PLCs are built to be dependable and tough, and they can endure the challenging conditions present in numerous industrial uses. They are a practical choice for many automation applications since they’re also quite simple to program.
Sensor input is activated by PLCs, causing them to turn on outputs to control equipment. Simple switches through sophisticated sensors can be used as inputs and outputs. The inputs and outputs are linked and interacted with according to the PLC’s software.
Ladder logic is a specific language used to program PLCs. A graphical language called ladder logic
Table of Contents
- PLC Full Form: Evolution
- PLC Full Form: How PLCs Work
- PLC Full Form: Application of PLCs
- PLC Full Form: Advantage
- PLC Full Form: PLC Programing Language
- PLC Full Form: Components of a PLC System
- PLC Full Form: Common Applications of PLCs in Industries
- PLC Full Form: Future Trends in PLC Technology and Industrial Automation
- PLC Full Form: Conclusion
- PLC Full Form: FAQs
Evolution of PLCs: From Relays to Digital Control


Here are some of the key milestones in the evolution of PLCs:
- 1968: The first PLC, the Modicon 084, is introduced by Modicon.
- 1970s: PLCs become widely adopted in the industrial automation market.
- 1980s: PLCs begin to incorporate features such as analog I/O, communication, and programming languages.
- 1990s: PLCs become even more powerful and flexible, with features such as networking, motion control, and advanced programming languages.
- 2000s: PLCs continue to evolve, with features such as embedded intelligence, web-based interfaces, and security.
- 2020s: PLCs are now used in a wide variety of industries, including manufacturing, food processing, and water treatment. They are a vital part of modern industrial automation.
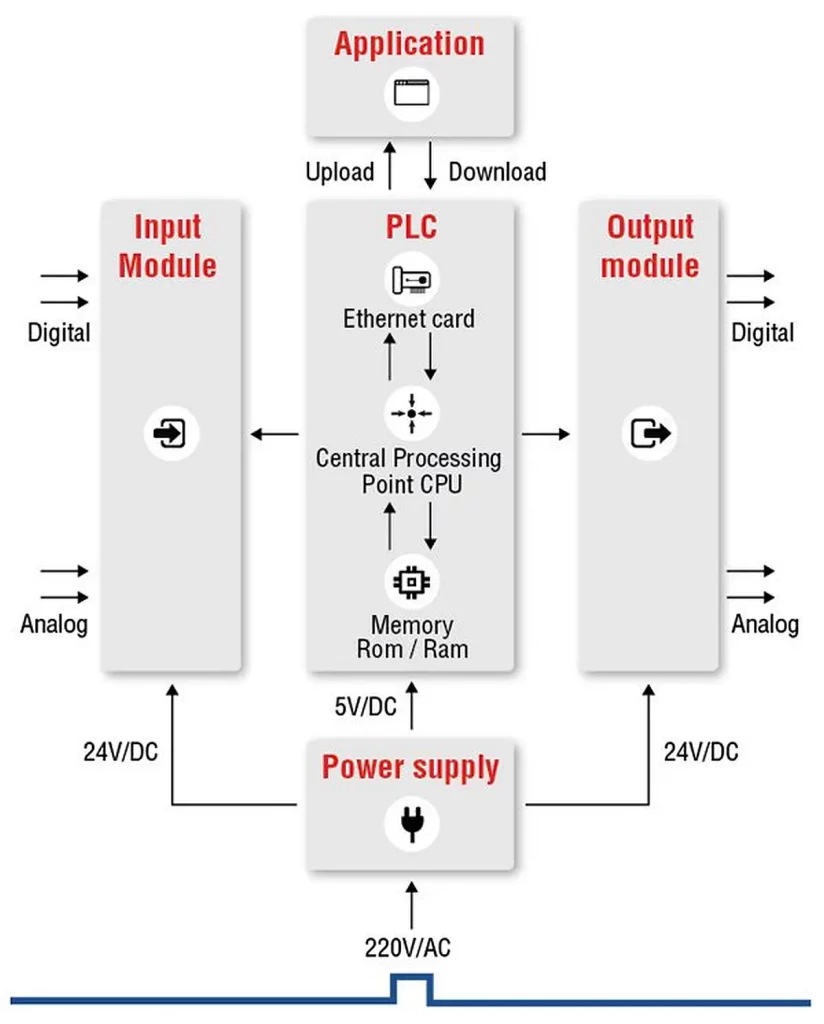
How PLCs Work: The Heart of Industrial Automation
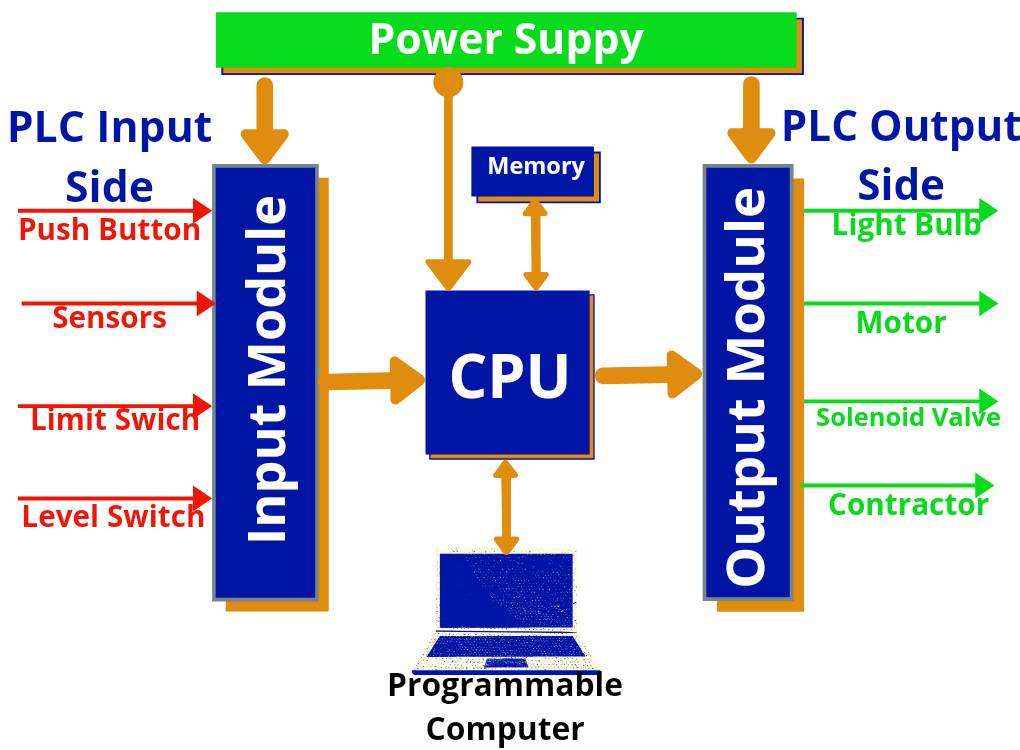
- Input and Output Modules
