Chemical Composition of Copper Sulphate
Here are 10 exact points on the chemical composition of copper sulfate, that specialize in its structure and diverse forms:
- Basic Compound: Copper sulfate ordinarily includes copper, sulfur, and oxygen. Its most fundamental shape is copper(II) sulfate, with the chemical components CuSO₄.
- Hydrated Forms: Copper sulfate commonly exists in several hydrated paperwork, the maximum frequent being copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO₄·5H₂O).
- Water of Hydration: In its pentahydrate form, copper sulfate includes five molecules of water. This water is indispensable to the crystal structure of the substance.
- Color: The pentahydrate form is famous for its bright blue colour, which is different among copper compounds.
- Anhydrous Form: When the water of hydration is eliminated, normally with the aid of heating, copper sulfate turns into anhydrous and is a white powder, which turns blue upon hydration.
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate is about 249.Sixty eight g/mol.
- Ionic Composition: In answer, copper sulfate dissociates into Cu²⁺ (copper ions) and SO₄²⁻ (sulfate ions).
- Solubility: Copper sulfate pentahydrate is surprisingly soluble in water, which allows its use in answers for diverse applications.
- Chemical Stability: Copper sulfate is chemically solid underneath normal conditions but will decompose upon heating, generating sulfur dioxide and oxygen.
- Applications Based on Composition: The chemical residences of copper sulfate, which includes its capability to act as an algaecide, fungicide, and herbicide, stem from its ionic composition, which lets in it to disrupt organic procedures in diverse organisms.
Raw Materials Needed for Preparation
To prepare copper sulfate, specially the copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate form, you would want numerous uncooked substances and a few gadget. Here is a list of the primary necessities:
- Copper Source: Copper metal scraps, copper twine, or copper turnings may be used as a source of copper. This will react with the sulfuric acid to shape copper sulfate.
- Sulfuric Acid: Concentrated sulfuric acid is wanted to react with the copper to supply copper sulfate.
- Water: Distilled water is vital for diluting the sulfuric acid and dissolving the copper sulfate formed, as well as for developing the pentahydrate shape via hydrating the anhydrous copper sulfate.
- Heating Equipment: A heat source inclusive of a hot plate or burner is required to heat the aggregate of copper and sulfuric acid, which aids in the response.
- Reaction Vessel: A box, generally made of glass or a warmness-resistant fabric that is non-reactive with sulfuric acid, is used to mix and heat the reactants.
- Stirring Device: A glass or plastic rod for stirring the answer to make certain even distribution of warmth and reactants all through the chemical reaction.
- Filtering Material: Filter paper or a nice mesh strainer is needed to split out unreacted solids from the liquid copper sulfate solution.
- Crystallization Containers: Shallow trays or dishes in which the copper sulfate solution may be allowed to evaporate and crystallize.
- Safety Equipment: Protective gloves, goggles, and in all likelihood a face mask to shield towards splashes and fumes from the sulfuric acid and the reaction method.
- Storage Containers: Proper bins for storing the copper sulfate crystals, usually made of plastic or glass with tight-becoming lids.
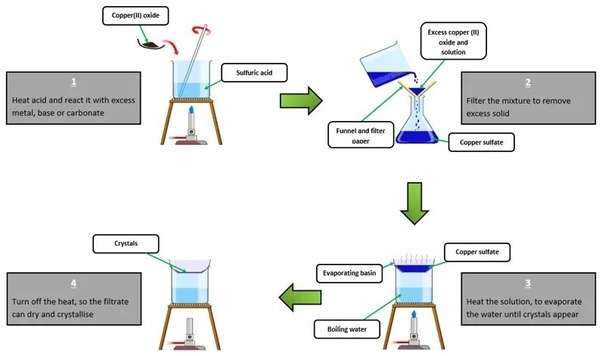
Step-by-Step Preparation Method
- Safety Preparation:
- Ensure you are sporting suitable safety equipment: gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Work in a well-ventilated vicinity to keep away from inhalation of fumes.
2. Dissolving Copper: - Place a small amount of copper turnings or scraps into a beaker.
- Carefully upload focused sulfuric acid to the copper. The amount of sulfuric acid have to be enough to cowl the copper portions.
- Heat the mixture gently on a hot plate. Avoid boiling but make sure the mixture is hot enough to promote reaction.
3. Reaction: - As the aggregate heats, copper reacts with sulfuric acid to form copper sulfate and sulfur dioxide gas is released.
- Continue heating till no greater reaction is found (no greater gasoline bubbles are formed).
4. Dilution: - Remove the beaker from the heat supply.
- Carefully upload distilled water to the new mixture to dilute the copper sulfate solution. This additionally helps to dissolve all the shaped copper sulfate.
