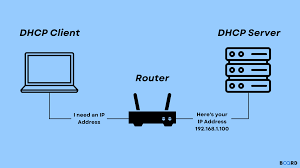
- DHCP is a client-server protocol. The DHCP server is responsible for storing and managing the IP addresses and other network settings. The DHCP client is a device that requests an IP address from the DHCP server.
- When a DHCP client boots up, it sends a DHCPDISCOVER message to the DHCP server. The DHCP server responds with a DHCPOFFER message, which contains an IP address and other network settings for the client. The client then sends a DHCPREQUEST message to the DHCP server to accept the offer.
- The DHCP server then leases the IP address to the client for a specified period of time. The client can renew the lease before the lease expires.
- Introduction to DHCP: DHCP full form
- DHCP message types: DHCP full form
- History : DHCP full form
- Basic Functioning: DHCP full form
- Advantages: DHCP full form
- Disadvantages : DHCP full form
- Characteristics : DHCP full form
- Components of CVA: DHCP full form
- CVA Calculation Methods
- Importance of CVA in Risk Management
- CVA and Derivatives Trading
- Mitigating Counterparty Risk
- Real-World Applications of CVA
- CVA Sensitivity Analysis
- Regulatory Implications of CVA
- Conclusion
- FAQs about CVA
Introduction to DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network.
- DHCP eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration, which can save time and reduce errors.
- It also makes it easier to manage network devices, as they can all be configured with the same IP address and other settings.
- DHCP works by having a DHCP server on the network that maintains a pool of IP addresses that it can assign to devices.
- When a device boots up, it sends out a DHCPDISCOVER message.
- The DHCP server responds with a DHCPOFFER message, offering the device an IP address and other configuration parameters.
- The device then sends back a DHCPREQUEST message to accept the offer.
- The DHCP server responds with a DHCPACK message to confirm the assignment.
Benefits of DHCP:
- Saves time and reduces errors by automating IP address configuration.
- Makes it easier to manage network devices by allowing them to be configured with the same IP address and other settings.
- Can improve network security by centralizing IP address management.
- Can reduce the number of duplicate IP addresses on the network.
Drawbacks of DHCP:
- DHCP servers can be a single point of failure.
- DHCP can be vulnerable to security attacks.
- DHCP can be complex to configure and manage.


DHCP message types
| Message Type | Description |
|---|---|
| DHCPDISCOVER | A message sent by a client to discover DHCP servers on the network. |
| DHCPOFFER | A message sent by a DHCP server to offer an IP address and other configuration parameters to a client. |
| DHCPREQUEST | A message sent by a client to request an IP address and other configuration parameters from a DHCP server. |
| DHCPACK | A message sent by a DHCP server to confirm the assignment of an IP address and other configuration parameters to a client. |
| DHCPNAK | A message sent by a DHCP server to deny the assignment of an IP address and other configuration parameters to a client. |
- DHCPDISCOVER: This message is sent by a client when it boots up or when its IP lease expires.
- DHCPOFFER: This message is sent by a DHCP server in response to a DHCPDISCOVER message.
- DHCPREQUEST: This message is sent by a client to accept an offer from a DHCP server.
- DHCPACK: This message is sent by a DHCP server to confirm the assignment of an IP address and other configuration parameters to a client.
- DHCPNAK: This message is sent by a DHCP server to deny the assignment of an IP address and other configuration parameters to a client.
History : DHCP full form
1984: The want for computerized IP address undertaking arose with the growing range of gadgets on networks.
1985: The Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) changed into brought as a precursor to DHCP, imparting fundamental IP configuration but requiring guide configuration for each device.
1993: DHCP changed into developed by means of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension to BOOTP, automating the procedure of IP deal with mission and configuration.
1994: The first legit DHCP specification, RFC 1531, became posted, defining how gadgets should automatically obtain IP addresses and different configuration settings.
1997: An updated specification, RFC 2131, become released, which stays the middle general for DHCP nowadays.
2003: DHCPv6 was introduced to aid the developing adoption of IPv6, taking into account the automated configuration of gadgets in an IPv6 community.
2006: The IETF launched RFC 3315, detailing the DHCPv6 protocol, which has similarities in purpose to DHCP for IPv4 however tailored for the distinct addressing scheme of IPv6.
