Carbon monoxide is a major air pollutant and is responsible for many deaths each year. It is important to be aware of the sources of carbon monoxide and to take steps to protect yourself from exposure.
Structure and bonding
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecular structure | Linear |
| Bond angle | 180 degrees |
| Bond type | Triple bond |
| Bond order | 3 |
| Bond dissociation energy | 1072 kJ/mol |
| Polarity | Polar |
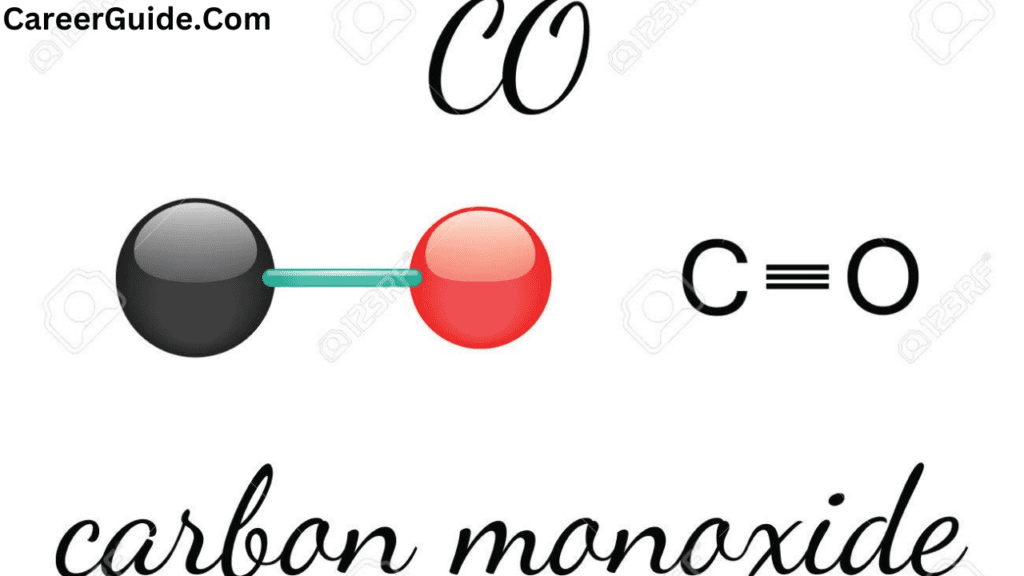
The triple bond in CO consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds. The sigma bond is formed by the overlap of head-on orbitals, while the pi bonds are formed by the overlap of side-by-side orbitals.
The triple bond in CO is very strong, which is why carbon monoxide is a stable molecule. It is also responsible for the molecule’s high polarity, as the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon atom.
Properties of Carbon monoxide
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | CO |
| Molar mass | 28.010 g/mol |
| Density | 1.249 kg/m³ (at 0 °C and 1 atm) |
| Melting point | -205.1 °C |
| Boiling point | -191.5 °C |
| Solubility in water | Low |
| State at room temperature | Gas |
| Color | Colorless |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Flammability | Flammable |
| Toxicity | Highly toxic |
Production of Carbon monoxide
Here are some of the specific ways in which carbon monoxide is produced:
- Combustion: Carbon monoxide is produced when any carbon-containing fuel is burned incompletely. This can happen in a variety of settings, including cars, trucks, buses, airplanes, homes, and businesses.
- Forest fires: Carbon monoxide is one of the main pollutants released by forest fires.
- Volcanic eruptions: Carbon monoxide is also released by volcanic eruptions.
- Tobacco smoke: Tobacco smoke contains significant amounts of carbon monoxide.
- Industrial processes: Carbon monoxide is also produced in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of steel, iron, and cement.
Uses
Here are some of the most common uses of carbon monoxide:
- Production of methanol: Methanol is a type of alcohol that is used as a fuel, a solvent, and a chemical feedstock. It is produced by reacting carbon monoxide with hydrogen gas.
- Production of synthetic fuels: Synthetic fuels are liquid fuels that are produced from coal, natural gas, or biomass. Carbon monoxide is used as a feedstock in the production of some synthetic fuels, such as Fischer-Tropsch diesel.
- Production of plastics: Carbon monoxide is used in the production of some plastics, such as polycarbonates and polymethyl methacrylate.
- Metallurgy: Carbon monoxide is used in a variety of metallurgical processes, such as the reduction of iron ore and the purification of nickel.
- Production of chemicals: Carbon monoxide is used in the production of a variety of chemicals, such as acetic acid, phosgene, and urea.
Safety
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is a poisonous gas that can cause death if inhaled in high concentrations.
Here are some safety tips to protect yourself from carbon monoxide exposure:
- Install a carbon monoxide detector in your home and test it regularly. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed on every level of your home, including the basement. Test your carbon monoxide detectors every month and replace the batteries every year.
- Never use a gas stove or oven to heat your home. Gas stoves and ovens produce carbon monoxide, which can build up in your home if they are not properly ventilated.
- Make sure your fireplace or wood stove is properly ventilated. Fireplaces and wood stoves can also produce carbon monoxide, so it is important to make sure that they are properly ventilated.
- Keep your car’s tailpipe clear of snow and ice. A blocked tailpipe can cause carbon monoxide to build up in your car.
- Avoid running your car engine in an enclosed garage. Even if you leave the garage door open, carbon monoxide can build up in the garage.
- Be careful when using generators and other portable gas-powered equipment. Generators and other portable gas-powered equipment can produce carbon monoxide, so it is important to use them outdoors and away from windows and doors.
FAQs
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is a poisonous gas that can cause death if inhaled in high concentrations.
Carbon monoxide is produced when carbon-containing fuels, such as coal, gasoline, and natural gas, are burned incompletely. It is also produced by the breakdown of organic matter, such as wood and leaves.
The symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning include headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, carbon monoxide poisoning can lead to unconsciousness and death.
There are a number of things you can do to protect yourself from carbon monoxide poisoning, including: * Install a carbon monoxide detector in your home and test it regularly. * Never use a gas stove or oven to heat your home. * Make sure your fireplace or wood stove is properly ventilated.






