Bottom Hole Pressure Definition refers to the pressure exerted at the lowest of a well, normally in oil and fuel drilling operations. It is a essential parameter for comparing the protection, balance, and productivity of a properly. Bottom hollow stress is the combined strain from the burden of the fluid column, the formation pressure, and any extra pressures from operations which include pumping or injecting fluids. Accurate dimension and management of backside hole pressure are vital for preventing blowouts, controlling fluid drift, and making sure foremost drilling performance. It also helps inside the layout and evaluation of drilling operations, of completion, and reservoir control techniques.
- What is Bottom Hole Pressure Definition (BHP)?
- Importance of Bottom Hole Pressure in Drilling Operations
- How Bottom Hole Pressure is Measured
- Difference Between Static and Dynamic Bottom Hole Pressure
- How Bottom Hole Pressure Impacts Mud Circulation
- Bottom Hole Pressure in Oil and Gas Reservoirs
- Techniques for Monitoring Bottom Hole Pressure in Real-Time
- Changes in Bottom Hole Pressure Affect Drilling Performance
- FAQ About Bottom Hole Pressure Definition
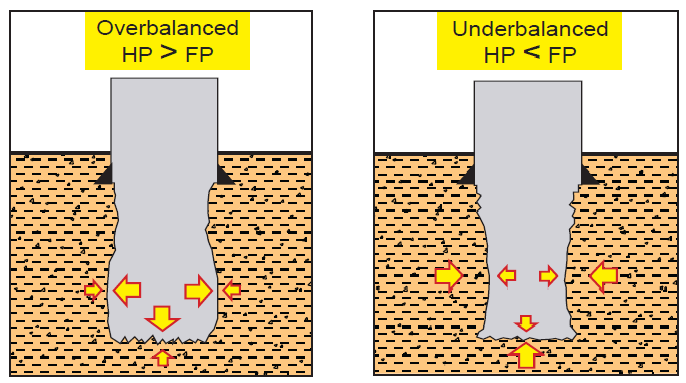
What is Bottom Hole Pressure Definition (BHP)?
The Bottom Hole Pressure Definition (BHP) refers to the pressure present at the bottom of a properly throughout oil and gas drilling operations. It is a important parameter for managing drilling sports and ensuring well protection. Bottom hollow pressure is the mixture of the pressure exerted with the aid of the column of drilling fluid and the strain from the formation. Accurate know-how of BHP is vital for preventing issues which include blowouts and well manipulate issues.
Key Points About Bottom Hole Pressure Definition (BHP):
- Formation Pressure: BHP includes the formation pressure at the well’s backside, which can range depending on the depth and area of the nicely.
- Drilling Fluid Column Pressure: The weight of the drilling fluid, also referred to as dust, contributes considerably to the Bottom Hole Pressure Definition, assisting to counterbalance formation strain and save you undesirable fluid influx.
- Importance in Well Control: Maintaining the proper BHP is essential for nicely manage. If the BHP is simply too low, it is able to cause a blowout, while too high a BHP can reason reservoir damage or formation fall apart.
- Measurement Techniques: BHP can be measured the use of downhole stress gauges or by using calculating it primarily based on dust weight and well intensity. Accurate measurements are essential for secure drilling operations.
- Impact on Drilling Efficiency: Understanding the Bottom Hole Pressure Definition (BHP) helps optimize drilling parameters, improving performance and lowering the hazard of steeply-priced operational delays.
- Influence on Formation Evaluation: BHP plays a function in evaluating the formation’s conduct and potential manufacturing abilties. It enables determine the stress stability and float costs of the reservoir.
Importance of Bottom Hole Pressure in Drilling Operations
- Well Control and Safety: The most great function of Bottom Hole Pressure Definition is in well manipulate. By balancing the pressure exerted through the formation with the strain from the drilling fluid column, BHP helps save you uncontrolled fluid inflow (kick) or blowouts, that could result in catastrophic injuries.
- Prevention of Blowouts: If the BHP is simply too low, it could fail to counterbalance the formation pressure, main to a blowout. Maintaining the precise Bottom Hole Pressure Definition guarantees that the nicely remains solid, preventing the uncontrolled release of gas or oil to the floor.
- Formation Evaluation: The BHP offers valuable records for comparing the pressure situations of the reservoir. By monitoring BHP, drilling engineers can better understand the formation’s behavior and make knowledgeable decisions about further drilling or manufacturing operations.
- Optimal Mud Weight Selection: The correct mud weight is essential for preserving the desired BHP. The Bottom Hole Pressure Definition helps determine the most fulfilling mud weight for a given properly depth and formation strain, ensuring that the drilling fluid can adequately support the wellbore while stopping wellbore collapse.
- Prevents Reservoir Damage: An excessively high BHP can result in harm to the reservoir by means of lowering its permeability or inflicting fractures inside the formation. Proper BHP management protects the reservoir’s integrity and long-term productiveness.
