LED stands for Light-Emitting Diode. LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are widely used in lighting, displays, and other applications due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. LEDs have transformed the lighting industry and offer sustainable and efficient lighting solutions.
What is the full form of LED?
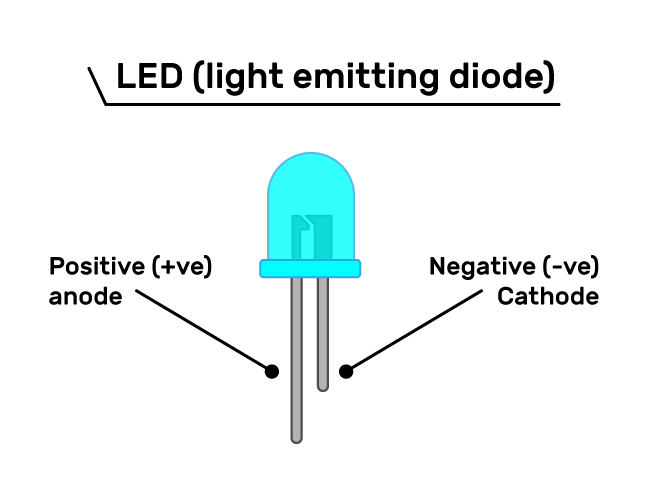


A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. LEDs are used in a wide variety of applications, including digital displays, traffic lights, and flashlights. LEDs are more efficient than traditional light sources, such as incandescent bulbs and fluorescent lamps. They also last longer and are more durable. As a result, LEDs are becoming increasingly popular in homes and businesses.
LEDs are available in a variety of colors, including red, green, blue, yellow, and white. They can also be dimmed, which makes them ideal for use in applications such as mood lighting. The first LED was invented in 1962 by Nick Holonyak, Jr., a researcher at General Electric. However, it took several years for LEDs to become commercially viable. In the early 1990s, LEDs began to be used in digital displays. Since then, their use has expanded to a wide variety of applications.
Today, LEDs are one of the most popular light sources in the world. They are used in everything from traffic lights to smartphones. As their efficiency and affordability continue to improve, LEDs are likely to become even more popular in the future.
Applications of LED
Application |
Description |
|---|---|
| Lighting | – General lighting for residential, commercial, and industrial settings. |
| – Energy-efficient and long-lasting light sources. | |
| Display and Signage | – Electronic billboards, outdoor advertising displays, stadium screens. |
| – Indoor digital signage, scoreboards, and information displays. | |
| Backlighting | – Backlighting for LCD screens in televisions, monitors, smartphones. |
| – Provides uniform and efficient lighting behind the screen. | |
| Automotive Lighting | – Headlights, taillights, turn signals, and interior lighting in vehicles. |
| – Offers improved visibility, energy efficiency, and design flexibility. | |
| Decorative and Architectural | – Decorative lighting in homes, hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues. |
| Lighting | – Accent lighting, architectural highlights, color-changing effects. |
| Outdoor and Landscape | – Streetlights, parking lot lighting, pathway lighting, and landscape illumination. |
| Lighting | – Energy-efficient and durable lighting solutions for outdoor areas. |
| Consumer Electronics | – Indicating device status in smartphones, tablets, laptops, wearables. |
| – Power on/off, battery charging, notifications. | |
| Medical and Scientific | – Medical diagnostics, phototherapy, fluorescence microscopy. |
| Applications | – Precise and controllable light sources for medical and scientific equipment. |
| Entertainment and Stage | – Stage lighting, concerts, theaters, television studios. |
| Lighting | – Vibrant colors, dynamic effects, versatile lighting atmospheres. |
| Industrial and Commercial | – Task lighting, high-bay lighting, signage, energy-efficient solutions in industries and retail stores. |
LED Models
- InGaN LED: This is a type of LED that uses indium gallium nitride as its semiconductor material. InGaN LEDs are known for their high brightness and efficiency. They are often used in applications where a lot of light is needed, such as headlights and stage lighting.
- GaN LED: This is another type of LED that uses gallium nitride as its semiconductor material. GaN LEDs are also known for their high brightness and efficiency. They are often used in applications where a high power output is required, such as laser pointers and high-power flashlights.
- AlGaInP LED: This is a type of LED that uses aluminum gallium indium phosphide as its semiconductor material. AlGaInP LEDs are known for their high color purity and efficiency. They are often used in applications where accurate color reproduction is required, such as museum lighting and retail displays.
- AlGaAs LED: This is a type of LED that uses aluminum gallium arsenide as its semiconductor material. AlGaAs LEDs are known for their high brightness and efficiency. They are often used in applications where a long lifespan is required, such as traffic lights and streetlights.
- Nichia 219B LED: This is a high-power LED that is known for its high brightness and efficiency. It is often used in applications where a lot of light is needed over a wide area, such as stadium lights and floodlights.
- Cree XP-G2 LED: This is a high-brightness LED that is known for its high efficiency and CRI. It is often used in applications where accurate color reproduction is required, such as museum lighting and retail displays.
- Osram Oslon SSL LED: This is a high-quality LED that is known for its high efficiency and durability. It is often used in applications where long life is required, such as streetlights and traffic lights.
- Lumileds Luxeon Rebel LED: This is a high-power LED that is known for its high brightness and efficiency. It is often used in applications where a lot of light is needed over a wide area, such as stadium lights and floodlights.
- Philips Lumileds LUXEON Rebel ES LED: This is a high-performance LED that is known for its high efficiency and CRI. It is often used in applications where accurate color reproduction is required, such as museum lighting and retail displays.
- Samsung LM301B LED: This is a high-output LED that is known for its high efficiency and CRI. It is often used in applications where a lot of light is needed with good color reproduction, such as grow lights and studio lighting.
- Epistar 2835 SMD LED: This is a low-cost LED that is known for its high efficiency and wide availability. It is often used in applications where cost is a primary concern, such as backlighting and signage.
LED Operating Principle
- An LED is made from a semiconductor material, such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) or gallium phosphide (GaP).
- The semiconductor material is doped with impurities, which create a region of positive charge (the anode) and a region of negative charge (the cathode).
- When an electric current is applied to the LED, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode.
- As the electrons flow through the semiconductor material, they collide with holes (the absence of electrons).
- When an electron collides with a hole, it releases energy in the form of a photon of light.
- The color of the light emitted by the LED depends on the energy of the photon.
LED Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| More efficient than traditional light sources | More expensive than traditional light sources |
| Last longer than traditional light sources | Can be more difficult to recycle |
| Produce less heat | Can flicker at high frequencies |
| Not as harmful to the environment | Can be difficult to find in certain colors |
Frequently Asked Question
The full form of LED is Light Emitting Diode.
LEDs can be more expensive than traditional light sources. They can also be more difficult to recycle.
Conclusion
LED stands for Light-Emitting Diode. LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are widely used in lighting, displays, and other applications due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. LEDs have transformed the lighting industry and offer sustainable and efficient lighting solutions.






