USG stands for ultrasound or ultrasonography. It is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and structures. USG is a non-invasive procedure that does not use radiation.
- USG Full Form: Introduction to USG
- USG Full Form: How Does Ultrasound Sonography Work?
- USG Full Form: Types of Ultrasound Sonography
- USG Full Form: Preparation for an Ultrasound Sonography
- USG Full Form: The USG Procedure
- USG Full Form: Benefits of USG
- USG Full Form: Uses
- USG Full Form: Conclusion
- USG Full Form: FAQs
Introduction to USG
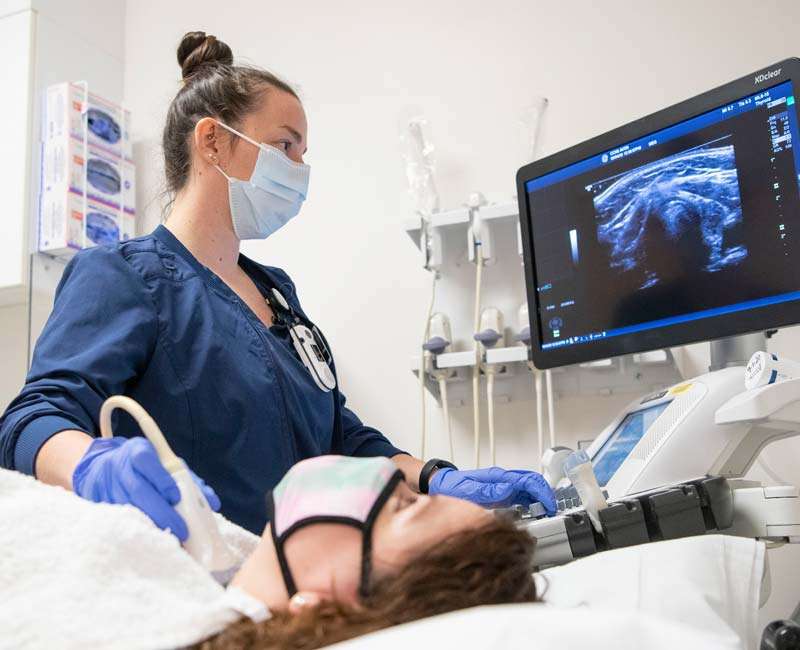


What is Ultrasound Sonography?
Ultrasound sonography, commonly known as ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate real-time images of the body’s internal organs, tissues, and blood flow. These images provide valuable insights into the structure and function of various body systems, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of medical conditions.
Importance and Applications of USG
Ultrasound sonography has become an integral part of medical practice due to its numerous advantages. Unlike other imaging techniques that use ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, ultrasound uses harmless sound waves, making it safe for patients of all ages, including pregnant women and infants. This safety profile has made it a preferred choice for various medical scenarios.
The applications of USG are vast and encompass a wide range of medical specialties.
Obstetricians use ultrasound to monitor fetal development during pregnancy, radiologists utilize it to detect abnormalities in organs like the liver, kidneys, and heart, and orthopedic specialists rely on ultrasound to visualize joints
How Does Ultrasound Sonography Work?
Sound Wave Emission: A transducer, which is a small handheld device, emits high-frequency sound waves into the body. These sound waves are typically in the range of 2 to 18 megahertz (MHz), far above the range of human hearing.
Propagation and Reflection: The sound waves travel through the body and interact with different tissues. When the sound waves encounter boundaries between tissues of different densities, such as between fluid and soft tissue or soft tissue and bone, some of the sound waves are reflected back to the transducer.
Echo Detection: The transducer detects the reflected sound waves (echoes). The time it takes for the echoes to return to the transducer and the strength of these echoes (echo intensity) are measured.
Image Reconstruction: The echoes are processed by a computer to create real-time images on a monitor. These images are formed based on the pattern of echoes received, allowing visualization of internal structures and organs in the body.
Diagnostic Utility: Ultrasound imaging is highly versatile and used for various diagnostic purposes. It is commonly used during pregnancy to monitor fetal development and detect any abnormalities. In non-obstetric settings, it helps in evaluating abdominal organs (such as liver, gallbladder, kidneys), assessing blood flow through vessels, diagnosing conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, and examining soft tissues and joints for injuries or diseases.
Safety Considerations: Ultrasound is considered safe because it uses non-ionizing radiation, unlike X-rays or CT scans, which use ionizing radiation. It does not pose the risks associated with radiation exposure and is generally painless and non-invasive.
Types of Ultrasound Sonography
Doppler Ultrasound: This technique evaluates blood waft via blood vessels and fundamental arteries and veins. It can assist diagnose situations including blood clots, arterial narrowing (stenosis), and issues with blood waft in organs.
