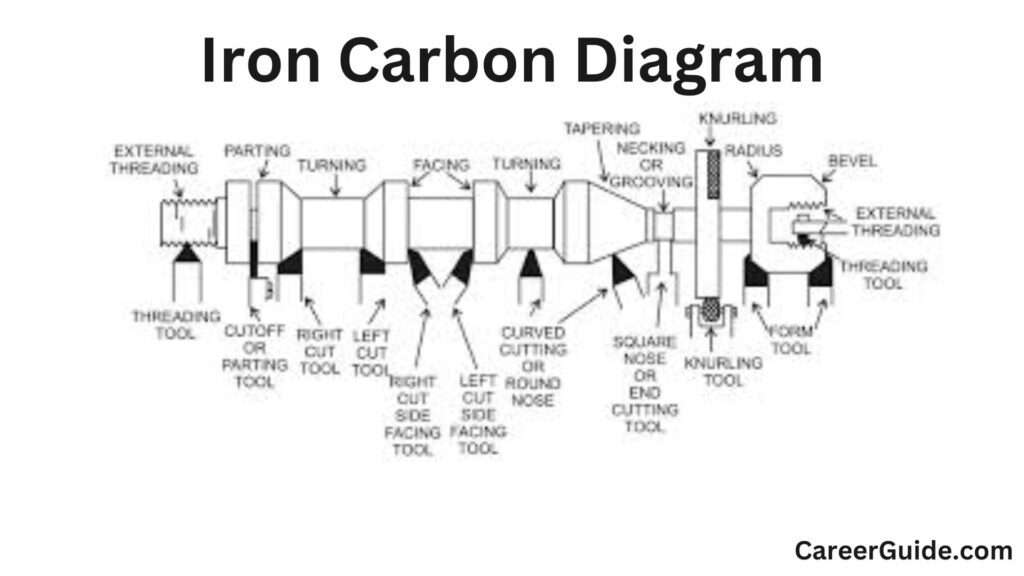
Components of a Lathe Machine
Bed
The mattress is the muse of the lathe machine. It is a inflexible and strong shape that helps all different additives and guarantees correct alignment and balance throughout machining operations. Typically crafted from forged iron, the mattress absorbs vibrations and gives a strong base for precision work.
Headstock
The headstock is established at the left stop of the lathe mattress and homes the primary spindle, gears, and pace manipulate mechanisms. It is accountable for protecting and rotating the workpiece. The headstock additionally helps numerous attachments consisting of chucks, collets, and faceplates that grip the workpiece.
Tailstock
The tailstock is placed at the proper facet of the mattress and may slide alongside it. It helps the opposite stop of the workpiece and may be adjusted to house exceptional lengths. The tailstock additionally holds gear consisting of drill bits and reamers, making an allowance for extra operations like drilling and boring.
Carriage
The carriage is a movable platform that slides alongside the mattress`s approaches and holds the slicing device. It includes numerous components consisting of the saddle, move-slide, compound rest, and apron. The carriage lets in specific motion of the slicing device in each longitudinal and move directions, permitting numerous machining operations.
Chuck
The chuck is a clamping tool connected to the spindle withinside the headstock. It holds the workpiece securely throughout machining. Chucks are available numerous types, consisting of three-jaw, four-jaw, and collet chucks, every appropriate for exceptional sizes and styles of workpieces. They make certain that the workpiece is targeted and strong throughout rotation.
Spindle
The spindle is a rotating shaft that extends from the headstock. It is pushed via way of means of the lathe’s motor and transmits energy to the workpiece. The spindle pace may be adjusted to healthy exceptional substances and slicing conditions. It is a vital factor that determines the precision and pleasant of the machining process.
Tool Post
The device submit is established at the carriage and holds the slicing device in place. It lets in for brief and clean modifications of gear and specific positioning. There are numerous kinds of device posts, consisting of the brief-alternate device submit and the four-manner device submit, every supplying exceptional tiers of pliability and comfort for the machinist.
