Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is a special chemical that loves to grab onto metal ions tightly. It’s like a little magnet for metals! People use EDTA in different things, like making sure metal ions don’t mess up processes or removing harmful metals from certain products.
- EDTA Full Form: What Is EDTA Full Form
- EDTA Full Form: Structure of EDTA
- EDTA Full Form: Interesting Facts About EDTA
- EDTA Full Form: Usage Of EDTA Acid
- EDTA Full Form: Benefits Of EDTA
- EDTA Full Form: Applications of EDTA in Medicine
- EDTA Full Form: Environmental Impact of EDTA
- EDTA Full Form: EDTA-Caused Diseases Include
- EDTA Full Form: Future Prospects and Research on EDTA
- Frequently Asked Question
- Conclusion
EDTA Full Form: What Is EDTA Full Form?


EDTA stands for Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. It is a chelating agent, which means that it can bind to metal ions. EDTA is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Medical
-
- EDTA is used to treat lead poisoning and other metal poisonings.
- EDTA is also used to remove calcium from the blood, which can be helpful in treating conditions such as hypercalcemia.
Laboratory
- EDTA is used in the laboratory to chelate metal ions and prevent them from interfering with analytical assays.
- EDTA is also used to preserve blood samples and other biological specimens.
- Industrial
- EDTA is used in the industrial sector to remove metal ions from water and other fluids.
- EDTA is also used in the manufacture of plastics, textiles, and other products.
EDTA is a safe and effective chelating agent with numerous applications. It should be noted that EDTA has the ability to chelate vital metal ions, hence it should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare practitioner.
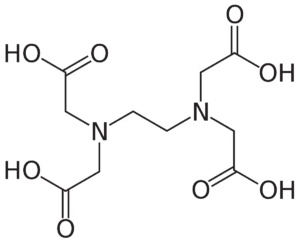
EDTA Full Form: Structure of EDTA
The structure of EDTA is a cyclic molecule with four carboxylic acid groups and two amine groups. The molecule is also known as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or ethylenediaminetetraacetate.
[CH2N(CH2CO2H)2]2NCH2CO2H
The two amine groups are located on the nitrogen atoms at the ends of the molecule, and the four carboxylic acid groups are located on the carbon atoms in the middle of the molecule.
EDTA is a hexadentate ligand, which means that it can bind to six metal ions. The two amine groups and four carboxylic acid groups can each bind to a metal ion, forming a stable complex.
The structure of EDTA is important for its ability to chelate metal ions. The chelating ability of EDTA is due to the presence of the two amine groups and four carboxylic acid groups. These groups can form strong bonds with metal ions, which helps to remove them from the body.
EDTA Full Form: Interesting Facts About EDTA
Here are some other interesting facts about EDTA:
- The name EDTA comes from the Greek word “chele,” which means “claw.” This is because EDTA has a claw-like molecular structure that binds to metal ions.
- EDTA is a white, water-soluble solid. It is odorless and tasteless.
- EDTA is a relatively stable compound. It is not easily broken down by heat or light.
- EDTA is a versatile compound. It can be used in a variety of applications.
EDTA Full Form: Usage Of EDTA Acid
Application |
Usage |
|---|---|
| Medical | |
| Treatment of lead poisoning and other metal poisonings | EDTA is used to bind to metal ions and remove them from the body. This can help to treat lead poisoning and other metal poisonings. |
| Removal of calcium from the blood | EDTA can be used to remove calcium from the blood. This can be helpful in treating conditions such as hypercalcemia, which is a condition where the level of calcium in the blood is too high. |
| Chelation therapy | EDTA is used in chelation therapy, which is a treatment for heavy metal poisoning. EDTA binds to heavy metals and removes them from the body. |
| Laboratory | |
| Chelation of metal ions | EDTA is used in the laboratory to chelate metal ions and prevent them from interfering with analytical assays. This is important because metal ions can often interfere with the accuracy of analytical tests. |
| Preservation of blood samples and other biological specimens | EDTA is used to preserve blood samples and other biological specimens. This is because EDTA binds to calcium, which can cause blood samples to clot. By binding to calcium, EDTA prevents blood samples from clotting and ensures that they remain fresh and viable for testing. |
| Industrial | |
| Removal of metal ions from water and other fluids | EDTA is used in the industrial sector to remove metal ions from water and other fluids. This is important because metal ions can often contaminate water and other fluids, making them unsafe to drink or use. |
| Manufacture of plastics, textiles, and other products | EDTA is used in the manufacture of plastics, textiles, and other products. This is because EDTA can help to improve the properties of these products. For example, EDTA can be used to make plastics more flexible and textiles more durable. |
| Other | |
| Cosmetics | EDTA is used in some cosmetics as a preservative. It can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and mold in cosmetics. |
| Food additives | EDTA is used in some food additives as a chelating agent. It can help to prevent the oxidation of food and the formation of free radicals. |
EDTA Full Form: Benefits Of EDTA
- It can be used to treat lead poisoning and other metal poisonings.