Obstetric Ultrasound: Also called prenatal ultrasound, this type is particularly used during pregnancy to screen fetal development, test for multiple pregnancies, investigate the placenta, and stumble on any abnormalities within the fetus.
Abdominal Ultrasound: This type examines organs within the abdomen, which includes the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen. It facilitates diagnose situations like gallstones, liver sickness, kidney stones, and belly loads.
Pelvic Ultrasound: Pelvic ultrasound is used to study the reproductive organs (uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes) in ladies. It allows diagnose conditions inclusive of ovarian cysts, fibroids, and abnormalities in the uterus.
Transvaginal Ultrasound: This is a specific form of pelvic ultrasound where the transducer is inserted into the vagina to get nearer photographs of the pelvic organs. It is frequently used for greater particular assessment of the uterus and ovaries.
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: This type focuses on imaging muscle groups, tendons, ligaments, joints, and soft tissues. It is used to diagnose conditions inclusive of tendon tears, joint inflammation (arthritis), and muscle accidents.
Cardiac Ultrasound (Echocardiography): Echocardiography uses ultrasound to create photographs of the heart. It enables check the shape and characteristic of the coronary heart, which include the valves and chambers. This is important in diagnosing coronary heart situations such as heart valve sicknesses, congenital coronary heart defects, and cardiomyopathy.
Breast Ultrasound: Breast ultrasound is often used as a supplemental imaging tool alongside mammography.
Preparation for an Ultrasound Sonography
Clothing: Wear snug, unfastened-fitting apparel. Depending on the location to be examined, you’ll be requested to trade into a sanatorium robe or put off positive apparel items that might intrude with the ultrasound scan.
Jewelry and Accessories: It’s really useful to leave jewelry and add-ons at home, in particular if they’re near the place to be examined. Metal gadgets can every now and then intervene with the ultrasound waves and have an effect on image nice.
Medications: In maximum cases, you may continue taking your medications as prescribed. If the ultrasound is being done to assess particular abdominal organs (just like the gallbladder), you may be requested to keep away from ingesting or consuming for a certain length before the exam. Follow any unique instructions furnished by using your healthcare issuer.
Food and Drink: Depending on the form of ultrasound, you may need to speedy for some hours before the procedure. This is commonplace for stomach ultrasounds to ensure clean photos of the organs with out interference from meals digestion.
Special Instructions: Your healthcare provider may also offer precise commands primarily based on the sort of ultrasound being completed. For example, in case you’re having a pelvic ultrasound, you’ll be instructed to have a complete bladder to help visualize the pelvic organs more clearly.
Inform the Technologist: Inform the ultrasound technologist if you have any hypersensitive reactions, medical situations, or previous surgeries that may be applicable to the exam. This allows ensure your protection and right interpretation of the ultrasound pics.
Relaxation: Ultrasound is a painless and non-invasive technique. Relaxation can assist improve the quality of the photographs obtained. The technologist will manual you via any essential positions or moves in the course of the scan.
The USG Procedure: What to Expect
Before the Procedure:
Preparation: Depending on the type of ultrasound being performed, you may be asked to change into a hospital gown and remove any jewelry or accessories that could interfere with the ultrasound waves.
Instructions: You might receive specific instructions regarding fasting (for abdominal scans), drinking fluids (for pelvic or abdominal scans), or bladder filling (for pelvic or obstetric scans) to ensure optimal imaging conditions.
During the Procedure:
Positioning: You will be positioned comfortably on an examination table, either lying down or sitting up, depending on the area of the body being examined.
Gel Application: A clear gel is applied to the skin over the area to be examined. This gel helps transmit the ultrasound waves and eliminates air pockets between the transducer (a handheld device) and your skin.
Transducer Movement: The ultrasound technologist or radiologist gently moves the transducer over the area of interest. The transducer emits sound waves and receives the echoes that bounce back from the internal structures.
Image Formation: As the echoes are captured by the transducer, they are converted into real-time images that appear on a monitor. The technologist may take screenshots or freeze frames of specific images for later review by a radiologist.
Intermittent Instructions: During the scan, you may be asked to change positions or hold your breath briefly to obtain clearer images or to visualize different angles of the organs or tissues.
Communication: The technologist may explain what you are seeing on the monitor and may ask you questions about symptoms or medical history relevant to the examination.
After the Procedure:
Gel Removal: After the scan is complete, the gel will be wiped off your skin. It is water-based and should not stain clothing.
Results: In some cases, preliminary findings may be discussed with you immediately after the scan. However, the final interpretation is usually provided by a radiologist who will compile a report based on the images obtained during the ultrasound.
