Quicklime is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Construction: Quicklime is used to make cement, mortar, and plaster. It is also used to produce quicklime bricks, which are strong and durable.
- Agriculture: Quicklime is used to improve soil quality and to produce fertilizers. It is also used to control pests and diseases.
- Water treatment: Quicklime is used to remove impurities from water and to make it safe to drink.
- Industrial processes: Quicklime is used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of paper, glass, and soap.
Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | CaO |
| Appearance | White, crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 2,572°C |
| Boiling point | 2,850°C |
| Density | 3.34 g/cm³ |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water |
| pH | 12.4 in a 10% solution |
| Heat capacity | 0.21 J/g°C |
Production
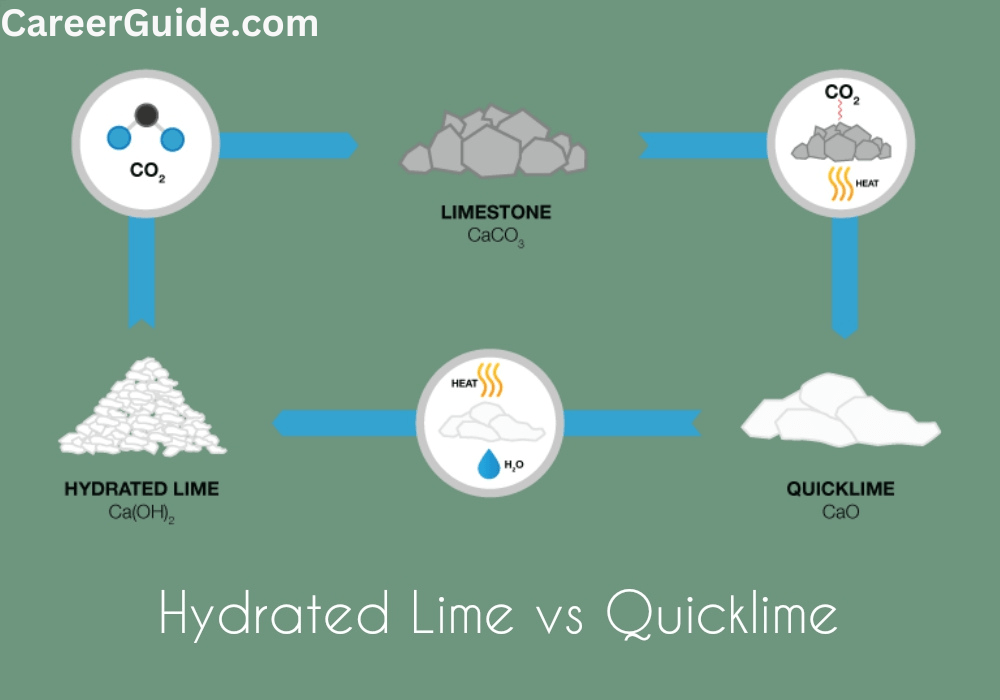
Quicklime, also known as calcium oxide (CaO), is produced by heating calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to a high temperature (800-900°C), which drives off the carbon dioxide (CO2). This process is known as calcination.
The following is a simplified overview of the quicklime production process:
- Quarrying: Calcium carbonate, also known as limestone, is quarried from the ground.
- Crushing and grinding: The limestone is crushed and ground into a fine powder.
- Calcination: The limestone powder is heated in a kiln to a high temperature (800-900°C). This drives off the carbon dioxide, leaving behind quicklime.
- Cooling and packaging: The quicklime is cooled and packaged for shipment.
Applications
| Application | Specific examples |
|---|---|
| Construction | Cement, mortar, plaster, quicklime bricks |
| Agriculture | Soil improvement, fertilizers, pest and disease control |
| Water treatment | Impurity removal |
| Industrial processes | Paper production, glass production, soap production |
Safety considerations
Here are some of the safety considerations when handling quicklime:
- Quicklime is a caustic substance and can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. It is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling quicklime, such as gloves, goggles, and a respirator.
- Quicklime is also a reactive substance and can react with water to form calcium hydroxide and with acids to form salts. It is important to store and handle quicklime carefully to avoid accidental reactions.
- Quicklime production kilns can generate high temperatures and toxic gases. It is important to operate and maintain quicklime production kilns safely to avoid accidents and injuries.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Quicklime is a caustic substance and can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. It is also a reactive substance and can react with water to form calcium hydroxide and with acids to form salts. Quicklime has a high melting point (2,572°C) and boiling point (2,850°C). It is also highly soluble in water.
Quicklime is produced by heating calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to a high temperature (800-900°C), which drives off the carbon dioxide (CO2). This process is known as calcination. Quicklime can be produced in a variety of kilns, including shaft kilns, rotary kilns, and fluidized bed calciners.
Quicklime is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Construction: Quicklime is used to make cement, mortar, and plaster. It is also used to produce quicklime bricks, which are strong and durable.
- Agriculture: Quicklime is used to improve soil quality and to produce fertilizers. It is also used to control pests and diseases.
- Water treatment: Quicklime is used to remove impurities from water and to make it safe to drink.