5. Filtration: - Set up a filtration gadget the use of a funnel and filter out paper.
- Pour the hot solution via the filter out to get rid of any undissolved copper or impurities.
6. Crystallization: - Transfer the filtered solution into an evaporation dish.
Allow the solution to cool slowly at room temperature. As it cools, copper sulfate will begin crystallizing out of the solution. - For large crystals, you may go away the answer to evaporate slowly over several days.
7. Harvesting Crystals: - Once a vast amount of crystals has formed and boom has ceased, pour off any closing answer.
- Wash the crystals with a small quantity of cold distilled water to take away any adhering impurities.
8. Drying: - Lay the washed crystals on a paper towel or a drying rack to permit them to dry absolutely.
9. Storage: - Store the dried copper sulfate crystals in a sealed box to save you them from absorbing moisture from the air.
Factors Affecting Crystal Growth
Crystal growth is stimulated by using different factors which could affect the dimensions, shape, and purity of the crystals fashioned. Here are some key elements that play a position within the crystal growth system:
- Supersaturation: The level of supersaturation of the answer determines the riding pressure for crystal increase. High supersaturation promotes rapid nucleation but can result in smaller, much less nicely-fashioned crystals, while decrease supersaturation favors the boom of large, extra well-described crystals.
- Temperature: Temperature immediately affects the solubility of the solute in the solvent. Lower temperatures normally lower solubility and inspire crystal boom, but the temperature have to be carefully controlled to keep away from too rapid crystallization which can bring about faulty structures.
- Rate of Cooling: The fee at which the answer is cooled can impact crystal length and nice. Slow cooling generally outcomes in fewer nuclei and the boom of larger crystals. Rapid cooling may additionally lead to the formation of many small crystals.
- Purity of the Solution: Impurities in the answer can inhibit or promote crystal boom. Some impurities may also get integrated into the crystal lattice, causing defects or alterations in crystal form.
- Solvent: The type of solvent used can influence crystal increase. Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared Solvents that dissolve the solute extra uniformly have a tendency to produce better-formed crystals.
- Volume of the Solution: The quantity of solvent relative to the quantity of solute can have an effect on how freely the crystals can develop. Too much solvent can also dilute the solution and gradual down crystallization, even as too little may additionally lead to rapid, uncontrolled boom.
- Stirring: Stirring impacts crystal boom with the aid of influencing the distribution of solute molecules and the elimination of heat from the answer. Controlled stirring can assist
Conclusion
In conclusion, Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared the technique of getting ready copper sulfate crystals and knowledge the factors affecting crystal growth illustrates the difficult stability of chemical reactions and physical situations. From the guidance related to copper and sulfuric acid to the cautious control of situations like temperature, supersaturation, and purity, every step plays a important role inside the formation of great crystals. The factors affecting crystal boom are important for tailoring crystal traits to specific needs, whether or not for academic functions, business programs, or superior materials technological know-how. By studying these variables, scientists and technicians can optimize crystal size, shape, and purity, enhancing the software and performance in their merchandise and experiments.
FAQs
Q: 1What materials are needed to prepare copper sulfate crystals?
Ans: Copper metal, concentrated sulfuric acid, distilled water, and standard lab equipment including a beaker, heat source, and crystallization dishes.
Q:2 How is copper sulfate formed from copper and sulfuric acid?
Ans: Copper reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid, producing copper sulfate and sulfur dioxide gas in an exothermic reaction.
Q:3 What is the role of water in the crystallization of copper sulfate?
Ans Water is used to dissolve copper sulfate in the solution and facilitate the formation of hydrated copper sulfate pentahydrate crystals upon evaporation.
Q: 4 How can the size of the copper sulfate crystals be controlled during preparation?
Ans: Crystal size can be controlled by adjusting the cooling rate, the degree of supersaturation, and the evaporation speed of the solution.
Certainly! Here are points to recall when surely stating the motive for go away:
- Be Specific: Clearly specify the exact purpose in your leave, which include contamination, personal emergency, family commitments, or planned scientific appointments.
- Provide Details: Include relevant info that specify the nature and urgency of your go away, which include the date(s) of absence and any specific circumstances that necessitate your time away.
- Professional Tone: Maintain a professional and respectful tone for the duration of your conversation, making sure readability and sincerity on your rationalization.
- Avoid Ambiguity: Avoid vague or ambiguous language when mentioning your motive for go away to save you misunderstandings and ensure that your request is known without a doubt.
- Brief and Direct: Keep your clarification brief and to the factor whilst presenting enough records to convey the seriousness or necessity of your go away request.
- Consideration for Impact: Acknowledge any ability effect your absence might also have to your paintings or duties, and provide to discuss or provide assistance in dealing with tasks throughout your absence if relevant.