Types of Lathe Machines
Engine Lathe
The engine lathe is one of the maximum not unusualplace and flexible kinds of lathes used withinside the industry. It is appropriate for a extensive variety of operations, consisting of turning, facing, threading, and drilling. The engine lathe is characterised via way of means of its easy construction, ease of operation, and capacity to carry out each small and big-scale machining responsibilities. It is broadly utilized in renovation shops, device rooms, and academic institutions.
Turret Lathe
The turret lathe is designed for excessive-extent manufacturing and repetitive machining operations. It functions a turret that could maintain more than one equipment, taking into account brief device adjustments and decreasing downtime. The turret may be turned around to deliver distinctive equipment into position, making it best for complicated machining responsibilities that require more than one operations. Turret lathes are usually used withinside the production of small, precision elements.
Capstan Lathe
Similar to the turret lathe, the capstan lathe is likewise used for excessive-extent manufacturing. The predominant distinction is that the capstan lathe functions a capstan head hooked up on a ram, taking into account faster and less complicated device adjustments. The capstan lathe is in particular appropriate for batch manufacturing and is frequently utilized in industries in which a big variety of same elements want to be produced efficiently.
Tool Room Lathe
The device room lathe is designed for precision paintings and is usually utilized in device and die making, in addition to in studies and improvement labs. It gives excessive accuracy and pleasant manipulate over machining operations. Tool room lathes are commonly smaller in length as compared to engine lathes and are ready with extra functions including variable velocity manipulate and improved device maintaining capabilities, making them best for tricky and exact paintings.
CNC Lathe
(Computer Numerical Control) lathes are the maximum superior form of lathe machines, incorporating pc generation to govern machining operations. CNC lathes provide excessive precision, repeatability, and automation. They can carry out complicated machining responsibilities with minimum human intervention, making them appropriate for big-scale manufacturing and tricky designs. CNC lathes are broadly used withinside the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries because of their performance and versatility.
Lathe Machine Accessories and Attachments
Lathe Centers
Facilities are crucial add-ons used to help the workpiece for the duration of machining. There are principal sorts:
Live Center: Mounted withinside the tailstock, it rotates with the workpiece, decreasing friction and warmth generation. It is good for excessive-pace operations and allows in preserving alignment and stability.
Dead Center: Also located withinside the tailstock, it does now no longer rotate and is used for lower-pace operations. Dead facilities are generally hardened to resist the friction and put on due to the rotating workpiece.
Steady Rest and Follower Rest
These are used to help lengthy or narrow workpieces that can bend or deflect below slicing forces.
Steady Rest: Mounted at the lathe bed, it helps the workpiece at a hard and fast point, presenting extra rigidity. It is specifically beneficial whilst machining lengthy shafts or bars.
Follower Rest: Attached to the carriage, it movements at the side of the slicing tool, presenting non-stop help to the workpiece close to the slicing zone. This is useful for preserving accuracy and stopping deflection for the duration of the machining of lengthy, narrow elements.
Lathe Chucks
Lathe chucks are clamping gadgets connected to the spindle for containing the workpiece securely for the duration of machining. Common sorts include:
Three-Jaw Chuck: Self-centering and perfect for containing spherical or hexagonal workpieces. It permits for brief and smooth centering however is much less unique for abnormal shapes.
Four-Jaw Chuck: Independently adjustable jaws make it appropriate for containing irregularly formed workpieces. It gives better precision and versatility in centering workpieces of diverse shapes.
Collet Chuck: Uses collets to keep the workpiece with excessive precision and grip. It is appropriate for small, cylindrical elements and gives high-quality centering and concentricity.
Faceplate
A faceplate is a flat, round plate hooked up at the spindle. It has slots and holes for securing workpieces which might be too big or irregularly formed to healthy right into a chuck. Workpieces may be bolted at once to the faceplate or clamped the use of diverse fixtures. Faceplates are normally used for turning operations on big, non-cylindrical elements or for operations requiring unique alignment and balancing.
