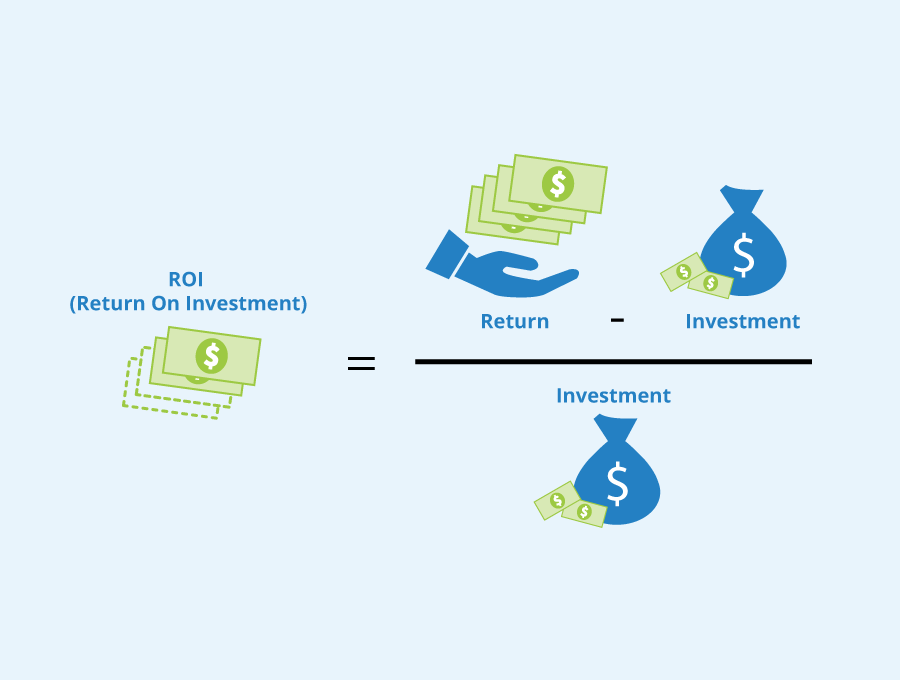
Return on investment (ROI) is a measure of the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by dividing the profit earned on an investment by the cost of that investment. For instance, an investment with a profit of $100 and a cost of $100 would have an ROI of 1, or 100% when expressed as a percentage.
- ROI Full Form: Introduction to ROI
- ROI Full Form: Types of ROI
- ROI Full Form: Measuring ROI in Different Scenarios
- ROI Full Form: Factors Affecting ROI
- ROI Full Form: Benefits of Tracking ROI
- ROI Full Form: Challenges of Calculating ROI
- ROI Full Form: Real-Life ROI Examples
- ROI Full Form: Conclusion
- ROI Full Form: FAQs
Introduction to ROI


In the dynamic landscape of business and finance, one metric stands out as a universal measure of success: Return on Investment (ROI). Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur, a marketing professional, or an investor, the concept of ROI is pivotal to informed decision-making and strategic planning. It’s a compass that guides you toward understanding the true value and impact of your investments.
At its core, ROI is a straightforward concept with profound implications. It’s the measure of how much you gain in comparison to what you put in. But beneath its simplicity lies a world of complexity, where calculations intertwine with strategy, and decisions hinge on its insights. In this blog post, we’ll journey into the realm of ROI, exploring its definition, calculations, applications, challenges, and so much more.
Why does ROI matter? How can you harness its power to enhance your business endeavors? What are the nuances of measuring ROI in different contexts? From tangible financial investments to the intangible realms of marketing and human capital, we’ll uncover the layers of ROI’s significance and unveil the strategies to maximize its potential.
Types of ROI
- Financial ROI:
This is the most common type of ROI, focusing on the financial gains relative to the initial investment. It’s a measure of profitability and is expressed as a percentage of the initial investment. Financial ROI provides a clear understanding of the returns generated from various financial ventures. - Marketing ROI:
In the realm of marketing, ROI measures the effectiveness of marketing campaigns or strategies. It helps assess whether the resources invested in marketing efforts are resulting in increased revenue or customer engagement. Marketing ROI takes into account both monetary gains and costs associated with marketing initiatives. - Social ROI:
In the context of social initiatives and corporate social responsibility, social ROI measures the positive impact of projects on society and the environment. It evaluates how much social or environmental value is generated compared to the resources invested. - Human Capital ROI:
Human capital ROI assesses the value of investments made in employee training, development, and well-being. It quantifies the impact of these investments on employee productivity, engagement, and overall organizational performance.
