Bacillus thuringiensis seems as a spectacular and all-natural pest management super hero in the complex network of nature’s remedies. This adaptive bacteria, sometimes referred to as BT, receives acclaim for its ability to control damaging pests while presenting no threat to people, pets, or the environment. In this comprehensive investigation, we delve into the world of Bacillus thuringiensis, exploring its workings, uses, and the revolutionary impact that it has had on agriculture and other fields.
Mechanism of Action: How Bacillus thuringiensis Works
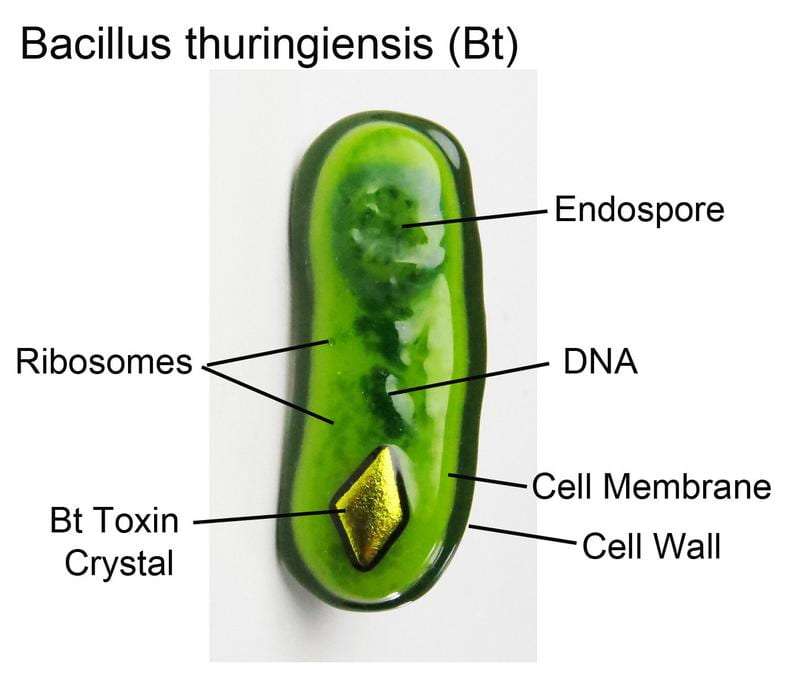


A gram-positive, soil-dwelling organisms named Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) generates insecticide crystal proteins also referred to as delta-endotoxins. These proteins are utilized in genetically engineered crops and as insecticides that are biological in nature since they are hazardous to some insect species.
Bt toxins work by creating holes in the membranes of the insect midgut epithelial cells. This causes the insect to die via cell lysis. The poisons are only found in a few types of insects and are not dangerous to people or other animals.
Applications in Agriculture: Pest Management Redefined
A naturally occurring soil bacteria called Bacillus thuringiensis (BT) produces proteins which are insecticidal. These proteins are utilized in genetically engineered crops and as insecticides that are biological in nature since they’re hazardous to some insect species.
Caterpillars, beetles, flies, and mosquitoes are merely a few of the nuisance insects that Bt is used to control in agriculture. Because the insecticidal proteins in Bt are intended to target the insect’s stomach, it is effective versus these pests. The proteins in Bt are activated and create holes in the gut cells of insects when they consume it. As a result, the insect gradually perishes due to cell death.


Bt Varieties: Tailoring Solutions for Different Crops
| Bt variety | Crop | Insect target |
|---|---|---|
| Bt kurstaki | Corn, cotton, potatoes, tomatoes, soybeans, rice | European corn borer, cotton bollworm, tobacco budworm, tomato hornworm, soybean looper, rice leaffolder |
| Bt aizawai | Cotton, potatoes, tomatoes | Pink bollworm, potato tuberworm, tomato fruitworm |
| Bt israelensis | Cotton, vegetables, fruits | Mosquitoes, blackflies, and other biting flies |
| Bt tenebrionis | Cole crops, potatoes, tomatoes | Cabbage looper, diamondback moth, potato tuberworm, tomato fruitworm |
| Bt galleriae | Corn, cotton, vegetables, fruits | Corn earworm, cotton bollworm, tobacco budworm, tomato fruitworm |
Bt Resistance: Challenges and Strategies


A naturally occurring soil bacteria called Bacillus thuringiensis (BT) produces proteins that are insecticidal. These proteins are utilized in genetically engineered crops and as insecticides that are biological in nature since they are hazardous to some insect species.
An insect pest’s ability to endure exposure to Bt toxins is known as Bt resistance. There are multiple methods for this to happen, including:
- mutations in the genes which encode for the Bt toxin receptors. An insect will be less vulnerable to a Bt toxin if it has a mutation in the gene that encodes the receptor for the poison.
- increased enzymes for detoxification synthesis. Some insects have the ability to create enzymes that render Bt poisons ineffective.
- changes to the stomach lining of the bug. Some insects have the ability to modify the lining of their guts to decrease their permeability to Bt toxins.
Safety Considerations: Human Health and Beyond
| Safety consideration | Human health | Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity to humans and animals | Bt is not toxic to humans or other animals, including mammals, birds, fish, and honeybees. | Bt is also not toxic to beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings. |
| Allergic reactions | There have been a few reports of allergic reactions to Bt, but these are rare. | Bt is not known to have any negative environmental impacts. |
| Resistance | Insects can develop resistance to Bt toxins, but this can be delayed by using multiple Bt toxins and other pest control methods. | Bt is not known to have any negative impacts on the environment, but it is important to use it responsibly and avoid overuse. |
Future Prospects: Innovations and Beyond
A naturally existing soil bacteria called Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) produces proteins that are insecticidal. These proteins are utilized in genetically engineered crops and as biological insecticides while they are dangerous for certain insect species.
Bt has a number of advantages over chemical pesticides, including:
- It is safe to use around humans and animals.
- It is not harmful to beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings.
- It is biodegradable and does not leave residues in the environment.
- It can be used to control insect pests that have developed resistance to chemical pesticides.






