HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It refers to a gadget used to modify the indoor surroundings of homes through supplying heating, cooling, and ventilation. HVAC structures are critical for keeping indoor air quality, temperature control, and thermal consolation in residential, commercial, and commercial homes.
The heating aspect guarantees warm temperature at some stage in chillier months, frequently the usage of furnaces, boilers, or warmth pumps. Ventilation includes the movement and filtration of air, eliminating pollutants, odors, and extra moisture to preserve easy and clean indoor air. The aircon element cools and dehumidifies the air, supplying consolation at some stage in hotter seasons.
- HVAC Full Form: Introduction to ISC
- HVAC Full Form: Heating Systems
- HVAC Full Form: Ventilation and Air Exchange
- HVAC Full Form: Air Conditioning Systems
- HVAC Full Form: HVAC Components and Equipment
- HVAC Full Form: Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- HVAC Full Form: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- HVAC Full Form in Construction
- What is HVAC system in building
- HVAC Full Form: Conclusion
- HVAC Full Form: FAQs
HVAC Full Form: Introduction to HVAC
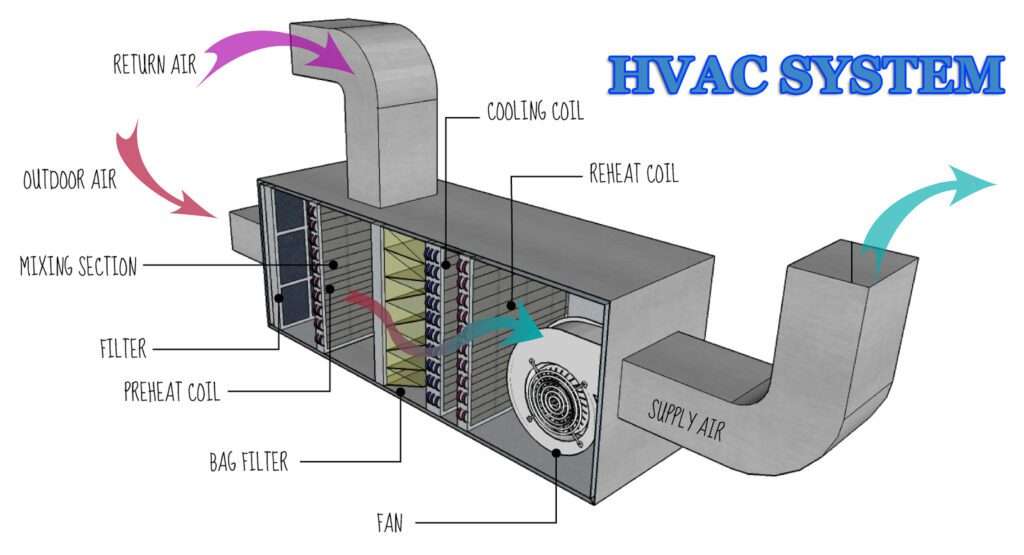


In the ever-changing landscape of modern living, the concept of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. From keeping us warm during frigid winters to providing cool respite in scorching summers, HVAC systems play a pivotal role in creating comfortable indoor environments. This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of HVAC systems, uncovering their significance, principles, and the transformative impact they have on our quality of life.
Understanding the Importance of HVAC HVAC systems are not mere luxuries; they are essential components that contribute to our overall well-being. Proper temperature control ensures that we remain cozy in winter and cool in summer, promoting health and comfort. Moreover, HVAC systems are instrumental in maintaining optimal indoor air quality, minimizing pollutants and allergens that can adversely affect our health.
How HVAC Enhances Comfort and Indoor Air Quality Imagine a winter’s day without the warmth of a heating system or a sweltering summer afternoon devoid of the cooling relief of air conditioning. HVAC systems create environments where we can work, relax, and sleep comfortably, regardless of the weather outside. Additionally, these systems regulate humidity levels and facilitate air exchange, ensuring that the air we breathe is fresh and free from contaminants.
HVAC Full Form: Heating Systems
Types of Heating Systems There’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to heating systems. Different environments and preferences call for different approaches. We’ll delve into various heating options, including:
- Furnaces: These common systems burn fuel (such as natural gas or oil) to generate heat that is then distributed throughout the building.
- Heat Pumps: Operating as both heaters and air conditioners, heat pumps extract heat from the outdoor air (or ground) and transfer it indoors.
- Boilers: Using water or steam, boilers distribute heat through radiators, baseboards, or underfloor heating systems.
