1 joule is equal to 10,000,000 ergs. The joule, a standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI), is used widely across various scientific disciplines. In contrast, the erg, a smaller unit of energy, is often utilized in physics. To convert joules to ergs, you simply multiply the number of joules by 10^7, reflecting the relationship where 1 joule equals 10^7 ergs. This conversion is essential for accurately measuring and comparing energy values in different scientific contexts.
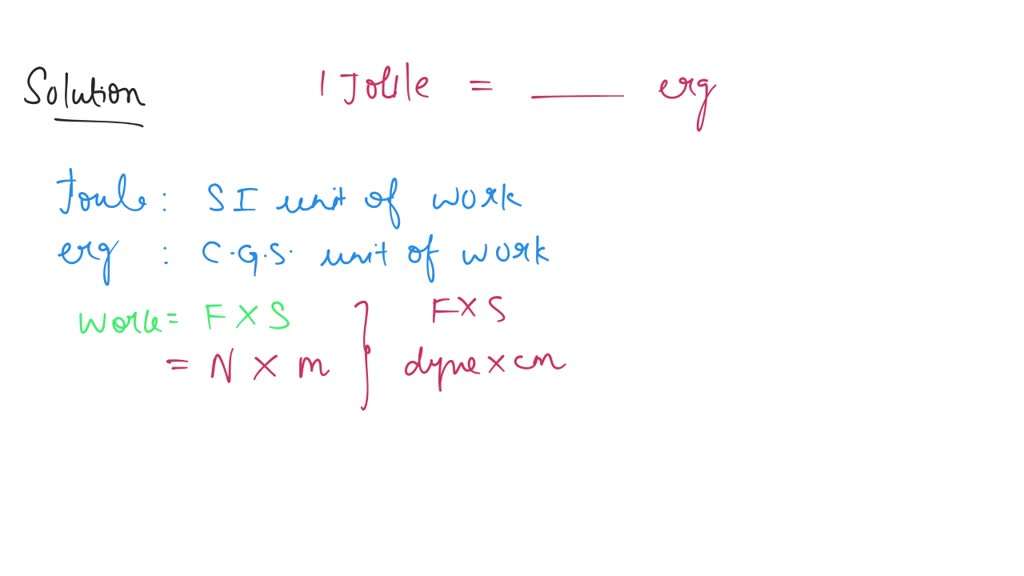
What is a Joule? Exploring the Unit of Energy
A Joule (J) is the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). Here’s a detailed point-wise exploration of the Joule:
- Definition:
- A Joule is the amount of energy transferred when a force of one newton is applied over a distance of one meter.
- Mathematically, 1 Joule = 1 Newton * 1 meter (1 J = 1 N·m).
2. SI Unit:
- The Joule is the SI unit for energy, work, and heat.
It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule.
3. Fundamental Units:
- In terms of fundamental SI units, a Joule is equivalent to one kilogram meter squared per second squared (1 J = 1 kg·m²/s²).
4. Relation to Other Units:
- 1 Joule is equal to 1 watt-second (1 J = 1 W·s).
- 1 Joule is also equal to 0.239 calories (1 cal = 4.184 J).
5. Examples in Daily Life:
- Lifting an apple weighing about 100 grams to a height of 1 meter uses approximately 1 Joule of energy.
- A 60-watt light bulb uses 60 Joules of energy per second.
6. Applications:
- Joules measure the energy released or consumed in physical, chemical, and biological processes.
- They are used in fields such as physics, engineering, chemistry, and environmental science.
7. Conversion Factors:
- 1 Joule = 0.000278 kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- 1 Joule = 0.7376 foot-pounds (ft·lb).
- 1 Joule = 9.8692 x 10^-4 BTU (British Thermal Units).
1 joule is equal to how many erg
- Conversion Factor:
- 1 joule (J) = 10,000,000 ergs (10^7 ergs).
2. Unit Relationship:
- Joule is a larger unit of energy compared to the erg.
3. Calculation:
- To convert joules to ergs, multiply the number of joules by 10^7.
4. Example:
- If you have 2 joules, it is equal to 2 × 10^7 = 20,000,000 ergs.
5. Scientific Use:
- This conversion is often used in physics and engineering to switch between larger and smaller energy measurements.
6. Practical Relevance:
- Understanding this conversion is crucial for precise scientific calculations and experiments.
Practical Applications of Joules in Daily Life
- Electricity Consumption: Household appliances like microwaves, refrigerators, and light bulbs consume energy measured in joules. For example, a 100-watt light bulb uses 100 joules of energy per second.
- Exercise and Fitness: Caloric expenditure during physical activities can be converted to joules. For instance, running might burn calories that are equivalent to thousands of joules of energy.
- Cooking: The energy required to heat food is often measured in joules. For example, microwaving a meal involves transferring a specific number of joules of energy to the food.
- Transportation: Fuel energy content in vehicles is measured in joules. The energy needed to accelerate a car or keep it running over a distance can be calculated in joules.
- Batteries and Gadgets: The energy stored in batteries for smartphones, laptops, and other gadgets is expressed in joules, indicating how long a device can operate before needing a recharge.
- Heating Systems: Energy used by heating systems in homes, such as electric heaters or water heaters, is measured in joules. This helps in understanding the efficiency and cost of heating.
- Sports and Physics: In sports, the kinetic energy of moving objects like balls and players can be measured in joules, which is useful for improving techniques and performance.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels and wind turbines generate energy measured in joules. Monitoring this helps in assessing their efficiency and the amount of power they contribute to the grid.
- Work and Mechanics: When lifting objects, the work done can be calculated in joules. For example, lifting a 10 kg object to a height of 2 meters requires approximately 196 joules of energy (assuming standard gravity)
- Thermal Insulation: The energy saved by insulating homes is often measured in joules, helping homeowners understand the benefits of insulation in reducing energy costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of joules and their practical applications in daily life is essential for grasping how energy is measured and utilized. From powering household appliances and calculating exercise output to determining the efficiency of renewable energy sources and heating systems, joules provide a standardized way to quantify energy. This not only aids in scientific and engineering calculations but also helps us make informed decisions about energy consumption and conservation. By appreciating the role of joules, we can better manage our energy use, leading to more efficient and sustainable practices in both our personal lives and broader technological advancements.
FAQs
Q: 1What is the exact conversion of joules to ergs?
Ans:: 1 joule is equal to 10,000,000 ergs (10^7 ergs).
Q: 2How do I convert joules to ergs?
Ans: To convert joules to ergs, multiply the number of joules by 10^7. For example, 3 joules is equal to 3 × 10^7 = 30,000,000 ergs.
Q:3 Why is the conversion factor between joules and ergs 10^7?
Ans: The conversion factor is 10^7 because the erg is a much smaller unit of energy compared to the joule. One joule is defined as 10 million ergs.
Q: 4 Can you provide a practical example of converting joules to ergs?
Ans: Sure! If a light bulb uses 5 joules of energy per second, it consumes 5 × 10^7 = 50,000,000 ergs of energy per second.






