CP full form Cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement and coordination. It is caused by damage to the brain that occurs before or during birth. Symptoms can vary widely, but they may include weakness, stiffness, and difficulty walking, talking, and eating. There is no cure for CP, but there are treatments that can help improve symptoms and quality of life.
- Introduction : CP full form
- Overview : CP full form
- Risk factors : CP full form
- Complications : CP full form
- Types : CP full form
- Causes and Risk Factors : CP full form
- Signs and Symptoms : CP full form
- Diagnosis and Evaluation : CP full form
- Treatment and Management : CP full form
- Living with Cerebral Palsy : CP full form
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction : CP full form


Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of permanent, non-progressive motor disorders that affect movement, muscle coordination, and posture. It’s a neurological condition that typically manifests early in childhood and affects a person’s ability to control their muscles. The term “cerebral” refers to the brain’s cerebrum, which is the part of the brain that primarily controls movement.
Overview : CP full form
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A neurological disorder affecting movement, muscle tone, and motor skills due to brain damage. |
| Types | – Spastic CP (stiff muscles) – Dyskinetic CP (involuntary movements) – Ataxic CP (balance issues) – Mixed CP (combination of types) |
| Symptoms | – Delayed motor skills – Muscle stiffness/floppiness – Coordination and balance issues – Involuntary movements – Speech/swallowing difficulties – Abnormal gait patterns |
| Causes | – Brain injury during pregnancy or birth – Lack of oxygen (hypoxia) – Infections during pregnancy – Genetic factors |
| Diagnosis | – Physical examinations – Developmental screenings – Imaging tests (MRI, CT scans) |
| Treatment | – Physical therapy – Occupational therapy – Speech therapy – Medications – Surgery |
| Prognosis | Varies widely; many individuals can lead fulfilling lives with appropriate support and interventions. |
| Support | Involvement of families, caregivers, and support groups is crucial for navigating challenges. |
Risk factors : CP full form
Premature Birth: Babies born before 37 weeks of gestation have a higher chance of growing CP, specifically in the event that they have low delivery weight.
Low Birth Weight: Infants weighing less than five.5 pounds (2,500 grams) at beginning are at an improved chance for CP.
Multiple Births: Twins or higher-order multiples have a extra likelihood of CP, partly because of complications throughout being pregnant and beginning.
Infections During Pregnancy: Maternal infections, together with rubella or cytomegalovirus, can affect fetal mind development and increase the danger of CP.
Lack of Oxygen During Birth: Any occasion leading to oxygen deprivation in the course of labor and delivery can make contributions to mind injury and result in CP.
Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations and familial predispositions may additionally boom the danger of cerebral palsy, even though the precise position of genetics is still being studied.
Maternal Health Issues: Conditions including diabetes, high blood strain, or thyroid issues within the mom during being pregnant can impact fetal improvement and increase the danger of CP.
Complications : CP full form
Muscle and Joint Problems: Individuals with CP may additionally revel in muscle stiffness (spasticity) or weak point, leading to joint deformities and problems with motion.
Speech and Communication Difficulties: Many people with CP have hassle with speech due to muscle manage problems, that may have an effect on their capability to talk successfully.
Feeding and Swallowing Issues: Difficulty coordinating the muscle tissue involved in swallowing can cause feeding challenges, increasing the threat of aspiration (meals or liquid entering the airway).
Seizures: Some people with CP might also have epilepsy or experience seizures, which can complicate control and care.
Cognitive Impairments: While no longer all individuals with CP have intellectual disabilities, some might also enjoy cognitive challenges that can have an effect on gaining knowledge of and hassle-fixing.
Vision and Hearing Problems: Many children with CP may additionally have associated sensory troubles, which include visible impairments (e.G., strabismus) or listening to loss.
Emotional and Behavioral Challenges: Individuals with CP may additionally face emotional and behavioral problems, including tension and melancholy, partially due to the challenges related to their condition.