Follow-Up: Your healthcare provider will discuss the results of the ultrasound with you during a follow-up appointment. Depending on the findings, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
Benefits of Ultrasound Sonography
Non-invasive: Ultrasound imaging does now not contain publicity to ionizing radiation, not like X-rays and CT scans. This makes it a more secure option, specifically for repeated examinations and for touchy populations such as pregnant women and children.
Real-time Imaging: Ultrasound presents real-time photos of the inner systems and organs in the body. This instantaneous feedback permits healthcare companies to study movement and function, along with coronary heart valve movements or fetal pastime throughout being pregnant, that can resource in accurate prognosis and treatment making plans.
Versatility: Ultrasound can be used to study a huge variety of anatomical structures, inclusive of belly organs (liver, kidneys, gallbladder), pelvic organs (uterus, ovaries), musculoskeletal gadget (muscular tissues, tendons, joints), and soft tissues. It is likewise precious for evaluating blood glide through vessels using Doppler ultrasound techniques.
Painless and Non-invasive: The manner itself is usually painless and non-invasive. It does not require injections, needles, or any incisions, making it well-tolerated by means of sufferers of all ages.
Accessibility and Portability: Ultrasound device is widely to be had in hospitals, clinics, or even in cell settings. Its portability permits for bedside examinations and quick assessment in emergency situations.
Dynamic Imaging: Unlike a few other imaging modalities that offer static images, ultrasound captures dynamic photographs. This functionality is in particular useful for assessing motion, such as the pumping motion of the heart or fetal actions all through being pregnant.
Cost-effective: Ultrasound imaging is generally extra low-cost as compared to other imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans. This makes it a price-powerful option for habitual screening and diagnostic purposes.
Uses
Obstetrics and Gynecology: Ultrasound is crucial for tracking fetal improvement at some stage in being pregnant, assessing the placenta, and detecting any abnormalities inside the fetus. It also facilitates diagnose situations affecting the female reproductive machine, such as ovarian cysts, fibroids, and uterine abnormalities.
Abdominal Imaging: Ultrasound is typically used to study stomach organs which include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen. It helps diagnose situations like gallstones, liver ailment, kidney stones, and abdominal masses.
Cardiology (Echocardiography): Echocardiography, a kind of ultrasound, is crucial for comparing the shape and function of the heart. It allows diagnose heart situations consisting of heart valve diseases, congenital heart defects, and cardiomyopathy by way of supplying distinctive pix of the coronary heart chambers, valves, and blood float.
Vascular Imaging: Doppler ultrasound is used to assess blood float thru arteries and veins. It helps diagnose conditions such as blood clots (deep vein thrombosis), arterial narrowing (stenosis), and peripheral vascular sickness by using evaluating the velocity and course of blood go with the flow.
Musculoskeletal Imaging: Ultrasound is precious for imaging muscular tissues, tendons, ligaments, joints, and gentle tissues. It helps diagnose conditions including tendon tears, irritation (tendonitis), joint effusions, and soft tissue hundreds. It is likewise used for directing injections into joints or tender tissue structures.
Breast Imaging: Ultrasound is regularly used along mammography to evaluate breast abnormalities detected at some point of screening or scientific exams. It facilitates distinguish among fluid-stuffed cysts and stable hundreds inside the breast tissue and aids in guiding breast biopsies.
Conclusion
Ultrasound sonography, with its non-invasive nature and real-time imaging capabilities, has transformed the field of medical diagnostics. From visualizing the intricate details of developing fetuses to assessing the health of vital organs, ultrasound plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient care. Its portability, safety profile, and ability to guide medical procedures make it an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals.
As technology continues to advance, ultrasound imaging is poised to reach new heights. Three-dimensional and four-dimensional imaging offer more comprehensive views of anatomical structures, while contrast-enhanced ultrasound provides even greater clarity in imaging blood vessels and other structures.
FAQs
Q1: What is the USG test for?
A: Ultrasound (USG) tests are used to visualize internal organs and structures, aiding in diagnosing conditions like pregnancy, tumors, and abdominal issues.
Q2: What is USG scanning for?
A: USG scanning is used to visualize organs, detect abnormalities, monitor pregnancies, assess blood flow, and guide medical procedures
Q3: What is the purpose of a USG?
A: The purpose of a USG is to non-invasively visualize internal organs and structures for diagnostic evaluation and monitoring of conditions.
Q4: What are the benefits of USG?
A: Benefits of USG include non-invasiveness, real-time imaging, safety (no ionizing radiation), versatility across organs, and guiding procedures like biopsies accurately.
Q5: Is water necessary for USG?
A:Water is not always necessary for ultrasound (USG) imaging. However, for certain types of scans, such as pelvic or obstetric ultrasounds, a full bladder may be required to enhance visualization of internal structures.