- It can be used to remove calcium from the blood.
- It can be used in chelation therapy, which is a treatment for heavy metal poisoning.
- It can be used to chelate metal ions in the laboratory and prevent them from interfering with analytical assays.
- It can be used to manufacture plastics, textiles, and other products.
EDTA Full Form: Applications of EDTA in Medicine
1. Chelation Therapy for Heavy Metal Poisoning
EDTA is used to deal with poisonous steel poisoning, including lead or mercury. It binds to metals withinside the bloodstream, permitting them to be excreted via urine, decreasing toxicity.
2. Treatment of Hypercalcemia
EDTA is applied to decrease improved calcium tiers withinside the blood, mainly in instances of hypercalcemia related to most cancers or different disorders. It binds calcium and enables its removal.
3. EDTA in Dialysis
In sufferers with kidney failure, EDTA is now and again hired for the duration of dialysis to save you calcium buildup withinside the blood. This allows preserve right mineral balance.
4. Anticoagulant Properties
EDTA is utilized in blood series tubes to save you clotting with the aid of using binding to calcium ions, which might be vital for blood clotting. This allows keep the integrity of blood samples for analysis.
5. Cardiovascular Disease Treatment
Some research endorse EDTA can also additionally enhance blood waft and decrease arterial plaque with the aid of using chelating calcium deposits in arteries, aleven though this software stays controversial.
6. Management of Iron Overload
EDTA has been explored as a remedy for situations like thalassemia, wherein iron overload from common blood transfusions occurs. It allows put off extra iron from the body.
7. Toxicity Reduction in Drug Overdose
EDTA has been investigated for decreasing toxicity from positive pharmaceutical overdoses, mainly in instances wherein poisonous steel contaminants can be involved.
8. As a Component in Antidotes
EDTA is blanketed in numerous medicinal antidotes to deal with poisoning from heavy metals and different poisonous substances. It works with the aid of using sequestering the dangerous sellers and facilitating their removal.
EDTA Full Form: Environmental Impact of EDTA
1. Persistence withinside the Environment
EDTA is rather chronic and does now no longer without difficulty degrade withinside the surroundings, main to its accumulation in soil and water over time. This staying power can bring about long-time period environmental impacts, particularly in aquatic ecosystems.
2. Impact on Aquatic Life
EDTA can bind to crucial metallic ions in water, disrupting the herbal metallic ion balance, that’s crucial for the fitness of aquatic organisms. High concentrations can have an effect on the boom and replica of fish and different aquatic species.
3. Soil Contamination
When EDTA is utilized in agricultural or commercial settings, it is able to leach into the soil, binding to metals and stopping their herbal cycling. This can result in long-time period infection and have an effect on soil fertility and plant fitness.
4. Bioaccumulation in Organisms
Although EDTA itself isn’t always rather toxic, it is able to purpose bioaccumulation of the metals it chelates, main to the switch of dangerous heavy metals up the meals chain. This will have dangerous consequences on flora and fauna and human fitness.
5. Effects on Water Treatment Processes
EDTA can intrude with water remedy tactics, specially in eliminating metals from infected water. Its presence in wastewater can lessen the effectiveness of conventional water remedy methods, making it greater tough to purify water.
6. Toxicity to Microorganisms
The presence of EDTA withinside the surroundings can adjust microbial pastime through disrupting the supply of hint metals that microbes want for boom. This can effect atmosphere function, particularly in soil and aquatic environments.
7. Regulations and Environmental Standards
Due to its environmental risks, numerous regulatory our bodies have set limits at the use and discharge of EDTA in water and wastewater. However, rules continue to be inconsistent, and its substantial use in commercial tactics increases ongoing concerns.