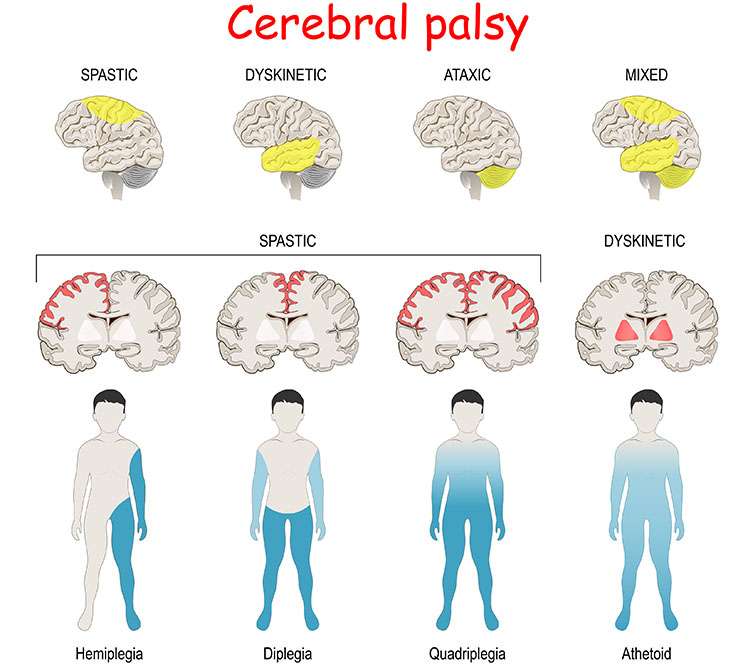
Types : CP full form
Spastic Cerebral Palsy:
Characteristics: Marked by way of stiff and tight muscle tissues, main to difficulties with motion and coordination.
Subtypes: It can be in addition categorized into spastic diplegia (affecting specifically the legs), spastic hemiplegia (affecting one aspect of the frame), and spastic quadriplegia (affecting all 4 limbs).
Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy:
Characteristics: Involves uncontrolled, involuntary actions that may be gradual or rapid.
Symptoms: This type may also result in problems with posture, balance, and nice motor capabilities, often supplying with abnormal muscle tone.
Ataxic Cerebral Palsy:
Characteristics: Characterized by bad coordination and stability, leading to an unsteady gait.
Symptoms: Individuals may additionally have problem with unique actions and might show off shaky or jerky motions.
Mixed Cerebral Palsy:
Characteristics: A combination of signs and symptoms from distinct types of CP, most commonly spastic and dyskinetic.
Symptoms: Individuals may additionally showcase varying motor impairments and difficulties, depending on the mixture of sorts present.
Hypotonic Cerebral Palsy:
Characteristics: This kind is marked via decreased muscle tone, leading to “floppiness” in the muscle mass.
Symptoms: Individuals may have difficulty maintaining posture and might war with fundamental motor abilties.
Causes and Risk Factors : CP full form
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Prenatal | |
| Brain Development Abnormalities | Issues with brain development during early stages of pregnancy, often influenced by genetic factors, infections, or exposure to harmful substances. |
| Genetic Factors | Genetic mutations or disorders that impact brain development in the fetus, either inherited or occurring spontaneously during fetal development. |
| Infections during Pregnancy | Certain infections during pregnancy (e.g., rubella, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis) can lead to brain damage in the fetus and increase the risk of Cerebral Palsy. |
| Maternal Health Issues | Maternal health conditions (e.g., thyroid disorders, seizures, untreated jaundice) that affect fetal brain development, potentially contributing to Cerebral Palsy. |
| Perinatal | |
| Hypoxia-Ischemia | Insufficient oxygen (hypoxia) or reduced blood flow (ischemia) to the brain during labor or delivery can cause brain damage, a significant risk factor for Cerebral Palsy. |
| Premature Birth | Babies born before 32 weeks of gestation, often with underdeveloped brains and fragile nervous systems, have a higher risk of developing Cerebral Palsy. |
| Low Birth Weight | Babies born with low birth weight due to premature birth or growth restriction during pregnancy are at an increased risk of Cerebral Palsy. |
Signs and Symptoms : CP full form
Motor Symptoms
- Spasticity:
Muscle stiffness and tightness, making movement jerky or abrupt. - Involuntary Movements: Uncontrolled movements, which can be slow and writhing (athetoid) or rapid and uncontrollable (chorea).
- Coordination and Balance Issues: Difficulty in coordinating movements and maintaining balance, leading to unsteady walking or frequent falls.
- Delayed Motor Milestones: Delays in reaching developmental motor milestones such as crawling, sitting, standing, or walking.
Non-Motor Symptoms
- Speech and Communication Difficulties: Challenges in speaking clearly, forming words, or coordinating facial muscles for speech.
