A test that captures the electrical activity of the heart is called an Electrocardiogram (ECG). It is a non-invasive, painless test that can be used to identify a number of different heart diseases. Additionally, a cardiac catheterization or other operations such as exercise can be monitored using an ECG. Electrodes are positioned on the skin at specified locations on the chest, arms, and legs to conduct an ECG. These electrodes pick up the electrical signals the heart produces and send them to a device that prints out a trace of them on paper or on a computer screen.


Introduction to ECG
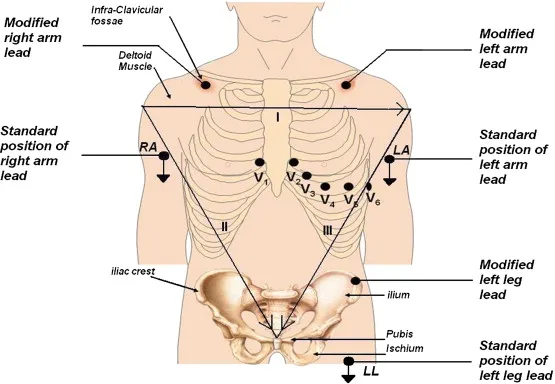
ECG stands for electrocardiogram. It is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart. The test is painless and usually takes a few minutes to perform. Electrodes are applied to the skin in order to conduct the ECG test. A device that records the electrical activity of the heart is attached to the electrodes.
An electrocardiogram, which is a trace of the electrical activity of the heart, is printed out by the machine. The ECG trace displays the size and shape of the electrical waves produced by the heart as well as its pace and rhythm. The ECG trace can be used by the doctor to identify heart issues and to track the heart’s condition over time.
Explaining the Acronym
Electrocardiogram is the technical term. It is a test that captures the heart’s electrical activity. It normally takes a few minutes to complete the painless test.
Cardiogram is a recording of the heart, and the word “electro” means electricity. The electrical activity of the heart is thus recorded by an ECG.
The cells of the heart produce the electrical activity of the heart. Electrical impulses are generated as these cells contract and relax. These electrical impulses are captured by the ECG machine, which graphs them.
The graph displays the size and shape of the electrical waves produced by the heart as well as its rate and rhythm. The doctor can monitor the heart’s health and diagnose heart issues using the ECG graph.
Here are some of the abbreviations used in ECG:
- P wave: The electrical activity of the atria, the heart’s upper chambers, is shown by this wave.
- The QRS complex: The lower heart chambers, or ventricles, exhibit electrical activity in the form of the QRS complex.
- T wave: The electrical activity of the ventricles following contraction is represented by this wave.
- After the T wave, the U wave can occasionally be observed. Its importance is not entirely clear.
Purpose and Function of ECG
Purpose |
Function |
|---|---|
| To diagnose heart conditions | The ECG can be used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions, including arrhythmias, heart attack, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and valve problems. |
| To monitor the heart’s condition | The ECG can be used to monitor the heart’s condition over time, which can help to detect changes in the heart’s electrical activity that may indicate a developing problem. |
| To assess the heart’s response to treatment | The ECG can be used to assess the heart’s response to treatment, such as medication or surgery. |
| To guide medical procedures | The ECG can be used to guide medical procedures, such as inserting a pacemaker or performing a heart catheterization. |
ECG Procedure
S. No. | Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation | The patient will be asked to remove any clothing that covers the chest and upper arms. The skin will be cleaned with an alcohol wipe. |
| 2. | Electrode placement | The technician will attach electrodes to the patient’s chest and upper arms. The electrodes are small, sticky pads that are connected to the ECG machine by wires. |
| 3. | Recording | The ECG machine will record the electrical activity of the heart for a few minutes. The patient will be asked to lie still during this time. |
| 4. | Interpretation | The technician will review the ECG tracing and interpret the results. The doctor will then review the results and discuss them with the patient. |
The ECG procedure is a painless and quick test. It usually takes about 5-10 minutes to complete. The patient may feel a slight tingling sensation when the electrodes are attached, but this is usually not painful.