- Enhanced Drilling Efficiency: Understanding and controlling Bottom Hole Pressure Definition lets in for smoother drilling operations. By retaining an finest BHP, drilling fees can be stepped forward, and the chance of encountering surprising complications can be minimized.
How Bottom Hole Pressure is Measured
- Pressure Gauges: The most common method for measuring Bottom Hole Pressure Definition is by means of using downhole stress gauges. These gauges are set up inside the wellbore at precise depths to immediately degree the strain at the bottom of the nicely.
- Hydrostatic Pressure Calculation: Bottom Hole Pressure Definition can also be expected by using calculating the hydrostatic stress exerted by means of the column of drilling fluid. This calculation takes under consideration the dust weight, nicely depth, and fluid density.
- Using a Blowout Preventer (BOP): BOP structures are geared up with stress sensors that can display the strain at the lowest of the nicely. These sensors offer real-time information to make sure right nicely manipulate and to save you blowouts.
- Surface Pressure Measurements: By measuring the stress at the surface and using known formulas, the BHP may be estimated, thinking about factors like mud weight and depth. This technique is normally used for initial estimates.
- Real-Time Monitoring Systems: Modern drilling operations use actual-time monitoring systems that constantly degree and transmit Bottom Hole Pressure Definition. These systems offer instantaneous data for decision-making and adjustments.
- Drill Stem Tests (DST): During drill stem assessments, equipment are decreased into the properly to degree the stress at the lowest of the properly without delay. This approach is used to attain correct BHP information in the course of precise well trying out stages.
- Mud Logging Systems: Mud logging systems reveal the residences of the drilling fluid and strain fluctuations in the course of drilling. By analyzing those statistics, the Bottom Hole Pressure Definition may be assessed.
Difference Between Static and Dynamic Bottom Hole Pressure
| Aspect | Static Bottom Hole Pressure | Dynamic Bottom Hole Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The pressure at the bottom of the well when there is no fluid movement. | The pressure at the bottom of the well while the fluid is flowing or during drilling operations. |
| Measurement Condition | Measured when the drilling fluid is at rest and the well is not in operation. | Measured during active drilling, fluid circulation, or when the well is in operation. |
| Fluid Flow | No fluid movement, so only the hydrostatic pressure of the drilling fluid is considered. | Includes both hydrostatic pressure and additional pressures from fluid flow or other dynamic factors. |
| Factors Affecting Pressure | Primarily determined by the weight of the drilling fluid and depth of the well. | Affected by the flow rate, pump rate, and other operational factors like mud properties. |
| Use in Well Control | Helps to determine the baseline pressure needed to prevent kick or blowout. | Provides real-time data for controlling wellbore stability and blowout prevention during operations. |
| Pressure Fluctuations | Constant and stable pressure unless there is a change in the drilling fluid column. | Pressure can fluctuate due to changes in flow rate or other operational activities. |
| Typical Measurement Devices | Downhole pressure gauges when the well is static or at rest. | Pressure sensors or real-time monitoring systems during active drilling. |
| Significance | Indicates the minimum pressure required to balance formation pressure at rest. | Reflects the actual working pressure required to control flow and maintain well stability during drilling. |
How Bottom Hole Pressure Impacts Mud Circulation
- Maintains Wellbore Stability:
Proper Bottom Hole Pressure Definition guarantees that the mud stream continues a balance between the formation strain and the pressure exerted by way of the drilling fluid, preventing wellbore instability. - Prevents Kick and Blowouts: Accurate Bottom Hole Pressure Definition is critical for stopping kicks or blowouts by using making sure the mud weight is sufficient to counterbalance formation pressures at some point of move.
- Controls Fluid Loss or Gain: Maintaining the right BHP facilitates manipulate fluid loss to the formation or inflow of formation fluids, maintaining the dust gadget balanced and stopping issues in the course of flow.
- Optimizes Circulation Rate: Adjusting Bottom Hole Pressure Definition lets in for optimizing the dust move price, making sure efficient removal of cuttings while stopping excessive pressure that could harm the wellbore.
- Enhances Drilling Efficiency: Proper BHP control reduces downtime and enhances drilling performance, making sure non-stop circulation without disruptions as a result of strain-related troubles.
- Prevents Well Control Issues: By monitoring and adjusting Bottom Hole Pressure Definition, operators can avoid over-pressurizing or beneath-pressurizing the nicely, mitigating nicely manipulate troubles all through move.
- Informs Mud Weight Adjustments: Accurate BHP size presents perception into whether or not dust weight desires to be adjusted at some stage in circulate to hold nicely manipulate and keep away from formation harm.
Bottom Hole Pressure in Oil and Gas Reservoirs
In oil and fuel reservoirs, Bottom Hole Pressure Definition performs a important position in ensuring green and secure extraction of hydrocarbons. Here’s how BHP is full-size in those environments:
- Formation Pressure Assessment: Bottom Hole Pressure Definition allows check the formation strain, that is vital for information the reservoir’s conduct. Accurate BHP measurements offer precious insights into the reservoir’s electricity, allowing operators to plot extraction strategies correctly.
