A Space Lattice Definition refers to a 3-dimensional arrangement of factors in space, in which every factor represents the location of an atom, ion, or molecule in a crystalline shape. This geometric arrangement follows a repeating pattern throughout the material. The lattice points are arranged in a ordinary and periodic manner, forming a framework that enables describe the homes and conduct of strong substances. The idea of a area lattice is fundamental in crystallography and materials technological know-how, because it allows scientists to look at and are expecting how one of a kind substances will behave beneath numerous situations.
- What is a Space Lattice?
- Structure and Geometry of Space Lattices
- Types of Lattices in Crystalline Solids
- Importance of Space Lattice in Crystallography
- Coordination Number and Its Role in Space Lattice
- Types of Space Lattice: Primitive vs. Non-Primitive
- Applications of Space Lattices in Material Science
- FAQ About Space Lattice Definition
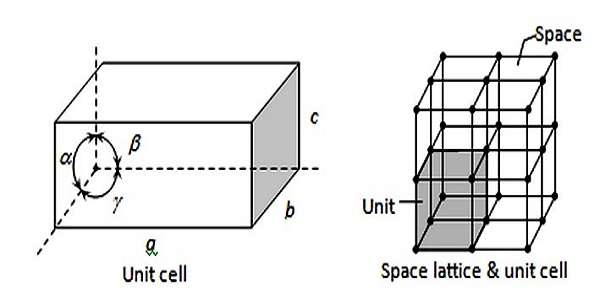
What is a Space Lattice?
The “Space Lattice Definition” is important in crystallography, because it describes the symmetry and periodicity of a crystal. The arrangement of atoms or ions at each issue inside the lattice can help expect the fabric’s bodily, chemical, and mechanical houses. The shape of the lattice may be categorized into differing types, which include cubic, tetragonal, or hexagonal, depending at the association of the lattice factors.
Some Key Points About Space Lattice:
- Repetition: A place lattice is shaped by way of the periodic repetition of a unit cell, this is the smallest repeating unit that defines the overall shape of the crystal.
- Lattice Points: The factors in the lattice represent the positions of atoms, ions, or molecules, and they’ll be related to form a 3D sample.
- Unit Cell: The essential building block of the distance lattice is the unit cellular, that’s a small part of the lattice that can be repeated to create the complete structure.
- Symmetry: The area lattice well-known symmetry, which means that the shape looks the identical from one in every of a kind instructions, this is vital for figuring out the crystal’s homes.
- Types of Space Lattices: There are numerous forms of space lattices, along with cubic, hexagonal, tetragonal, and orthorhombic, every described by using way of the angles and lengths of the unit mobile.
- Crystallographic Axis: The location lattice is defined by way of manner of three crystallographic axes that constitute the instructions wherein the unit cells repeat.
- Crystal Properties: The association of atoms or ions inside the place lattice determines the crystal’s physical properties, together with hardness, electric powered conductivity, and thermal conductivity.
Structure and Geometry of Space Lattices
- Unit Cell: The primary repeating unit in a space lattice is the unit cell, which defines the geometry of the complete crystal. It is the smallest portion that, whilst repeated in all instructions, forms the full shape of the crystal.
- Crystallographic Axes: The area lattice is defined with the aid of 3 crystallographic axes, typically denoted as a, b, and c, which represent the guidelines of the unit mobile’s facets. These axes may additionally vary in length and angle relying at the lattice type.
- Angles Between Axes: In a area lattice, the angles among the crystallographic axes (α, β, γ) play a vital position in figuring out the geometry of the lattice. These angles can vary, contributing to the classification of various lattice types.
- Types of Space Lattices: Based on the symmetry and geometry of the unit cellular, area lattices are categorised into seven crystal systems: cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, monoclinic, triclinic, and rhombohedral.
- Symmetry: The geometry of a area lattice is inherently symmetrical. The arrangement of atoms or ions repeats periodically in space, ensuring that the crystal shape exhibits symmetrical residences from extraordinary directions.