Mandrel
A mandrel is a cylindrical shaft inserted into the workpiece to help it for the duration of machining. It is used for containing hole or tubular workpieces, making sure they stay concentric for the duration of operations. Mandrels are available in diverse sorts, inclusive of increasing mandrels that grip the inner floor of the workpiece and tapered mandrels that healthy into tapered holes. They are important for correct inner machining and completing operations.
Basic Lathe Machine Operations
Lathe machines carry out numerous important operations that form substances into specific and useful additives. The fundamental operations encompass turning, facing, parting, drilling, dull, and reaming, every with unique features and techniques.
Turning
Turning is the number one operation wherein a slicing device eliminates cloth from a rotating workpiece to create cylindrical shapes. This operation may be divided into tough turning, which speedy eliminates big quantities of cloth, and end turning, which achieves specific dimensions and a clean floor end. Turning is vital for generating correct and symmetrical parts.
Facing
Facing includes developing a flat floor on the stop of a workpiece through transferring the slicing device perpendicular to its axis of rotation. This operation is important for squaring the ends of the workpiece or getting ready it for next machining processes. A clean, flat floor guarantees right becoming and meeting in mechanical additives.
Parting
Parting, or cutoff, is the method of slicing a chunk from the workpiece the use of a slim blade-like device. The device is fed into the workpiece perpendicular to its axis to split a completed component or eliminate undesirable sections. This operation is critical for generating man or woman additives from longer workpieces.
Drilling
Drilling on a lathe makes use of a drill bit held withinside the tailstock to create holes withinside the rotating workpiece. This operation is essential for starting up holes that may be similarly machined thru dull or reaming. Drilling is vital in getting ready workpieces for inner capabilities and connections.
Boring
Boring enlarges an present hollow the use of a single-factor slicing device held withinside the device post. This operation will increase the hollow`s diameter and complements its floor end and accuracy. Boring is important for accomplishing specific inner dimensions and making sure additives match collectively correctly.
Reaming
Reaming is a completing operation that improves the dimensions and floor end of a drilled or bored hollow the use of a multi-part slicing device referred to as a reamer. This operation eliminates a small quantity of cloth, making sure the hollow’s diameter is correct and the floor is clean. Reaming is important for accomplishing tight tolerances and incredible finishes in mechanical assemblies.
Advanced Lathe Machine Operations
Knurling
Knurling is an operation that creates a patterned texture at the floor of a workpiece. This texture, normally withinside the shape of a chain of crossed or immediately lines, is produced the use of a knurling device with hardened rollers. Knurling improves grip on handles and knobs and is regularly used for cultured purposes. This operation is crucial in generating non-slip surfaces and improving the advent of metallic elements.
Thread Cutting
Thread reducing on a lathe includes growing helical grooves at the workpiece to supply threads, which may be both inner or external. This operation calls for specific manipulate of the lathe`s lead screw and reducing device to make sure an appropriate pitch and intensity of the threads. Thread reducing is vital for production screws, bolts, and threaded additives that require specific mating with different elements.
Taper Turning
Taper turning is the system of regularly lowering the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece alongside its length, growing a tapered form. This operation may be done with the aid of using placing the compound relaxation at an angle, offsetting the tailstock, or the use of a taper attachment. Taper turning is essential in programs wherein elements want to healthy collectively with a sluggish extrade in diameter, together with in device device spindles and force shafts.
Forming
Forming includes shaping the workpiece right into a favored profile the use of a forming device that has the inverse form of the very last contour. This operation lets in for the advent of complicated shapes and profiles in a unmarried pass. Forming is extensively used withinside the manufacturing of ornamental items, tricky additives, and elements requiring steady and specific shapes.
Grooving
Grooving is the system of reducing a narrow, recessed channel into the workpiece. This operation is done the use of a grooving device, that’s specially designed to create grooves of various depths and widths. Grooving is vital in programs wherein elements want to have particular capabilities together with O-ring seats, preserving rings, and different mechanical interlocking additives. It guarantees that the grooves are appropriately positioned and feature an appropriate dimensions for his or her supposed use.
