Want create site? Find Free WordPress Themes and plugins.
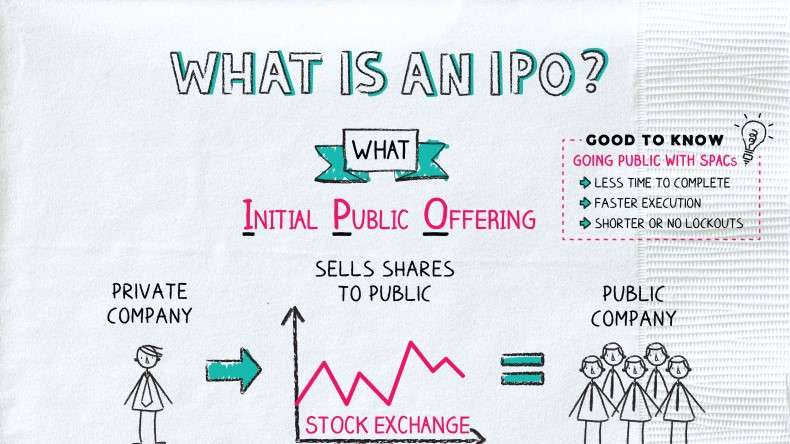
Privately held companies have long been lured to start a revolutionary journey known as a **Initial Public Offering (IPO)** by the appeal of the stock market and the promise of growth. We explain the intricate nature of IPOs in this guide, from the justification for going public to the careful processes required in the process. Join us as we delve into the world of IPOs, the process by which private companies become publicly listed businesses.
IPO Process: From Private to Public



A private firm will initially offer shares of its stock to the general public through an initial public offering (IPO). This makes it possible for the business to raise funds and then go public.
The IPO procedure can take months or even years to complete because of its complexity. The main phases in an IPO are outlined below:
- choosing a bank for investment. Selecting a financial institution to assist the company with the IPO process is the first stage. The investment bank will give suggestions and direction on every facet of the IPO, including share price, offering promotion, and risk underwriting.
- Diligent work. The investment bank will carry out due diligence on the company to make sure it is a wise choice for consumers as a whole. This include looking at the business’s financial records, operations, and management group.
Benefits and Risks of Going Public
Going public offers a multitude of benefits, including access to capital, increased visibility, and enhanced credibility. However, it also comes with inherent risks, such as regulatory compliance, financial scrutiny, and the potential loss of control. We delve into the pros and cons that companies must weigh before taking the IPO plunge.




Choosing Underwriters and Investment Banks
| Investment Bank | Underwriting Experience | Industry Focus | Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goldman Sachs | Extensive experience in all types of underwriting, including IPOs, debt offerings, and equity offerings | Financial services, technology, healthcare, and consumer goods | 20% |
| Morgan Stanley | Strong track record in IPOs and equity offerings | Financial services, technology, and healthcare | 15% |
| JPMorgan Chase | Wide range of underwriting experience, with a focus on large deals | Financial services, energy, and real estate | 12% |
| Bank of America Merrill Lynch | Experience in all types of underwriting, with a focus on large deals | Financial services, technology, and consumer goods | 10% |
| Deutsche Bank | Strong track record in European IPOs and debt offerings | Financial services, technology, and healthcare | 8% |
Preparing for an IPO: Legal, Financial, and Regulatory Considerations





The following are some legal, financial, and regulatory factors to take into account as you get ready for an IPO:
- Legal Considerations
- Securities Act of 1933: According to this law, businesses must register their securities with the SEC before making them accessible to consumers. This involves submitting a registration statement to the SEC with thorough information about the business, the company, and its financial standing.
- Securities Exchange Act of 1934: The trading of securities on public exchanges is regulated by this law. Companies are required to submit periodic reports, such as annual reports, quarterly reports, and current reports, to the SEC. Trading by insiders and market manipulation are also forbidden.
2.
Financial Considerations
- Financial statements:
Companies must prepare audited financial statements that meet SEC requirements. These statements must be prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). - Valuation: The company must be valued appropriately in order to set a fair share price for the IPO. This is a complex process that involves considering a variety of factors, such as the company’s financial performance, its growth prospects, and its competitive landscape.
3. Regulatory Considerations
- Exchange listing requirements: Companies must meet the listing requirements of the stock exchange where they want to list their shares.
- Industry regulations: Companies may be subject to additional regulations in their industry, such as those governing healthcare or financial services.
Roadshow and Investor Relations: Building Momentum
The IPO roadshow is a captivating ballet of presentations, meetings, and interactions with potential investors. We dissect the art of the roadshow, highlighting its significance in generating investor interest and securing strong market demand.
Future Trends and Innovations in IPOs
The world of IPOs continues to evolve with technological advancements, changing regulations, and shifting investor preferences. We peer into the future, exploring emerging trends and innovations that promise to reshape the IPO landscape.
Conclusion
The Initial Public Offering (IPO) journey is a transformative endeavor that reshapes the destiny of companies and reshuffles the economic landscape. From the allure of Wall Street to the meticulous preparations, an IPO is a symphony of strategic decisions, financial prowess, and calculated risks. As we demystify the IPO process, we uncover the tapestry of ambitions, aspirations, and entrepreneurial spirit that fuel this thrilling voyage from private to public.
FAQs
While many companies can go public, the decision depends on factors such as financial health, growth prospects, market conditions, and regulatory compliance.
The IPO price is determined through a combination of market analysis, investor demand, and valuation considerations. Underwriters play a key role in helping set the final offering price.
Companies go public to raise capital, gain access to a larger pool of investors, enhance brand visibility, and facilitate acquisitions and growth opportunities.
Did you find apk for android? You can find new Free Android Games and apps.