Present: DHCP remains extensively utilized in networks of all sizes, offering a critical for the automated challenge and management of IP addresses in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
Basic Functioning: DHCP full form
| Step | Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. DHCP Discovery | Client Broadcasts Request | The DHCP client (e.g., a computer or mobile device) sends a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message to find available DHCP servers. |
| 2. DHCP Offer | Server Offers IP Address | A DHCP server responds with a DHCPOFFER message, offering an available IP address along with other network configuration details. |
| 3. DHCP Request | Client Requests Offered IP | The client sends a DHCPREQUEST message to the server, indicating acceptance of the offered IP address. |
| 4. DHCP Acknowledgment | Server Confirms IP Allocation | The server sends a DHCPACK message, confirming the lease of the IP address to the client. |
| 5. Lease Renewal | Client Renews IP Lease | Periodically, the client will send a DHCPREQUEST to renew its lease on the IP address before it expires. |
| 6. Lease Expiration | IP Address Returned to Pool | If the lease is not renewed, the IP address is released and returned to the pool of available addresses for reassignment. |
| 7. DHCP Release | Client Releases IP Address | When the client no longer needs the IP address, it sends a DHCPRELEASE message, releasing the address back to the server. |
Advantages: DHCP full form
Automatic IP Address Assignment: DHCP simplifies community control via mechanically assigning IP addresses to gadgets at the network. This automation eliminates the need for manual access, reducing the risk of configuration errors and ensuring that every device receives a completely unique IP address. It’s in particular useful in environments with a large variety of gadgets, as it guarantees seamless connectivity with out person intervention.
Centralized Management: DHCP lets in network directors to manipulate IP deal with allocation from a relevant server. This centralized technique makes it easier to oversee and control the community’s IP address scheme, follow changes consistently throughout the network, and troubleshoot problems. It also simplifies the deployment of recent devices, as they can automatically get hold of their network configuration from the DHCP server.
Efficient IP Address Utilization: DHCP dynamically allocates IP addresses from a predefined pool, which optimizes the use of to be had IP addresses. When a tool no longer desires an IP cope with (e.G., it disconnects from the network), DHCP can reclaim and reassign that deal with to every other device. This dynamic allocation prevents IP cope with exhaustion, in particular in networks with restricted address area.
Ease of Network Changes: DHCP enables smooth transitions while network configurations need to alternate, which includes adjusting subnet mask, gateways, or DNS settings. Since DHCP robotically offers up to date configurations to all devices, there’s no want for manual reconfiguration. This flexibility is important for networks that need to conform to evolving necessities or combine new offerings.
Disadvantages : DHCP full form
Single Point of Failure: If the DHCP server is going down, gadgets at the community might also fail to gain IP addresses, main to connectivity troubles. Without redundancy (e.G., a backup DHCP server), the whole network might be disrupted.
Limited Control Over IP Allocation: While DHCP automates IP cope with undertaking, it gives much less control over which precise IP deal with is assigned to every tool. This can be an difficulty in environments in which static IPs are needed for particular gadgets (e.G., servers, printers).
Security Vulnerabilities: DHCP does no longer inherently encompass sturdy safety capabilities, making it vulnerable to sure assaults, such as rogue DHCP servers that could offer false IP configurations. This can lead to hijacking or denial-of-provider (DoS) assaults.
IP Address Conflicts: Although DHCP is designed to prevent IP deal with conflicts, issues can nevertheless rise up if more than one DHCP servers are improperly configured or if devices with static IP addresses are within the DHCP range. This can cause community disruptions and connectivity problems.
Dependency on Network Infrastructure: DHCP relies at the underlying network infrastructure (e.G., routers, switches) to deliver IP configuration messages. In case of network issues or misconfigurations, DHCP may additionally fail to function effectively, affecting all related devices.
Difficulty in Troubleshooting: Diagnosing network problems associated with DHCP can be tough, mainly in big or complicated networks. Misconfigurations, rent expirations, or server failures can motive intermittent connectivity troubles that are tough to trace.
Characteristics : DHCP full form
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Allocation | DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices from a pool of available addresses, ensuring efficient use of IP space. |
| Centralized Management | All IP address assignments and network configurations are managed from a single DHCP server, simplifying network administration. |
| Automatic Configuration | Devices receive their IP address and other network settings (e.g., subnet mask, gateway) automatically upon connecting to the network. |
| Lease-Based | IP addresses are assigned with a lease time, after which the client must renew the lease or obtain a new IP address. |
| Support for Multiple Protocols | DHCP supports both IPv4 and IPv6, providing automatic configuration for networks using either protocol. |
| Scalability | DHCP is capable of managing IP address allocation in networks of all sizes, from small office setups to large enterprise environments. |
| Dynamic Reconfiguration | Changes to network settings (e.g., DNS servers) are automatically propagated to all clients without manual reconfiguration. |
| Conflict Avoidance | DHCP servers use mechanisms to avoid IP address conflicts, ensuring that each device on the network receives a unique IP address. |
DHCPDISCOVER
DHCPDISCOVER is a message sent by a DHCP client to discover DHCP servers on the network. It is the first message sent by a DHCP client when it boots up or when its IP lease expires.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the client’s MAC address and a list of DHCP options that the client is interested in.