- Swallowing Difficulties (Dysphagia): Difficulty in swallowing food or liquids safely and effectively.
- Drooling: Inability to control saliva, leading to drooling.
- Oral Motor Dysfunction: Difficulty with tasks involving the mouth, such as chewing, sucking, or blowing.
Diagnosis and Evaluation : CP full form
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Clinical Assessment | |
| Medical History | Detailed review of the individual’s medical and birth history, including prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal factors that might contribute to the diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy. |
| Developmental Milestones | Evaluation of developmental milestones (e.g., sitting, crawling, walking) to identify any delays or abnormalities in motor development. |
| Diagnostic Procedures | |
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | Imaging technique to visualize brain structure and identify any abnormalities, lesions, or damage that may help in diagnosing Cerebral Palsy. |
| CT (Computed Tomography) Scan | X-ray-based imaging to provide detailed images of the brain, often used in cases where MRI is not feasible or appropriate. |
| Neurological Assessment | |
| Electroencephalogram (EEG) | Measures electrical activity in the brain, helping diagnose seizures or abnormal brain function, which may be associated with Cerebral Palsy. |
| Evoked Potentials | Evaluates electrical activity in the brain in response to stimuli (e.g., auditory, visual), assisting in assessing nerve pathway function and detecting brain abnormalities. |
Treatment and Management : CP full form
- Early diagnosis: Prompt identification of Cerebral Palsy in infancy or early childhood to facilitate timely interventions.
2. Multidisciplinary approach: Involvement of a team of healthcare professionals for a comprehensive treatment plan, including neurologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and more.
3. Physical therapy (PT):
Stretching and strengthening exercises: Customized exercises to enhance muscle tone, flexibility, and strength.
Mobility training: Techniques and aids to improve movement, posture, and coordination.
4. Occupational therapy (OT):
Activities of daily living (ADL) training: Skills development for independent daily tasks like dressing, eating, and grooming.
5. Speech therapy:
Speech and communication training: Techniques to improve speech clarity and communication skills.
Living with Cerebral Palsy : CP full form
| Living with Cerebral Palsy | Description |
|---|---|
| Coping Strategies | |
| Emotional Support | Seeking emotional support from friends, family, support groups, or therapists to cope with the challenges and emotional aspects of living with Cerebral Palsy. |
| Self-Efficacy | Developing a belief in one’s ability to achieve goals and overcome challenges, promoting a positive mindset and determination to adapt and thrive in daily life. |
| Daily Living | |
| Adaptive Techniques | Learning and utilizing adaptive techniques and tools to perform daily activities more easily, maintaining independence and improving quality of life. |
| Time Management | Developing effective time management strategies to balance daily responsibilities, therapies, medical appointments, and leisure activities. |
| Education and Employment | |
| Inclusive Education | Advocating for inclusive educational settings that accommodate individuals with Cerebral Palsy, fostering equal opportunities for learning and development. |
Conclusion
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a complex neurological condition affecting motor function, often diagnosed in early childhood. It stems from brain abnormalities or injuries during fetal development, birth, or shortly after. This condition manifests in various forms, impacting muscle tone, coordination, and movement.
Early intervention is paramount, focusing on a multidisciplinary approach involving physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. These therapies, along with assistive devices, can significantly enhance an individual’s mobility and overall quality of life. Medications and orthopedic interventions can address specific symptoms and musculoskeletal issues.
FAQs
Q1: What is CP full form?
A: Cerebral Palsy is a neurological disorder that affects movement, muscle tone, and motor skills due to damage to the developing brain, often occurring during pregnancy, birth, or shortly after.
Q2: What causes Cerebral Palsy?
A: CP can result from various factors, including premature birth, low birth weight, lack of oxygen during birth, maternal infections during pregnancy, and genetic factors.
Q3: What are the different types of Cerebral Palsy?
A: The main types of CP are spastic, dyskinetic, ataxic, mixed, and hypotonic, each characterized by different movement and muscle tone issues.
Q4: How is Cerebral Palsy diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis typically involves physical examinations, developmental screenings, and imaging tests like MRI or CT scans to assess brain structure and function.
Q5: What are the symptoms of Cerebral Palsy?
A: Common symptoms include delayed motor skills, muscle stiffness or weakness, difficulties with coordination and balance, involuntary movements, speech issues, and abnormal gait.