PLCs interface with the physical world through input and output modules. Input modules collect data from sensors and switches, while output modules control actuators, motors, and other devices. - Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is the brain of the PLC, executing the control program and managing communication between input, output, and memory modules. - Programming Logic
PLCs are programmed using specialized software that employs various programming languages. These programs define the logic that determines how the PLC responds to different inputs.


Applications of PLCs in Industries
- Manufacturing and Production
PLCs play a pivotal role in optimizing manufacturing processes. They ensure consistent product quality, streamline production lines, and enable rapid reconfiguration for different product runs. - Energy and Utilities
In energy and utility sectors, PLCs control power distribution, monitor equipment performance, and manage energy consumption, contributing to efficient resource utilization. - Automotive and Robotics
PLCs are integral in automotive assembly lines and robotics, orchestrating complex sequences of tasks with precision and speed.
Advantages of Using PLCs



- Precision and Accuracy
PLCs offer high accuracy in control tasks, reducing errors and minimizing wastage in industrial processes. - Flexibility and Adaptability
PLCs are easily programmable and reconfigurable, allowing industries to adapt to changing production requirements swiftly. - Cost and Time Savings
The automation capabilities of PLCs lead to reduced manual labor, lower maintenance costs, and increased overall efficiency.
PLC Programming Languages
- Ladder Logic
Ladder Logic, resembling electrical relay diagrams, is a popular programming language for PLCs. It’s intuitive and widely used in industries. - Structured Text
Structured Text allows for complex programming tasks and is similar to traditional programming languages like C or Pascal. - Function Block Diagram
Function Block Diagram provides a visual representation of functions and their interactions, aiding in programming complex systems.