- Primitive vs. Non-Primitive Lattices: A primitive lattice has lattice factors best at the corners of the unit mobile, whilst a non-primitive lattice has lattice points at additional positions inclusive of faces or frame facilities.
- Lattice Points: Each factor inside the area lattice corresponds to an atom, ion, or molecule, and the arrangement of those factors in area determines the geometric shape of the crystal.
Types of Lattices in Crystalline Solids
- Cubic Lattice: In this kind of lattice, the unit mobile is dice-shaped with all aspects identical in duration, and all angles are ninety°. The atoms are positioned on the corners, and in some cases, at the center of the faces or body of the cube.
- Simple Cubic (SC): Atoms are located most effective at the corners.
- Body-Centered Cubic (BCC): Atoms are at the corners and on the center of the unit mobile.
- Face-Centered Cubic (FCC): Atoms are at the corners and at the middle of every face of the unit cellular.
2. Tetragonal Lattice: In a tetragonal lattice, two sides of the unit cellular are equal in length, but the third facet is distinctive. The angles between the axes are all 90°, developing a rectangular prism with one unequal aspect.
Body-Centered Tetragonal (BCT): Atoms are at the corners and at the center of the unit cell.
3. Orthorhombic Lattice: The orthorhombic lattice has 3 aspects of unequal period, with all angles being 90°. It creates a rectangular prism with out a same aspects.
4. Hexagonal Lattice: This lattice features a unit mobile that resembles a hexagon when viewed from the pinnacle. The two horizontal axes are of equal period, while the 0.33 axis is perpendicular to them. The angles among the horizontal axes are 120°, and the attitude among the 1/3 axis and the bottom is ninety°.
5. Rhombohedral (Trigonal) Lattice: In a rhombohedral lattice, all 3 axes are of same duration, but the angles between them are not ninety°. This creates a tilted, rhombus-fashioned unit cellular.
6. Monoclinic Lattice: In the monoclinic lattice, two of the axes are unequal, and one of the angles is 90°, even as the alternative are not. This Space Lattice Definition creates a skewed square prism.
7. Triclinic Lattice: The triclinic lattice has 3 unequal axes, and none of the angles between the axes are 90°. This consequences in a completely abnormal-fashioned unit cellular.
Importance of Space Lattice in Crystallography
- Material Properties: The Space Lattice Definition determines the bodily homes including hardness, density, and conductivity of materials.
- Crystal Symmetry: It helps outline the symmetry of crystals, influencing their shape and inner association.
- Crystal Classification: The Space Lattice Definition is used to classify crystals into unique systems, along with cubic, tetragonal, or monoclinic.
- Atomic Interactions: The association of atoms in the area lattice affects how atoms have interaction, affecting the fabric’s behavior.
- Crystallographic Analysis: The lattice shape is essential for strategies like X-ray diffraction, which allows decide the crystal’s atomic association.
- Material Design: Understanding area lattices aids in designing materials with specific homes like power or conductivity.
- Phase Transitions: Changes inside the space lattice can lead to phase transitions, changing cloth houses.
- Electronic Properties: The Space Lattice Definition impacts the cloth’s electronic structure, determining if it’s a conductor, semiconductor, or insulator.
- Crystal Growth: The lattice structure affects how crystals shape and grow in unique environments.
Coordination Number and Its Role in Space Lattice
- Determining Atomic Arrangement: The coordination range directly affects how atoms are organized inside the area lattice, influencing the symmetry and packing efficiency of the structure.
- Influencing Crystal Stability: Higher coordination numbers generally bring about greater strong crystals. Atoms are packed greater closely collectively, reducing empty space within the space lattice and contributing to stronger bonds among atoms.
- Determining Lattice Type: The coordination number facilitates classify the type of lattice. For instance, in a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure, the coordination wide variety is 12, indicating a close-packed association.
- Physical Properties: The coordination quantity affects the fabric’s properties, including melting factor, hardness, and density, as the arrangement of atoms within the space lattice determines how atoms interact with every other.