- Well Control During Production: Monitoring Bottom Hole Pressure Definition is critical to save you out of control production, which could lead to blowouts or reservoir harm. Maintaining proper BHP enables make sure that manufacturing stays inside secure limits.
- Enhanced Recovery Techniques: In improved oil restoration (EOR) operations, accurate BHP measurements manual decisions on injecting water, gas, or other materials to boom production. These strategies rely on knowing the strain at the bottom of the well to optimize injection fees.
- Prevents Formation Damage: Maintaining top-quality Bottom Hole Pressure Definition prevents damage to the formation, that may end result from immoderate pressure for the duration of manufacturing. Over-pressurizing or under-pressurizing can lead to the lack of permeability or even reservoir compaction.
- Optimization of Mud Weight and Drilling Fluid: Accurate BHP guarantees that the drilling fluid or mud weight is effectively adjusted to maintain wellbore balance and prevent fluid influx from the reservoir. The right BHP helps keep the mud stream in stability, optimizing drilling operations.
Techniques for Monitoring Bottom Hole Pressure in Real-Time
- Downhole Pressure Gauges: Bottom Hole Pressure Definition is immediately measured using downhole stress gauges, which can be located inside the wellbore at precise depths. These gauges provide real-time statistics on the strain at the lowest of the properly in the course of drilling and manufacturing operations.
- Wireline Pressure Measurement Tools: Wireline gear are lowered into the well to measure Bottom Hole Pressure Definition at numerous depths. These tools can offer real-time stress readings and are regularly used throughout testing or while making adjustments to the nicely.
- Real-Time Data Transmission Systems: Advanced monitoring systems transmit Bottom Hole Pressure Definition facts to the surface in real time. These structures use sensors located in the nicely to send pressure statistics, permitting operators to make timely choices based totally on accurate measurements.
- Blowout Preventer (BOP) Pressure Sensors: The BOP system, used for nicely control, is ready with stress sensors that degree Bottom Hole Pressure Definition. These sensors are continuously monitored for the duration of operations to ensure secure drilling and save you blowouts with the aid of preserving choicest pressure.
- Mud Logging Systems: Mud logging gadgets are regularly equipped with pressure sensors that display changes in Bottom Hole Pressure Definition all through drilling. These systems song pressure fluctuations and offer valuable statistics for adjusting dust weights and retaining nicely manipulate.
- Continuous Monitoring Using Automated Systems: Automated systems constantly degree and record Bottom Hole Pressure Definition, imparting operators with actual-time feedback. These systems combine records from numerous sensors and offer an usual image of the well’s overall performance.
Changes in Bottom Hole Pressure Affect Drilling Performance
- Wellbore Stability: Changes in Bottom Hole Pressure Definition can purpose the wellbore to emerge as volatile. If BHP is just too low, the properly might also fall apart, while excessively high BHP can result in formation damage. Maintaining a stable BHP is important for wellbore integrity and smooth drilling operations.
- Kick and Blowout Prevention: A unexpected drop or increase in Bottom Hole Pressure Definition can cause a kick, in which formation fluids flow into the well. If no longer managed, this can increase to a blowout. Proper BHP control is important to save you these risky conditions.
- Mud Circulation Efficiency: Fluctuations in Bottom Hole Pressure Definition can affect mud move rates. If the BHP is simply too low or high, it can reason inefficient elimination of drill cuttings from the wellbore, growing the danger of clogging or device failure. Stable BHP ensures most suitable dust go with the flow and efficient cuttings delivery.
- Drilling Rate Optimization: Inconsistent Bottom Hole Pressure Definition can avert the price of penetration (ROP). An most excellent BHP permits for consistent drilling speeds, at the same time as BHP fluctuations can reason the drill bit to both end up too competitive (main to damage) or useless, slowing down drilling progress.
- Formation Damage: Bottom Hole Pressure Definition directly impacts the likelihood of formation damage. If the strain is too high, it can fracture the formation or purpose the invasion of drilling fluids into the rock. If the strain is simply too low, the formation may not be nicely sealed, main to leakage and contamination.
FAQ About Bottom Hole Pressure Definition
1.What is Bottom Hole Pressure (BHP)?
Bottom Hole Pressure refers to the pressure at the bottom of a well, which is exerted by the column of drilling fluid or the reservoir fluids in the wellbore. It plays a crucial role in maintaining well stability and preventing blowouts.
2.Why is Bottom Hole Pressure Important?
BHP is essential in well control as it helps prevent influxes of formation fluids into the well, such as gas or oil, by balancing the pressure exerted by the column of drilling mud against the formation pressure.
3.How is Bottom Hole Pressure Measured?
BHP can be measured using specialized pressure sensors placed at or near the bottom of the well. These sensors are part of the downhole tools or during the circulation process of drilling fluids.
4 What Factors Affect Bottom Hole Pressure?
Factors like the depth of the well, the density of the drilling fluid, and the pressure from surrounding rock formations influence the Bottom Hole Pressure.