- DHCP servers on the network respond to the DHCPDISCOVER message with a DHCPOFFER message, offering the client an IP address and other configuration parameters.
- The client then selects one of the offers and sends back a DHCPREQUEST message to accept the offer.
- The DHCP server then sends back a DHCPACK message to confirm the assignment of the IP address and other configuration parameters to the client.
Here are some additional details about DHCPDISCOVER:
- The DHCPDISCOVER message is sent to the broadcast address (255.255.255.255).
- The DHCPDISCOVER message is encapsulated in a UDP packet with a destination port of 67.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message is typically 32 bytes in size.
DHCP options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Subnet mask |
| 3 | Router |
| 6 | DNS server |
| 12 | Domain name |
| 15 | Lease time |
| 43 | Vendor class identifier |
- DHCP options are a way for DHCP servers to pass additional configuration information to DHCP clients.
- DHCP options are identified by a number.
- The most common DHCP options are 1, 3, 6, 12, and 15.
- DHCP options can be configured on DHCP servers and DHCP clients.
DHCP configuration
DHCP configuration is the process of setting up a DHCP server to assign IP addresses and other configuration parameters to DHCP clients.
- The DHCP server must be configured with a pool of IP addresses that it can assign to clients.
- The DHCP server must also be configured with the DHCP options that it will pass to clients.
- The DHCP server can be configured to use a DHCP relay agent to forward DHCP requests from clients that are not on the same subnet as the DHCP server.
- The DHCP server can also be configured to use DHCPv6 to assign IP addresses to IPv6 clients.
Here are some of the most important DHCP configuration settings:
- IP address pool: This is the range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to clients.
- Lease time: This is the length of time that a client can use an assigned IP address.
- DHCP options: These are the additional configuration parameters that the DHCP server will pass to clients.
- DHCP relay agent: This is a device that forwards DHCP requests from clients to DHCP servers.
- DHCPv6: This is the IPv6 equivalent of DHCP.
DHCP troubleshooting
Tip |
Description |
|---|---|
| Check the DHCP server configuration. | Make sure that the DHCP server is configured correctly and that it has a pool of IP addresses available to assign to clients. |
| Check the DHCP client configuration. | Make sure that the DHCP client is configured to use DHCP and that it has the correct DHCP server IP address. |
| Restart the DHCP server and DHCP clients. | This can sometimes clear up temporary problems. |
| Use a DHCP troubleshooting tool. | There are a number of DHCP troubleshooting tools available that can help you to diagnose and resolve DHCP problems. |
| Check the network cable connections. | Make sure that the network cables are properly connected and that there are no physical problems with the cables. |
| Check the DHCP logs. | The DHCP server logs can provide valuable information about DHCP problems. |
| Disable the DHCP server and see if the clients can get IP addresses from a different DHCP server. | This can help you to determine if the problem is with the DHCP server or with the clients. |
| Contact the DHCP server administrator. | If you are unable to resolve the problem, you may need to contact the DHCP server administrator for assistance. |
conclusion
- DHCP is a complex protocol, but it is essential for the smooth operation of any network. By understanding the basics of DHCP and how to troubleshoot problems, you can help to ensure that your network is always running smoothly.
- DHCP is a powerful tool that can be used to manage and automate network configuration. By understanding how DHCP works, you can use it to simplify your network management tasks and improve the security of your network.
FAQs about DHCP
Q1:What is DHCP?
A: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network.
Q2: How does DHCP work?
A: DHCP operates through a client-server model. The client sends a broadcast message (DHCPDISCOVER) to find a DHCP server.
Q3: What is an IP lease in DHCP?
A: IP lease is a temporary allocation of an IP address to a client. The lease has a set duration, after which the client must renew the lease or the IP address will be returned to the pool for reassignment.
Q4: What are DHCP reservations?
A: DHCP reservations allow administrators to assign a specific IP address to a particular device based on its MAC address. This ensures that the device always receives the same IP address from the DHCP server.
Q5: What is a DHCP relay agent?
A: A DHCP relay agent is a network device that forwards DHCP messages between clients and servers when they are on different subnets. This allows a single DHCP server to service multiple subnets.






