The use of computers to produce or modify images is known as computer-generated imagery (CGI). It is a broad phrase that covers a variety of methods, from producing straightforward 2D cartoons to producing lifelike 3D models.
CGI is now a crucial component of the movie and television industries, in addition to being employed in a wide range of different sectors including video games, advertising, and architecture.
The way we produce and consume images has been changed by CGI. Images may now be produced that are more thrilling, engaging, and lifelike than ever before.
Introduction to Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI)
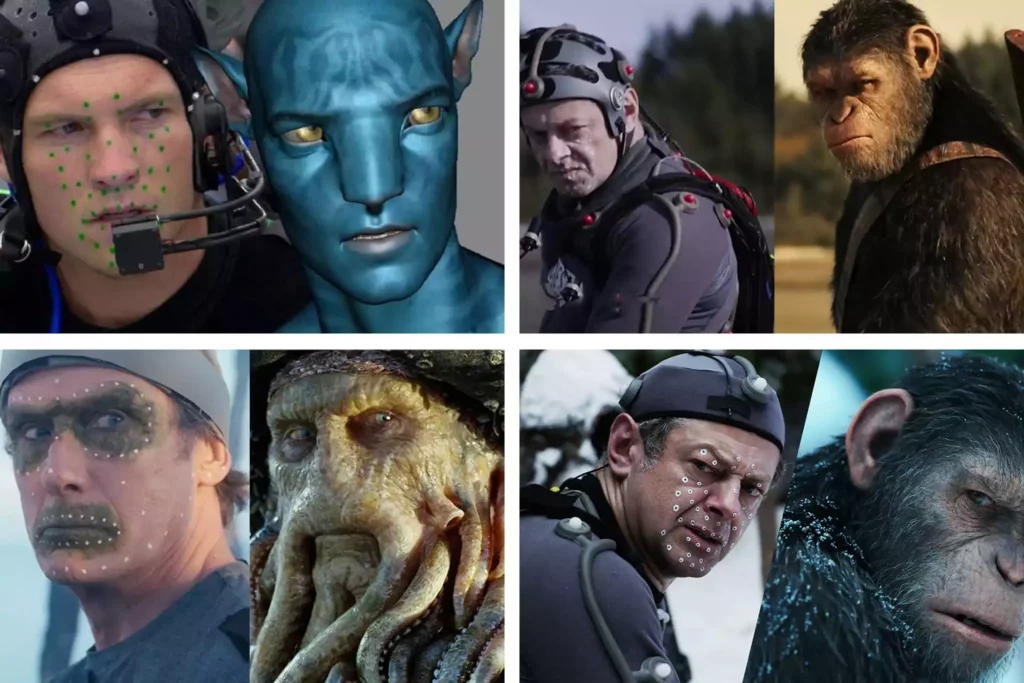



Here are some of the basics of CGI:
- 3D modeling: This is the process of creating three-dimensional objects using computer software.
- 3D animation: This is the process of creating the illusion of movement in three-dimensional objects.
- Rendering: This is the process of creating a final image from a 3D model or animation.
The Evolution of CGI: From Pixels to Photorealism
With several major turning points along the road, the development of CGI has been a protracted and difficult process. The following are some of the most important advancements in CGI history:
- 1960s: The first computer-generated images were created using mainframe computers. These images were very primitive, but they represented a major breakthrough.


- 1970s: The development of minicomputers made it possible to create more complex CGI images. These images were still not very realistic, but they were starting to look more like real objects.
- 1980s: The introduction of personal computers made CGI more accessible to a wider range of people. This led to a boom in the development of CGI software and techniques.
- 1990s: CGI became an essential part of the film industry, with groundbreaking films like Jurassic Park (1993) and Toy Story (1995) demonstrating its potential.
- 2000s: CGI continued to evolve, with the development of new techniques such as motion capture and procedural animation. These techniques made it possible to create even more realistic and complex CGI images.
- 2010s: The rise of 3D movies and video games further popularized CGI. These technologies allowed people to experience CGI images in a more immersive way.
- 2020s: CGI is now used in a wide variety of industries, from film and television to video games and architecture. The development of new technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning is making it possible to create even more realistic and lifelike CGI images.
Applications of CGI in Entertainment
- Film and Television
In the realm of cinema and television, CGI has allowed filmmakers to bring to life stories that were once deemed too complex or expensive to depict on screen. From epic battles to otherworldly realms, CGI has expanded the horizons of visual storytelling. - Video Games
The gaming industry has embraced CGI as a cornerstone of game design. Virtual worlds, characters, and immersive environments are all made possible through the creative use of computer-generated imagery. - Advertising and Marketing
CGI has transformed the way products are presented to consumers. From eye-catching product visualizations to imaginative advertisements, CGI plays a pivotal role in capturing attention and conveying messages.
The Magic Behind CGI: How It Works



- Modeling and Rendering
CGI begins with creating 3D models of objects, characters, or scenes. These models are then rendered, a process where the computer calculates how light interacts with the surfaces to generate realistic images. - Texturing and Lighting
Texturing adds depth and detail to the 3D models, while lighting replicates real-world illumination, adding realism and dimensionality to the CGI. - Animation and Simulation
CGI animation involves creating lifelike movements for characters or objects. Simulation, on the other hand, generates realistic effects like water, fire, and cloth dynamics.
Challenges and Innovations in CGI
- Achieving Realism
One of the ongoing challenges in CGI is achieving photorealism—creating visuals that are indistinguishable from reality. Continual advancements in technology and techniques contribute to narrowing this gap. - Balancing Creativity and Technology
While CGI offers unlimited creative possibilities, it’s essential to strike a balance between utilizing technology and preserving artistic expression.