- Effect on Bonding: In sure lattices, a higher coordination quantity manner more atoms are worried in bonding, which could affect the fabric’s electric and thermal conductivity.
- Defining Crystalline Structure: The coordination wide variety helps in know-how the geometry of the crystal shape. For example, in easy cubic systems, the coordination quantity is 6, affecting the shape and length of the unit mobile in the area lattice.
- Impact on Ionic Compounds: In ionic crystals, the coordination number performs a key role in figuring out the ion association and the stableness of the crystal, based at the electrostatic interactions Space Lattice Definition between the ions within the space lattice.
- Crystal Packing Efficiency: A higher coordination variety typically leads to a more efficient packing arrangement inside the space lattice, which impacts the cloth’s standard density and structural integrity.
Types of Space Lattice: Primitive vs. Non-Primitive
The Space Lattice Definition refers to the periodic association of points in area that represent the positions of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystal. These lattices are labeled into main kinds: primitive and non-primitive. Here’s a breakdown of the 2 sorts:
1. Primitive Space Lattice (Simple Lattice):
Definition: A primitive space lattice has lattice points best on the corners of the unit cell. Each nook lattice factor is shared among adjoining unit cells.
Atoms consistent with Unit Cell: There is successfully one atom consistent with unit cellular (1/eighth of every corner atom is shared by way of eight unit cells).
Examples: Simple cubic (SC) lattice.
Symmetry: The lattice has primary symmetry with fewer atoms within the unit mobile compared to non-primitive lattices.
2. Non-Primitive Space Lattice:
Definition: Non-primitive space lattices have lattice points not handiest at the corners but also at positions inside the unit cellular (which include faces, edges, or the center).
Types:
Body-Centered Cubic (BCC): Lattice points are at the corners and one within the middle of the unit cell.
Face-Centered Cubic (FCC): Lattice factors are on the corners and on the facilities of every face of the unit cellular.
Base-Centered (BC): Lattice factors are at the corners and on the 2 contrary faces of the unit cellular.
Atoms in step with Unit Cell: These lattices contain a couple of atom in keeping with unit cellular because Space Lattice Definition of the extra lattice points inside the unit mobile.
Examples: BCC, FCC, and others.
Applications of Space Lattices in Material Science
- Crystal Structure Analysis: The area lattice definition helps categorize and take a look at distinctive crystal systems, which influences fabric properties like hardness and flexibility.
- Predicting Properties: Understanding the space lattice aids in predicting thermal and electrical conductivity, in addition to optical houses of substances.
- Material Design: The area lattice definition lets in scientists to layout stronger, extra durable alloys and composites through manipulating atomic preparations.
- Nanotechnology: Space lattice principles are crucial for growing nanomaterials with precise mechanical and electric residences.
- Semiconductor Industry: The area lattice definition is crucial for semiconductor manufacturing, impacting electronic devices like computer systems and solar panels.
- Strength and Durability: Space lattice helps in know-how how defects in atomic preparations affect the material’s power and resilience.
- Superconductivity: The space lattice shape impacts substances’ capability to conduct strength without resistance in superconductors.
- Optical Materials: The space lattice performs a function in materials used in lasers, lenses, and other optical gadgets because of their atomic shape.
- Energy Storage: Understanding the distance lattice is prime in growing efficient substances for batteries and capacitors, enhancing electricity garage.
FAQ About Space Lattice Definition
1. What is a space lattice?
A space lattice definition refers to the regular, repeating arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline solid. It provides the structural framework of the material.
2.Why is space lattice important in material science?
The space lattice definition is crucial because it influences the properties of materials, including their strength, conductivity, and optical characteristics, making it essential for material design.
3. How does the space lattice affect material properties?
The arrangement in the space lattice determines how atoms or ions interact within the material, affecting characteristics like hardness, flexibility, and conductivity.
4 What are the different types of space lattices?
There are several types of space lattices, including cubic, hexagonal, and tetragonal, each with unique geometric properties that impact the material’s behavior.