Measuring ROI in Different Scenarios
- ROI for Business Investments:
When evaluating financial investments, ROI is calculated by comparing the net gain from the investment to the initial cost of the investment. This could apply to purchasing equipment, expanding facilities, or investing in stocks. The formula is: ROI = (Net Gain / Initial Cost) * 100%. - ROI for Marketing Campaigns:
In marketing, ROI is computed by considering the revenue generated from the campaign and subtracting the costs incurred. The result is divided by the campaign costs and multiplied by 100 to get the ROI percentage. This provides insights into whether the campaign’s impact justifies the expenses. - ROI for Employee Training and Development:
Measuring ROI for training programs involves assessing the performance improvements resulting from the training and comparing them to the costs of the program. The ROI formula considers increased productivity, reduced errors, and other performance metrics as gains. - ROI for Digital Marketing:
In the digital realm, ROI calculation involves measuring the revenue generated from online marketing efforts (e.g., pay-per-click advertising) and comparing it to the costs of the campaign. This helps marketers evaluate the efficiency of their online strategies.
Factors Affecting ROI
- Risk and Uncertainty:
Higher-risk investments often come with the potential for greater returns. However, increased risk also introduces the possibility of losses. The risk-return trade-off varies among different investments and industries. - Timeframe of Investments:
The duration of an investment significantly affects its ROI. Short-term investments may yield quick returns, while long-term investments require patience as the benefits accumulate over time. - External Economic Factors:
Economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and market volatility, influence investment returns. A favorable economic environment can boost returns, while unfavorable conditions can hamper growth. - Industry and Market Trends:
ROI can be influenced by the trends and dynamics of a specific industry or market. Staying attuned to these trends helps investors make informed decisions.
Benefits of Tracking ROI
- Informed Decision-Making:
Tracking ROI provides data-driven insights that guide decision-making. It helps prioritize investments, projects, and strategies that generate the highest returns. - Resource Allocation Optimization:
By analyzing ROI, businesses can allocate resources more effectively. Investments that offer higher ROI take precedence over those with lower returns, resulting in efficient resource utilization. - Performance Evaluation:
Monitoring ROI allows businesses to evaluate the success of various initiatives. It’s a yardstick to measure the effectiveness of strategies and make adjustments if needed. - Accountability and Transparency:
ROI serves as an objective measure of success. Tracking it fosters transparency and accountability within teams and organizations. - Risk Assessment and Mitigation:
ROI analysis includes evaluating the risks associated with investments. This helps businesses make informed choices that align with their risk tolerance.
Challenges of Calculating ROI
- Data Accuracy and Availability:
Accurate ROI calculation requires reliable data on both costs and gains. Inaccurate or incomplete data can skew results and lead to inaccurate assessments of value creation. - Intangible Benefits:
Not all benefits generated from an investment are easily quantifiable. Intangible benefits like improved brand reputation or employee morale can be challenging to assign monetary values to. - Timeframe Considerations:
The timing of costs and gains is crucial in ROI calculations. Determining when benefits occur and aligning them with corresponding costs can impact the accuracy of the ROI figure. - Complexity of Investments:
Some investments involve multifaceted costs and returns. These complexities, such as variable revenue streams or multiple contributing factors, can complicate the ROI calculation. - Isolating Causality:
When multiple factors influence an outcome, isolating the exact contribution of a specific investment to the outcome can be intricate. Other variables may confound the ROI calculation.
Real-Life ROI Examples
- Business Expansion:
Imagine a retail business considering opening a new location. They invest in renting a space, renovating it, and hiring staff. After a year, they calculate the revenue generated from the new location and subtract all associated costs. If the revenue far exceeds the investment, the business enjoys a high ROI, validating the decision to expand. - Digital Marketing Campaign:
A company invests in a digital marketing campaign to promote a new product. They track the campaign’s impact by measuring the increase in website traffic, leads generated, and ultimately, the number of converted customers. If the revenue from these conversions surpasses the marketing costs, the campaign demonstrates a positive ROI. - Employee Training Program:
An organization invests in training programs to enhance employee skills. After the training, they observed increased productivity, reduced errors, and improved team collaboration. By quantifying the improved performance and comparing it to the cost of training, they can calculate the ROI of the training initiative.
Conclusion
In the realm of business and decision-making, Return on Investment (ROI) emerges as a guiding star, illuminating the path to value creation and informed choices. As we conclude our journey through the world of ROI, the significance of this metric becomes abundantly clear. From financial investments to marketing strategies, employee development, and beyond, ROI serves as a powerful tool that transcends industries and scenarios.
ROI isn’t just a number; it’s a story of impact. It tells the tale of resources wisely allocated, risks carefully assessed, and goals effectively pursued. It’s a story of calculated decisions that lead to success, whether in the form of revenue, cost savings, enhanced efficiency, or improved customer satisfaction.
FAQs
ROI is a financial metric used to measure the profitability or effectiveness of an investment. It quantifies the return or gain generated from an investment relative to the initial cost.
ROI provides insights into the efficiency and success of investments, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. It helps businesses and individuals assess the value created from their endeavors.
ROI is calculated using the formula: ROI = (Net Gain / Initial Cost) * 100%. Net Gain is the revenue generated minus the costs incurred.
Different types of ROI include financial ROI, marketing ROI, social ROI, human capital ROI, customer ROI, and more. Each type assesses value creation in specific contexts.