How Heating Systems Work Understanding the inner workings of heating systems provides insight into their efficiency and functionality. We’ll explore concepts like combustion, heat exchange, and distribution methods. Furnaces, for instance, involve burning fuel in a combustion chamber to produce heat, while boilers use water to distribute heat through radiators or pipes.
Energy Efficiency and Heating Options With sustainability at the forefront of modern living, energy-efficient heating options have gained traction. We’ll delve into how different heating systems fare in terms of energy consumption and environmental impact. We’ll also touch on considerations like insulation and home design that can significantly impact a heating system’s efficiency.
HVAC Full Form: Ventilation and Air Exchange
Role of Ventilation in Indoor Air Quality Ventilation is the process of exchanging indoor air with fresh outdoor air. It serves as a vital component of maintaining good indoor air quality by diluting pollutants, allergens, and odors that accumulate indoors. Proper ventilation also helps control humidity levels, reducing the risk of mold growth and promoting a healthier living environment.
Types of Ventilation Systems We’ll explore two main types of ventilation systems: natural and mechanical.
- Natural Ventilation: Utilizing natural forces such as wind and temperature differences to facilitate air movement through windows, doors, and vents.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Employing mechanical systems, such as fans and ductwork, to actively exchange indoor and outdoor air. Mechanical ventilation offers more control and efficiency, especially in tightly sealed modern buildings.
Air Exchange Rate and Fresh Air Intake The air exchange rate, measured in Air Changes per Hour (ACH), quantifies how often the air within a space is replaced with fresh air. We’ll discuss the factors that influence the optimal air exchange rate for different environments, ensuring a balance between air quality and energy efficiency. Fresh air intake mechanisms, such as air filters and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs), play a crucial role in enhancing indoor air quality.
HVAC Full Form: Air Conditioning Systems
Principles of Air Conditioning At the heart of air conditioning lies the principle of refrigeration. This process involves the circulation of refrigerant, a fluid that undergoes phase changes to absorb and release heat, allowing for effective cooling. Understanding these fundamental principles is key to grasping how air conditioning systems create indoor comfort.
Types of Air Conditioning Systems Air conditioning isn’t a one-size-fits-all concept. Different spaces and requirements call for different solutions. We’ll delve into various air conditioning options, including:
- Central Air Conditioning: These systems cool an entire building by distributing cool air through a network of ducts and vents.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ideal for spaces lacking ductwork, these systems consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units that provide localized cooling.
- Window and Portable Units: These smaller, standalone units are suitable for cooling individual rooms or specific areas.
Cooling Load Calculation and Sizing Determining the appropriate size of an air conditioning system is crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency. We’ll discuss the concept of cooling load calculation, which takes into account factors such as the size of the space, insulation, windows, and climate.
HVAC Full Form: HVAC Components and Equipment
Thermostats and HVAC Controls Thermostats serve as the command center of HVAC systems, allowing users to set desired temperatures and control system operation. We’ll explore the evolution of thermostats, from traditional manual models to modern programmable and smart thermostats that enhance energy efficiency and convenience.
Ductwork and Air Distribution Systems Ductwork acts as the circulatory system of HVAC systems, carrying conditioned air from central units to different rooms. We’ll delve into the types of ductwork and their design considerations. Additionally, we’ll discuss air distribution systems, such as vents and registers, that ensure even air distribution throughout the space.
Filters, Humidifiers, Dehumidifiers Filters play a vital role in maintaining indoor air quality by capturing dust, allergens, and pollutants. We’ll explore different filter types and their efficiency levels. Additionally, we’ll discuss the role of humidifiers and dehumidifiers in regulating indoor humidity, creating a comfortable and healthy environment.
HVAC Full Form: Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
HVAC and Energy Consumption HVAC systems are significant energy consumers in residential and commercial buildings. We’ll delve into the factors that contribute to energy consumption, such as system efficiency, insulation, building design, and user behavior. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed choices to reduce energy usage.
Energy-Efficient HVAC Practices We’ll uncover a range of strategies to enhance the energy efficiency of HVAC systems, including:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensuring that HVAC systems are well-maintained helps them operate at peak efficiency.
- Proper Sizing: Selecting the right-sized equipment prevents energy waste and discomfort.
- Programmable Thermostats: These devices optimize energy use by adjusting temperatures based on occupancy patterns.
- Duct Sealing and Insulation: Properly sealed and insulated ductwork minimizes energy losses.
Role of HVAC in Green Buildings HVAC plays a vital role in achieving the objectives of green building design, which prioritizes resource efficiency and sustainability. We’ll explore how design strategies like passive solar heating, natural ventilation, and energy recovery ventilation contribute to energy-efficient and eco-friendly buildings.