Lathe Machine Tools and Cutting Instruments
Types of Cutting Tools
Lathe machines make use of a number reducing gear designed for diverse operations. The maximum not unusualplace include:
Turning Tools: These gear are vital for casting off cloth from the outer floor of a rotating workpiece, shaping it right into a cylindrical form. They are available in diverse profiles, along with roughing gear for heavy cloth elimination and completing gear for attaining clean floor finishes.
Parting Tools: Narrow, blade-like gear used to reduce off sections from the workpiece. They are vital for isolating completed elements or trimming extra cloth.
Boring Bars: Used to expand current holes with precision. These gear are established withinside the device put up and are adjustable to obtain the favored inner diameter.
Tool Materials
The cloth from which reducing gear are made influences their overall performance and durability:
High-Speed Steel (HSS): Known for its durability and resistance to excessive temperatures, HSS is usually used for general-cause gear. It keeps its sharpness and reducing performance at excessive speeds.
Carbide: Extremely tough and wear-resistant, carbide gear are best for excessive-velocity and precision machining. They are used for reducing tough substances and retaining a pointy facet longer than HSS gear.
Ceramics: Offer fantastic warmness resistance and are appropriate for excessive-velocity applications, especially in completing operations in which excessive floor nice is required.
Tool Geometry
Tool geometry performs a vital position withinside the effectiveness of reducing gear. Key geometric capabilities include:
Rake Angle: The perspective among the device face and a line perpendicular to the reducing floor. Positive rake angles assist lessen reducing forces and are high-satisfactory for softer substances, even as terrible rake angles provide higher manipulate for tougher substances.
Clearance Angle: This perspective prevents the device from rubbing in opposition to the workpiece, lowering friction and wear. It is vital for extending device lifestyles and retaining accuracy.
Cutting Edge Angle: The perspective fashioned with the aid of using the reducing facet and the workpiece floor, affecting the device`s reducing performance and penetration ability.
Tool Holding Devices
Effective device protecting is important for precision and safety. Common gadgets include:
Tool Posts: Adjustable mounts that maintain the reducing gear in place, permitting specific positioning and movement.
Tool Holders: Secure the reducing gear withinside the device put up and may be quick-alternate or fixed, relying at the application.
Collet Chucks: Provide a specific grip on gear and are regularly used for excessive-accuracy operations.
Workholding Techniques on a Lathe Machine
Effective workholding is essential for precision machining on a lathe machine. Various strategies make certain that the workpiece is securely held and efficaciously aligned in the course of operations. The number one workholding strategies encompass chuck preserving, faceplate workholding, among facilities, and collet preserving.
Chuck Holding
Chuck preserving is one of the maximum not unusualplace and flexible strategies for securing a workpiece on a lathe. Chucks are clamping gadgets installed at the lathe`s spindle. The primary sorts of chucks are:
Three-Jaw Chuck: Self-centering and perfect for containing spherical or hexagonal workpieces. It routinely facilities the workpiece, making it appropriate for maximum popular lathe operations.
Four-Jaw Chuck: Features independently adjustable jaws that permit specific centering of irregularly fashioned or asymmetrical workpieces. It presents better accuracy however calls for guide adjustment for centering.
Universal Chuck: A form of four-jaw chuck with extra modifications for each radial and axial movements, supplying more flexibility in preserving one of a kind workpiece shapes.
Faceplate Workholding
Faceplates are used for containing huge, irregularly fashioned, or non-cylindrical workpieces. They are flat, round plates installed at the lathe spindle, and the workpiece is secured to the faceplate the usage of clamps or bolts. This technique is useful for machining elements which can be too huge for a chuck or have complicated shapes. The faceplate guarantees balance and precision, making it appropriate for each turning and milling operations on large additives.
Between Centers
Holding a workpiece among facilities entails helping it at each ends the usage of lathe facilities. The workpiece is installed at the lathe`s headstock spindle and tailstock, which preserve the facilities. This method is right for turning long, slim additives and guarantees that the workpiece stays concentric in the course of machining. It is likewise used for operations requiring excessive precision and alignment, including cylindrical turning and grinding.
