In today’s dynamic and competitive job market, pursuing further education has become increasingly essential. Many aspire to advance their careers and expand their horizons through higher education, with one popular option being an MBA. But what does an MBA stand for? In this article, we will unravel the full form of MBA, delve into its significance, and explore the benefits it offers to individuals seeking personal and professional growth.
Introduction to MAN
- Definition: A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a computer network that spans a specific metropolitan area or city, offering high-speed data connectivity to various locations within that urban region.
- Scope: MANs are designed to cover larger geographical areas than Local Area Networks (LANs) but are more limited in scope compared to Wide Area Networks (WANs).
- Purpose: The primary purpose of a MAN is to connect multiple LANs within a city, facilitating efficient data transfer and communication among them.
- Components: MANs typically consist of switches, routers, fiber optic cables, and access points, ensuring seamless data flow.
- Advantages: MANs provide cost-effective networking solutions, high bandwidth, low latency, and secure data transmission within metropolitan areas.
- Applications: They find use in educational institutions, healthcare facilities, government offices, and various businesses, enhancing connectivity and communication.
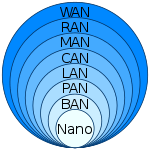


MAN vs. LAN vs. WAN
| Network Type | Scope | Definition | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) | Larger than LAN, Smaller than WAN | A MAN is a computer network that spans a specific metropolitan area, connecting multiple LANs within the city. | – Covers a city or metropolitan area. – Connects multiple LANs. – Offers high-speed data transfer within the urban region. – Intermediate scope between LAN and WAN. |
| LAN (Local Area Network) | Small, Typically a Building or Campus | A LAN is a network confined to a small geographical area, like an office, building, or campus, connecting devices within the same location. | – Limited to a small area. – Connects devices within a building or campus. – High-speed data transfer within a localized area. |
| WAN (Wide Area Network) | Vast, Across Cities or Countries | A WAN is a network that covers a large geographical area, often spanning multiple cities, countries, or continents, connecting devices across long distances. | – Spans extensive geographical regions. – Connects devices globally. – Involves long-distance data transmission. – Includes the internet as a prime example. |
Components of a MAN
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) comprises several crucial components that work together to facilitate efficient data transmission within a metropolitan area. These components include:
Switches and Routers: Switches and routers serve as the backbone of a MAN. They manage data traffic, ensuring it is directed efficiently to its destination within the network.
- Fiber Optic Cables: High-speed fiber optic cables are the preferred medium for data transmission in MANs. They enable rapid data transfer over longer distances with minimal signal loss.
- Access Points: Access points provide wireless connectivity within the MAN, allowing devices to connect seamlessly to the network. This flexibility is particularly valuable for mobile devices and remote access.
- Network Servers: Network servers host applications, data, and services that are accessible to users within the MAN. These servers play a vital role in providing resources and services to connected LANs.
- Firewalls and Security Measures: MANs often incorporate firewalls and security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of transmitted information.
Advantages of Using a MAN
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost-Effective Networking | MANs provide a cost-effective solution, offering high-speed connectivity without the extensive infrastructure costs of WANs. |
| High Bandwidth | MANs offer high bandwidth, ensuring efficient data transfer and accommodating data-intensive applications seamlessly. |
| Low Latency | With low latency, data travels quickly within the MAN, making it ideal for real-time applications and video conferencing. |
| Efficient Communication | MANs facilitate efficient communication and data sharing between multiple LANs, enhancing collaboration and productivity. |
| Scalability | MANs can be easily scaled to accommodate growing network demands, making them adaptable to evolving business needs. |
| Localized Data Management | Data management and resource sharing can be localized within the MAN, enhancing data control and minimizing data transfer times. |
Applications of MAN
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) find a wide range of applications across various sectors and industries, primarily due to their ability to connect multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within a metropolitan area. Here are some key applications of MANs:
- Educational Institutions: MANs connect different departments and buildings within universities and colleges, facilitating the sharing of educational resources and research data.
- Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and healthcare institutions use MANs to interconnect various medical facilities, ensuring seamless communication of patient data and medical records.
- Government Offices: Government agencies employ MANs to link their offices and departments within a city, improving administrative efficiency and data sharing.
- Businesses: Medium-sized enterprises and corporations benefit from MANs to establish a reliable and high-speed network infrastructure for their operations, supporting data-intensive tasks and remote offices.
- Media and Entertainment: Broadcasting companies and media outlets rely on MANs for the quick transfer of large media files and real-time content distribution.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and financial organizations use MANs for secure and high-speed data transmission between branches, ensuring efficient financial transactions and customer service.
- Manufacturing and Industry: MANs support automation and control systems in manufacturing plants, enhancing production efficiency and data monitoring.
- Transportation and Logistics: MANs assist in tracking and managing transportation and logistics operations within urban areas, optimizing routes and ensuring timely deliveries.