The ECG results will be interpreted by a doctor or other healthcare professional. The results may be normal, or they may show signs of a heart condition. If the results are abnormal, the doctor may recommend further testing or treatment.
Interpreting ECG Results
Abnormal ECG Result |
Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Fast heart rate (tachycardia) | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, exercise, and certain medications. |
| Slow heart rate (bradycardia) | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart block, medication, and electrolyte imbalances. |
| Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, and medications. |
| Widened QRS complex | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart block, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications. |
| Depressed ST segment | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart attack, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications. |
| Elevated ST segment | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart attack, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications. |
| T wave inversion | Can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart attack, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications. |
Clinical Applications of ECG
- ECG is one of the most often utilised diagnostics for the diagnosis of cardiac problems. A wide range of heart diseases, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and valve issues, can be diagnosed using this test.
- An ECG can be used to keep an eye on the condition of the heart throughout time. This can assist in identifying variations in the electrical activity of the heart that can point to an emerging issue.
- ECG can be used to determine how well the heart is responding to various types of treatment, including medication and surgery.
- ECG can be used to direct medical procedures, such the insertion of a pacemaker or the performance of a heart catheterization.
- ECG can be used to test persons who are at high risk for heart disease for the condition.
- An ECG stress test is one that is carried out when the patient is stressed or exercising. This kind of test can be used to identify heart problems and gauge how the heart reacts to physical activity.
- A portable ECG gadget called a holter monitor can record the electrical activity of the heart for up to 24 hours. This kind of test can be used to identify arrhythmias and determine how well the heart is functioning on a daily basis.
- An event monitor is a wearable ECG that can be activated by the patient when they feel symptoms like palpitations or chest pain. This kind of test can be used to identify arrhythmias and evaluate the status of the heart during particular events.
Different Types of ECGs
Type of ECG | Description |
|---|---|
| Resting ECG | This is the most common type of ECG. It is performed while the patient is lying still and resting. |
| ECG stress test | This type of ECG is performed while the patient is exercising or under stress. This type of test can be used to diagnose heart conditions and to assess the heart’s response to exercise. |
| Holter monitor | This is a portable ECG device that can record the heart’s electrical activity for 24 hours or more. This type of test can be used to diagnose arrhythmias and to assess the heart’s condition during daily activities. |
| Event monitor | This is a portable ECG device that can be worn by the patient and activated when the patient experiences symptoms such as chest pain or palpitations. This type of test can be used to diagnose arrhythmias and to assess the heart’s condition during specific events. |
| ECG treadmill test | This is a type of ECG stress test that is performed on a treadmill. The patient walks on the treadmill at a gradually increasing speed and incline. |
| ECG bicycle test | This is a type of ECG stress test that is performed on a bicycle. The patient pedals the bicycle at a gradually increasing resistance. |
| ECG echocardiogram | This is a type of ECG that is performed during an echocardiogram. An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart. The ECG can be used to assess the heart’s electrical activity during the echocardiogram. |
| ECG ambulatory monitoring | This is a type of ECG that is performed over a period of time, typically 24 hours or more. The patient wears a portable ECG device that records the heart’s electrical activity. |
| ECG signal-averaged electrocardiography (ECG SAECG) | This is a type of ECG that is used to detect early signs of heart disease. The ECG SAECG records the heart’s electrical activity over a period of time and looks for small changes in the heart’s rhythm. |
| ECG T-wave alternans | This is a type of ECG that is used to detect early signs of heart disease. The ECG T-wave alternans records the heart’s electrical activity over a period of time and looks for changes in the shape of the T wave. |
Significance of ECG in Emergency Medicine
A test that captures the electrical activity of the heart is called an electrocardiogram (ECG). A range of cardiac diseases, including arrhythmias, heart attacks, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and valve issues, can be identified using this rapid and painless test.
