Water, the essence of life itself, is a substance that holds incredible significance for all living beings. From sustaining ecosystems to nurturing human health, its multifaceted role is truly awe-inspiring. We will explore water’s many facets, significance, and significant effects on our environment in this post.
Table of Contents
- MSP Full-Form: Introduction
- MSP Full-Form The Chemistry of Water
- MSPFull-Form: The Role of Water in Living Organisms
- MSP Full-Form: Water’s Influence on Human Health
- VC Full-Form: Water Scarcity: A Global Challenge
- VC Full-Form: Water Conservation Strategies
- VC Full-Form: The Economic Value of Water
- VC Full-Form: Water in Culture and Spirituality
- VC Full-Form: Exploring Aquatic Ecosystems
- VC Full-Form: Water’s Role in Climate Regulation
- VC Full-Form: Challenges in Water Pollution
- VC Full-Form: The Future of Water Sustainability
- VC Full-Form: Conclusion
- VC Full-Form: Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Introduction
Water is a fundamental substance that is crucial for the existence of life on Earth. Its unique properties, such as high heat capacity and solvent abilities, make it the cornerstone of many natural processes.
The Chemistry of Water
Water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, forming the chemical formula H2O. The arrangement of its molecules gives water exceptional properties, including surface tension and capillary action.



The Role of Water in Living Organisms
From tiny microorganisms to towering trees, water plays an indispensable role in biological systems. It acts as a medium for countless biochemical reactions, facilitates nutrient transport, and maintains cell structure.
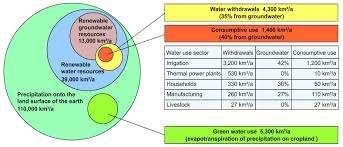


Water's Influence on Human Health
Staying hydrated is paramount for human health. Water regulates body temperature, aids digestion, and supports organ functions. It also contributes to healthy skin and cognitive function.
Water Scarcity: A Global Challenge
Despite water covering over 70% of the Earth’s surface, only a fraction is freshwater suitable for consumption. Water scarcity affects millions of people worldwide, leading to social, economic, and political ramifications.
Water Conservation Strategies
To counter water scarcity, various conservation methods are essential. Rainwater harvesting, efficient irrigation practices, and reducing water wastage at home contribute to sustainable water management.
The Economic Value of Water
Water’s importance extends to economies. It drives agriculture, energy production, and manufacturing processes. Water scarcity can disrupt industries and affect global markets.
Water in Culture and Spirituality
Exploring Aquatic Ecosystems
Oceans, rivers, and lakes are home to diverse ecosystems. These habitats support a wide array of species and help maintain the balance of nature.
Water's Role in Climate Regulation
Water bodies play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate. Oceans act as heat reservoirs, influencing weather patterns and helping to moderate temperatures.
Innovations in Water Technology
Advancements in technology have led to water purification methods, desalination techniques, and efficient wastewater treatment. These innovations address water quality and scarcity challenges.
Challenges in Water Pollution
Water pollution poses a significant threat to aquatic life and human health. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste contribute to the degradation of water bodies.
The Future of Water Sustainability
As the global population grows, ensuring water sustainability becomes paramount. Collaborative efforts, policy changes, and community engagement are crucial to securing water resources for future generations.
Conclusion
The importance of water cannot be emphasized. It’s a force that gives life, supports ecosystems, promotes health, and molds society. We must put water conservation first, accept creative solutions, and recognize the importance of this extraordinary resource if we want to preserve a healthy world.
VC- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
The ability of water’s particular molecular structure to dissolve a variety of compounds has given it the moniker “universal solvent.”
Innovative methods include reverse osmosis, UV disinfection, and nanotechnology-based filtration.
In agriculture, a lack of water can result in lower crop yields, restricted irrigation, and higher production costs.
The Pacific Ocean’s Great Pacific Garbage Patch is a significant buildup of plastic waste that draws attention to the problem of marine pollution.
By stopping leaks, utilizing water-saving equipment, and using water sparingly throughout the day, people may preserve water.