MAN Protocols
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| Ethernet | Ethernet is a widely used protocol in MANs, offering reliable and high-speed data transmission over Ethernet cables. It defines how data packets are formatted and transmitted within the network. |
| SONET (Synchronous Optical Network) | SONET is a standard for optical telecommunications, providing a robust framework for MANs to transmit data using optical fiber. It ensures synchronization and error correction for reliable data transmission. |
| ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) | ATM is a switching technology used in MANs to transmit data in fixed-size cells. It offers high bandwidth and low latency, making it suitable for real-time applications and multimedia content delivery. |
| Frame Relay | Frame Relay is a protocol that MANs employ for efficient data packet forwarding. It simplifies the network structure, making it suitable for connecting multiple LANs within a metropolitan area. |
| IP (Internet Protocol) | MANs may use IP for routing and addressing data packets, enabling communication between different LANs within the network. IP ensures that data reaches its intended destination efficiently. |
How Does MAN Work?
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) function by interconnecting multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within a specific metropolitan area, enabling efficient data transfer and communication. Here’s how MANs work:
- Interconnection of LANs: MANs link together individual LANs within the metropolitan area, allowing them to communicate with each other as if they were on a single network.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Data packets are sent between LANs using high-speed connections, typically via fiber optic cables. This ensures rapid data transmission even over longer distances.
- Routing and Switching: Switches and routers within the MAN direct data traffic, ensuring that packets reach their intended destinations within the network.
- Access Points: Access points provide wireless connectivity within the MAN, offering flexibility for mobile devices and remote access.
- Data Security: MANs often employ security measures like firewalls to protect data from unauthorized access or cyber threats during transmission.
- Efficient Communication: MANs facilitate efficient communication and data sharing between LANs, enhancing collaboration among connected entities.
Challenges and Limitations of MAN
| Challenge/Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Security Concerns | MANs may be vulnerable to security breaches and unauthorized access, necessitating robust security measures and protocols. |
| Complex Scalability | Expanding or modifying a MAN can be complex and costly, requiring careful planning and infrastructure upgrades. |
| Cost of Implementation | Building and maintaining a MAN infrastructure can be expensive, particularly for small businesses and startups. |
| Limited Coverage | MANs are designed for specific metropolitan areas, making them unsuitable for connecting remote or rural locations. |
| Data Transmission Distance | While suitable for metropolitan distances, MANs may struggle with extremely long-distance data transmission compared to WANs. |
| Interoperability Challenges | Integrating MANs with existing network infrastructure can pose interoperability challenges, requiring compatible equipment and protocols. |
| Maintenance and Monitoring Complexity | Keeping a MAN running smoothly necessitates ongoing maintenance and monitoring, adding to operational complexity. |
Future of MAN
The future of Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) holds several promising developments as technology continues to evolve and urban areas become increasingly interconnected. Here are some key aspects of the future of MANs:
- 5G Integration: The integration of 5G technology into MANs will provide ultra-fast and low-latency connectivity, enabling a wide range of applications, including IoT and smart city initiatives.
- IoT Expansion: MANs will play a vital role in supporting the exponential growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) by providing the necessary infrastructure for smart devices and sensors in urban environments.
- Edge Computing: MANs will facilitate edge computing, enabling data processing and analysis closer to the data source, reducing latency, and improving real-time applications.
- Increased Reliability: Advancements in redundancy and failover mechanisms will enhance the reliability of MANs, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity for critical services.
- Enhanced Security: Security protocols and encryption techniques will continue to evolve, making MANs more resilient against cyber threats.
- Smart City Integration: MANs will be integral to the development of smart cities, supporting innovations in transportation, healthcare, energy management, and public safety.
Conclusion
| Key Takeaways | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficient Connectivity | MANs efficiently connect multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within a city, enabling seamless data transfer and communication. |
| Versatile Applications | MANs find applications in education, healthcare, government, businesses, and more, enhancing productivity and services. |
| Reliable Protocols | MANs rely on protocols like Ethernet, SONET, and IP to ensure reliable data transmission and communication within the network. |
| Future-Ready Infrastructure | The future of MANs holds promise with 5G integration, IoT expansion, and smart city initiatives reshaping urban landscapes. |
| Security and Scalability | Overcoming challenges in security and scalability will be essential as MANs evolve to meet the growing demands of urban areas. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) is a network that covers a specific metropolitan area, while the internet is a global network connecting the entire world.
MANs offer cost-effective networking solutions, high bandwidth, and low latency, making them suitable for various applications.
MANs can be secure, but they require robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or interception.
A LAN covers a small area like an office, a WAN spans large geographical regions like countries, and a MAN falls in between, covering a metropolitan area.
MANs are expected to become more critical in urban areas as the demand for high-speed, reliable connectivity continues to grow.