In emergency medicine, ECGs are used to:
- Diagnose heart conditions: ECGs can be used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions, including arrhythmias, heart attack, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and valve problems.
- Assess the severity of a heart condition: ECGs can be used to assess the severity of a heart condition, such as a heart attack.
- Determine the best course of treatment: ECGs can be used to determine the best course of treatment for a heart condition, such as medication or surgery.
- Monitor the patient’s condition: ECGs can be used to monitor the patient’s condition over time, which can help to detect changes in the heart’s electrical activity that may indicate a developing problem.
- Guide medical procedures: ECGs can be used to guide medical procedures, such as inserting a pacemaker or performing a heart catheterization.
Advances in ECG Technology
ECG technology has advanced significantly in recent years. Some of the most notable advances include:
- Wireless ECG: Without being connected to an ECG machine, wireless ECG devices enable patients to record their heart’s electrical activity for lengthy periods of time. This is useful for identifying arrhythmias and other heart problems that might only manifest sporadically.
- Holter monitors: Portable ECG devices that can record the electrical activity of the heart for up to 24 hours. This can be useful for identifying heart disorders like arrhythmias and others that might only manifest themselves during particular activities or times of the day.
- Event monitors: Patient-activated event monitors are portable ECG devices that can be used to detect symptoms like palpitations or chest pain. This can be useful for identifying heart problems like arrhythmias and others that might only manifest during particular occurrences.
- ECG artificial intelligence: To automate the analysis of ECGs, ECG artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are being created. This might improve the effectiveness and precision of ECG interpretation.
- ECG wearables: To monitor the electrical activity of the heart, wearable ECG devices are worn on the wrist or chest. This might make ECG monitoring more practical and available for patients.
These are just a few of the advances that have been made in ECG technology in recent years. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more advances in ECG technology in the future.
Limitations and Challenges of ECG
ECG is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions, but it is not without its limitations and challenges. Here are some of the most common limitations:
- ECG can be used to diagnose a number of different heart problems, although it is not always able to identify all cardiac conditions. For instance, an ECG may not be able to identify heart disorders that do not alter the electrical activity of the heart or early stages of heart disease.
- Other factors can influence ECG readings, including drugs, electrolyte abnormalities, and movement. As a result, diagnosing heart problems and interpreting ECG readings may be challenging.
- The ECG is a static test, which means that it only records a moment in time’s worth of the electrical activity of the heart. Because of this, it may be challenging to diagnose heart diseases that come and go or alter over time.
- ECG interpretation is susceptible to subjectivity, which means that several medical professionals may have varying interpretations of the same ECG readings. This may make it challenging to draw a firm diagnosis from an ECG.
Future Directions and Innovations
Future Direction or Innovation |
Description |
Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Wearable ECG devices | These devices can be worn on the wrist or chest to record the heart’s electrical activity. This could make ECG monitoring more convenient and accessible for patients. | More patients could be monitored for heart conditions, which could help to improve early detection and treatment. |
| Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered ECG interpretation | AI algorithms are being developed to automate the interpretation of ECGs. This could potentially make ECG interpretation more efficient and accurate. | ECG interpretation could be made more efficient and accurate, which could lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions. |
| ECG-based risk stratification | ECG data can be used to assess a patient’s risk of developing heart disease or other heart conditions. This could help doctors to identify patients who are at high risk and who may need early intervention. | Early intervention could help to prevent or delay the onset of heart disease and other heart conditions. |
| ECG-based personalized medicine | ECG data can be used to develop personalized treatment plans for patients with heart conditions. This could lead to improved patient outcomes. | Personalized treatment plans could lead to better symptom control, improved quality of life, and reduced risk of complications. |
| ECG-based remote patient monitoring | ECG data can be used to monitor patients remotely. This could help patients to stay connected with their healthcare providers and to receive care more quickly if they experience problems. | Patients could receive care more quickly and easily, which could lead to improved outcomes. |