HVAC Full Form: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Importance of Regular Maintenance Regular maintenance is the key to preventing breakdowns, maximizing energy efficiency, and prolonging the lifespan of your HVAC system. We’ll discuss the benefits of scheduling routine maintenance, including improved performance, lower energy bills, and enhanced indoor air quality.
Common HVAC Issues and Troubleshooting Tips HVAC systems may encounter issues over time. Understanding these common problems and learning how to troubleshoot them can help you take proactive measures. We’ll cover issues such as uneven heating or cooling, poor airflow, unusual noises, and more. Troubleshooting tips can range from checking air filters to verifying thermostat settings.
HVAC Full Form in Construction
1.Introduction to HVAC in Construction
Full Form and Definition of HVAC
Importance of HVAC Systems in Buildings
Role of HVAC in Modern Construction Projects
2.Components of HVAC Systems
Heating Systems (Furnaces, Boilers, Heat Pumps)
Ventilation Systems (Exhaust Fans, Air Ducts, Filters)
Air Conditioning Systems (Split Units, Central AC, Chillers)
3.Types of HVAC Systems
Centralized HVAC Systems
Decentralized HVAC Systems
Hybrid HVAC Systems
4.HVAC Design and Installation
Planning HVAC Requirements for Construction Projects
Designing for Energy Efficiency and Load Calculation
Installation of HVAC Ducts, Piping, and Units
5.Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems
Use of Energy-Efficient Equipment (SEER Ratings)
Smart HVAC Controls and Automation
Renewable Energy Integration (Solar HVAC, Geothermal Systems)
6.Maintenance and Management of HVAC
Regular Inspections and Servicing
Troubleshooting Common HVAC Issues
Extending the Lifespan of HVAC Systems
7.HVAC Standards and Regulations
Building Codes and Compliance (ASHRAE Standards)
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Requirements
Environmental Guidelines for HVAC Systems
8.Advancements in HVAC Technology
Smart HVAC Systems and IoT Integration
Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) Systems
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly HVAC Innovations
What is HVAC system in building
1.Introduction to HVAC Systems
Full Form of HVAC: Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
Purpose of HVAC Systems in Buildings
Importance of Indoor Climate Control
2.Key Components of HVAC Systems
Heating Units (Boilers, Heat Pumps, Radiators)
Ventilation Systems (Air Ducts, Filters, Exhausts)
Air Conditioning Units (Chillers, Split Systems, Central AC)
3.Types of HVAC Systems
Centralized HVAC Systems
Decentralized HVAC Systems
Hybrid HVAC Systems
4.Working of HVAC Systems
How Heating Works (Heat Transfer and Distribution)
How Ventilation Works (Airflow and Filtration)
How Air Conditioning Works (Cooling and Humidity Control)
5.HVAC System Design in Buildings
Calculating Heating and Cooling Loads
Zoning and Airflow Management
Space and Energy Efficiency Considerations
6.Benefits of HVAC Systems
Improving Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
Thermal Comfort for Occupants
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
7.Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Servicing
Common HVAC Problems (Leaks, Poor Airflow, Noise)
Tips for Ensuring Optimal HVAC Performance
8.Advanced HVAC Technologies
Smart HVAC Systems with IoT Integration
Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) Systems
Use of Renewable Energy (Geothermal and Solar HVAC Systems)
Conclusion
The journey through the realm of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) has been a fascinating exploration of the systems that shape our indoor environments. From the warmth of efficient heating systems to the cool comfort provided by air conditioning, and the fresh air exchange facilitated by ventilation, HVAC is the backbone of modern living.
Through this comprehensive guide, we’ve uncovered the intricate workings of HVAC systems, delved into their components and technologies, and explored the importance of energy efficiency and sustainability. HVAC is more than just temperature control; it’s about creating environments that enhance our well-being, health, and productivity.
FAQs
HVAC is an acronym that stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. A residential HVAC system is a complete home comfort system that can heat and cool your home, as well as provide improved indoor air quality and humidity control. There are many different types of HVAC systems.
HVAC is an acronym that stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. A residential HVAC system is a complete home comfort system that can heat and cool your home, as well as provide improved indoor air quality and humidity control. There are many different types of HVAC systems.
Central air conditioning cools an entire building using ducts and vents, while ductless mini-split systems provide localized cooling without the need for ductwork. Each indoor unit in mini-split systems serves a specific area or room.
Regular maintenance, proper sizing, sealing and insulating ductwork, using programmable thermostats, and adopting energy-efficient technologies like variable-speed systems can enhance energy efficiency.