PLC Full Form: Components of a PLC System
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is the mind of the PLC. It approaches inputs, executes the programmed logic, and controls outputs primarily based totally at the user-described instructions. It handles facts garage and conversation tasks.
2. Power Supply
The strength deliver unit presents the important electric strength to the PLC device and its components. It commonly converts AC voltage to DC voltage required for operation.
3. Input Modules
Input modules interface with outside gadgets like sensors, switches, and transducers. They acquire facts from the sphere and convert it right into a layout that the CPU can process.
4. Output Modules
Output modules manage outside gadgets which include motors, actuators, and alarms. They acquire instructions from the CPU and translate them into actionable outputs.
5. Programming Device
The programming device, which include a laptop or hand held programmer, is used to create, edit, and add the PLC program. It communicates with the CPU through specialised software.
6. Communication Ports
Communication ports facilitate facts change among the PLC and different structures or gadgets. They guide protocols like Ethernet, Modbus, and Profibus for commercial conversation.
7. Memory Units
Memory gadgets keep the PLC program, facts, and operational settings. It consists of each unstable memory (RAM) and non-unstable memory (ROM/EEPROM).
8. Backplane or Chassis
The backplane or chassis is the bodily framework that holds all PLC modules together. It guarantees right strength distribution and facts conversation among the modules.
PLC Full Form: Common Applications of PLCs in Industries
1. Manufacturing Process Control
PLCs automate responsibilities like meeting line manage, packaging, and nice checks. They enhance performance and decrease human blunders in production operations.
2. Industrial Machinery Automation
Machinery which includes CNC machines, robot arms, and conveyor belts rely upon PLCs for specific operations. This guarantees easy and correct manufacturing cycles.
3. Power Plant Operations
PLCs screen and manage turbines, generators, and strength distribution systems. They decorate reliability and protection in strength generation.
4. Water and Wastewater Treatment
PLCs manipulate pumps, filters, and chemical dosing systems. They make certain powerful water remedy and compliance with environmental regulations.
5. Automotive Industry Applications
From assembling cars to checking out components, PLCs streamline manufacturing withinside the car industry. They make certain consistency and amazing outputs.
6. Food and Beverage Industry
PLCs manage mixing, bottling, and packaging processes. They assist preserve hygiene requirements and optimize manufacturing.
7. Oil and Gas Industry
PLCs are used for drilling, pipeline monitoring, and refinery operations. They decorate protection and performance in unsafe environments.
8. Building Automation Systems
PLCs manage HVAC systems, elevators, and lights in current buildings. They make a contribution to power performance and consumer comfort.
PLC Full Form: Future Trends in PLC Technology and Industrial Automation
1. Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT)
PLC structures are more and more more being related to IoT gadgets, allowing real-time tracking and manage of business processes. This integration improves performance and information-pushed decision-making.
2. Adoption of Edge Computing in PLCs
With area computing, PLCs can system information locally, lowering latency and dependence on centralized structures. This method is crucial for time-important programs in automation.
3. Use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Future PLCs will contain AI and ML abilities to are expecting system failures, optimize operations, and automate complicated responsibilities past conventional logic-primarily based totally controls.
4. Enhanced Cybersecurity for PLC Systems
As PLCs emerge as extra related, sturdy cybersecurity measures are being advanced to guard business structures from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
5. Cloud-Based PLC Systems
Cloud integration permits PLCs to save and examine huge datasets remotely, presenting superior analytics, faraway access, and scalability for business programs.
6. Wireless Connectivity and Communication
Wireless-enabled PLCs cast off the want for substantial cabling, making installations quicker and permitting seamless integration with different wi-fi gadgets withinside the automation ecosystem.
7. Increased Use of Open-Source Platforms
The upward push of open-supply structures in PLC improvement encourages customization and flexibility, making automation answers extra adaptable and cost-effective.
8. Miniaturization and Energy Efficiency
Future PLCs have become smaller and extra energy-efficient, allowing their use in compact areas and contributing to sustainable business practices.
Conclusion
FAQs
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an industrial computer designed to automate manufacturing processes, machinery control, and other industrial applications. It uses programmable software to execute logic-based operations.
PLCs are used in industries such as automotive, manufacturing, food and beverage, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, power generation, and water treatment for automation and process control.
Yes, modern PLCs can communicate over networks using protocols like Ethernet/IP, Modbus, and Profinet, enabling integration with IoT systems and SCADA software.