Collet Holding
Collets are used for containing small-diameter workpieces with excessive precision. They are cylindrical gadgets that grip the workpiece tightly and evenly, supplying tremendous concentricity and balance. Collets are installed at the lathe spindle and may accommodate a number workpiece sizes. They are specifically beneficial for small elements and excessive-precision operations, including threading and nice finishing. Collet chucks may be quick-extrade or guide, supplying flexibility and comfort for numerous machining tasks.
Lathe Machine Safety Practices
Ensuring protection at the same time as working a lathe system is essential to save you injuries and injuries. Adhering to protection practices enables create a steady running environment. Key protection practices consist of the usage of non-public defensive system (PPE), following secure working procedures, and being privy to not unusualplace dangers and a way to keep away from them.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Safety Glasses: Protects the eyes from flying debris, chips, and dirt generated at some stage in machining operations.
Face Shields: Provides extra face safety along side protection glasses, specifically whilst coping with high-velocity slicing or massive workpieces.
Hearing Protection: Earplugs or earmuffs must be worn to shield towards immoderate noise tiers produced via way of means of the lathe.
Gloves: While gloves provide hand safety, they must be used cautiously. Loose-becoming gloves can turn out to be entangled in shifting elements. Ensure gloves are comfortable and appropriate for the unique task.
Safe Operating Procedures
Read the Manual: Always get yourself up to speed with the lathe`s consumer guide and protection pointers unique to the system.
Inspect the Machine: Before starting, take a look at the lathe for any symptoms and symptoms of put on, harm, or unfastened elements. Ensure all protection guards are in region and functioning well.
Secure the Workpiece: Ensure that the workpiece is well secured withinside the chuck, faceplate, or collet. Loose workpieces can reason vibration and bring about misguided machining or injuries.
Adjust Settings: Set the system`s velocity and feed charges in keeping with the cloth and sort of operation. Incorrect settings can cause negative consequences or system harm.
Keep Hands Away: Always hold arms and different frame elements farfar from shifting elements. Use gear or gadgets designed for secure coping with of the workpiece and slicing gear.
Maintain Cleanliness: Keep the paintings region easy and loose from clutter. Remove any chips, debris, or limitations that would intrude with the operation or pose tripping dangers.
Common Hazards and How to Avoid Them
Entanglement: Loose clothing, hair, or earrings can get stuck in shifting elements. To keep away from this, put on outfitted clothing, steady lengthy hair, and do away with earrings earlier than working the lathe.
Flying Debris: Chips and fragments can fly off at some stage in machining. Use protection glasses and face shields to shield your eyes and face.
Machine Malfunctions: Faulty or unmaintained system can cause injuries. Regularly look into and hold the lathe to make sure it operates safely.
Overloading: Overloading the system with immoderate cloth or wrong settings can reason harm and protection dangers. Adhere to the system`s potential and advocated settings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the purpose of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in lathe machine operations?
PPE is essential for protecting operators from potential injuries and hazards associated with lathe machine operations. Safety glasses shield the eyes from flying debris, face shields offer additional protection, hearing protection guards against loud noise, and gloves and work boots provide hand and foot safety.
2. What should I check before starting the lathe machine?
Before starting the lathe, inspect the machine for any signs of wear or damage. Ensure that all safety guards are in place and functioning properly.
3. How should I secure the workpiece on a lathe machine?
The workpiece should be securely mounted using the appropriate method—whether it’s a chuck, faceplate, or collet. Ensure the workpiece is tightly clamped and centered to prevent vibration or movement during machining.
4. What are some common hazards when using a lathe machine?
Common hazards include entanglement with loose clothing or hair, flying debris from cutting operations, machine malfunctions due to poor maintenance, overloading the machine, and inadequate lighting. Proper PPE and adherence to safety procedures can help mitigate these risks.
5. Why is it important to stop the machine before making adjustments?
Stopping the machine before making adjustments is crucial to prevent accidents. Moving parts can cause serious injuries if touched while in motion. Ensuring the machine is completely stopped allows for safe and precise adjustments.