8. Biodegradability Challenges
EDTA is understood for its sluggish biodegradation, which makes it complex for ecosystems. Researchers are exploring methods to beautify its degradation via microbial and chemical means, however those answers aren’t but substantial.
EDTA Full Form: EDTA-Caused Diseases Include
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Ingestion of high amounts of EDTA can cause stomach upset, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Hypocalcemia: EDTA can bind to calcium ions, which can lead to low levels of calcium in the bloodstream (hypocalcemia). This can result in muscle cramps, twitching, and in severe cases, life-threatening complications.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to EDTA, resulting in skin rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Kidney Damage: In rare cases, excessive exposure to EDTA can lead to kidney damage or renal toxicity.
In addition to the side effects listed above, there have been some reports of EDTA causing other diseases, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: A small study published in 1990 found that EDTA may trigger rheumatoid arthritis in some people. However, more research is needed to confirm this finding.
- Neurotoxicity: EDTA has been shown to cause neurotoxicity in animals, and there is some concern that it may also cause neurotoxicity in humans. However, more research is needed to confirm this finding.
EDTA Full Form: Future Prospects and Research on EDTA
1. Biodegradable EDTA Alternatives
Ongoing studies specializes in growing biodegradable options to EDTA to lessen environmental concerns. These options goal to imitate EDTA`s chelating skills whilst being extra eco-friendly.
2. EDTA in Green Chemistry
EDTA`s capacity in inexperienced chemistry is being explored, specially for its function in lowering poisonous waste in commercial processes. Researchers are running on optimizing its performance in sustainable applications.
3. EDTA in Nanotechnology
The use of EDTA in nanotechnology is expanding, specifically withinside the stabilization of nanoparticles. Research is aimed toward enhancing its interplay with nanomaterials for diverse biomedical and commercial applications.
4. EDTA in Water Treatment
EDTA’s function in water purification and waste remedy is beneathneath investigation, specially for heavy steel removal. New strategies are being researched to make water remedy extra cost-powerful and efficient.
5.Improved Methods for EDTA Recycling
As EDTA is used in lots of commercial processes, efforts are being made to increase techniques for its recycling and reuse. This could lessen environmental effect and make EDTA extra sustainable for long-time period use.
6. EDTA in Biomedical Research
The capacity use of EDTA in drug shipping structures and as a healing agent in sure illnesses is being explored. Studies are specializing in its function in improving drug bioavailability and remedy outcomes.
7. Regulatory and Safety Advances in EDTA Use
Research is specializing in improving protection protocols for EDTA use, specially in agriculture and meals industries. This consists of growing safer, decrease doses and enhancing protection measures to decrease toxicity.
8. Role of EDTA in Circular Economy
EDTA`s function in a round financial system is a developing place of studies, specially in how it may be reused in diverse industries, inclusive of electronics recycling. Researchers goal to comprise EDTA into closed-loop structures for extra sustainable aid management.
Frequently Asked Question
EDTA stands for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. It is a chelating agent, which means that it can bind to metal ions. EDTA is used in a variety of applications.
EDTA is generally safe when used under the supervision of a healthcare professional. However, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects of EDTA and to monitor your blood levels closely if you are taking EDTA.
EDTA prevents clotting by binding to calcium ions, which are essential for blood clotting. This effectively prevents the formation of a blood clot. EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is a chelating agent, which means that it can bind to metal ions. Calcium is a metal ion that is essential for blood clotting. By binding to calcium ions, EDTA prevents them from participating in the clotting cascade, thereby preventing blood clots from forming.
EDTA lasts for about 12 hours in a blood sample.
Yes, EDTA is used as a food additive (with the E number E385) to prevent oxidation and extend the shelf life of certain products by binding metal ions that may catalyze spoilage reactions.
EDTA can pose environmental concerns because it is stable and may not easily break down in the environment. It can bind to metal ions in water systems, potentially affecting aquatic life if it accumulates.
Conclusion
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, or EDTA, is a chelating agent that can bind to metal ions. It is used in a variety of medical applications, including the treatment of lead poisoning and other metal poisonings. EDTA is also used in the laboratory to chelate metal ions and prevent them from interfering with analytical assays.






