Definition of Simple Tissues and Complex Tissues
In plant life, tissues are categorized into two most important kinds primarily based on their shape, composition, and feature:
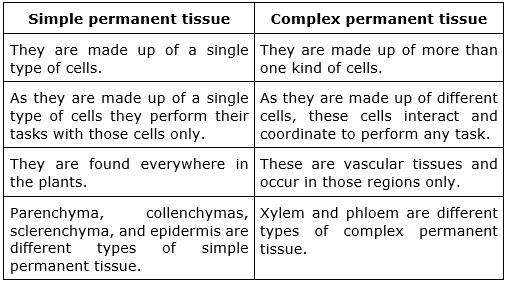
Simple Tissues:
- Simple tissues are composed of cells that are structurally and functionally similar. They carry out not unusual responsibilities together within the plant. Examples consist of:
- Parenchyma: Parenchyma cells are thin-walled and regularly have massive crucial vacuoles. They are versatile and carry out capabilities along with photosynthesis, storage of nutrients, and secretion.
- Collenchyma: Collenchyma cells have inconsistently thickened primary cellular walls, in general composed of cellulose and pectin. They provide mechanical aid and flexibility to young plant components.
- Sclerenchyma: Sclerenchyma cells have thick, lignified secondary cellular partitions that offer inflexible guide and safety to mature plant tissues. They are lifeless at adulthood and contribute to strengthening structures like stems and seed coats.
Complex Tissues:
- Complex tissues are composed of different forms of cells that work collectively to carry out specialized capabilities. These tissues are prepared into precise systems and consist of:
- Xylem: Xylem tissue transports water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant. It includes several cell kinds, inclusive of vessel elements, tracheids, fibers, and parenchyma cells.
- Phloem: Phloem tissue transports organic nutrients which include sugars from photosynthetic tissues (typically leaves) to different components of the plant. It consists of sieve tube elements, accomplice cells, fibers, and parenchyma cells.
Structural Differences Between Simple and Complex Tissues
The structural variations among simple and complex tissues in flowers are based totally on their composition, enterprise, and specialised features:
Composition:
- Simple Tissues: Simple tissues consist of cells which can be structurally and functionally similar in the course of. They commonly encompass one type of cellular or a few sorts with similar traits.
- Complex Tissues: Complex tissues are composed of various varieties of cells that work together to carry out specialised functions. These tissues frequently consist of a couple of cellular kinds organized into precise arrangements.
2. Organization: - Simple Tissues: Cells in easy tissues are commonly loosely packed and have much less specialised systems. They are uniform in appearance and characteristic.
- Complex Tissues: Cells in complicated tissues are organized into unique systems or systems that facilitate their specialized functions. These tissues regularly have wonderful cell types arranged in styles that guide their roles in transport, guide, or garage.
3. Function: - Simple Tissues: Simple tissues perform basic features inclusive of storage, help, and photosynthesis. They make contributions to the general structure and metabolic techniques of the plant.
- Complex Tissues: Complex tissues are specialized for transporting fluids (xylem and phloem), imparting structural assist (sclerenchyma fibers), or accomplishing metabolic sports (vascular tissues). They play important roles within the boom, development, and model of vegetation to their environments.
4. Examples: - Simple Tissues: Examples encompass parenchyma cells for storage and photosynthesis, collenchyma cells for support in growing plant components, and sclerenchyma cells for structural guide How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants in mature tissues.
- Complex Tissues: Examples encompass xylem for transporting water and minerals, phloem for t
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants
| Feature | Simple Tissues | Complex Tissues |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Composed of structurally similar cells | Composed of different types of cells |
| Cell Types | Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma | Xylem, Phloem, Vascular bundles, etc. |
| Organization | Cells are loosely packed and less specialized | Cells are organized into specific structures |
| Function | Basic functions like storage, support, and photosynthesis | Specialized functions like transport and support |
| Examples | Parenchyma (storage), Collenchyma (support), Sclerenchyma (protection) | Xylem (water transport), Phloem (nutrient transport) |
| Location | Found throughout the plant body | Found in specific regions (e.g., vascular bundles) |
| Characteristics | Thin-walled, living cells with diverse roles | Thick-walled, often dead cells specialized for transport |
| Adaptation | General adaptation to various plant functions | Adapted to specific roles in plant physiology |
Significance and Applications in Plant Biology
In plant biology, understanding the significance and applications of tissues, both simple and complex, is crucial for studying plant structure, function, and adaptation. Here are some key points highlighting their importance:
- Structural Support: Simple tissues like collenchyma and sclerenchyma provide mechanical support to plant organs, helping them withstand environmental stresses such as wind, gravity, and physical damage. This support is vital for plant growth and stability.
- Metabolic Functions: Parenchyma cells, a type of simple tissue, play essential roles in photosynthesis, storage of nutrients (such as starch and proteins), and secretion of substances like resins and latex. These functions contribute to plant metabolism and energy storage.
- Transport of Water and Nutrients: Complex tissues such as xylem and phloem facilitate the transport of water, minerals, and organic nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves, while phloem transports sugars and other organic compounds from leaves to other plant parts.
- Adaptation to Environmental Conditions: Tissues adapt to environmental changes such as drought, heat, and nutrient availability. For example, xylem can adjust its water-conducting capacity, and phloem can regulate the distribution of sugars according to plant needs and environmental cues.
- Biotechnological Applications: Understanding tissue functions and structures is crucial in plant biotechnology for applications such as tissue culture, genetic modification, and crop improvement. Techniques like tissue culture rely on the ability to manipulate and grow plant tissues under controlled conditions for cloning and propagation.
- Medical and Industrial Uses: Plant tissues and their components are utilized in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and biofuels. For instance, fibers derived from sclerenchyma cells are used in textiles, while cellulose from plant tissues serves as a renewable source for biofuels and other industrial products.
- Research and Education: Studying plant tissues provides insights into fundamental biological processes, evolutionary adaptations, and ecological interactions. It forms the basis for research in plant physiology, ecology, and genetics, contributing to advancements in agriculture and environmental conservation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants plant tissues, whether simple or complex, are essential components that contribute to the structure, function, and adaptability of plants. Simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma perform basic yet vital roles such as support, storage, and protection. They enable plants to withstand mechanical stresses and environmental fluctuations. Complex tissues such as xylem and phloem specialize in the efficient transport of water, nutrients, and organic compounds throughout the plant. This vascular system is critical for plant growth, development, and survival in diverse habitats.
FAQs
Q: 1What are simple tissues composed of?
Ans: Simple tissues are composed of cells that are structurally and functionally similar throughout. They consist of one or a few types of cells performing common tasks like storage, support, or photosynthesis.
Q:2 What are complex tissues composed of?
Ans: Complex tissues are composed of different types of cells that are organized into specific structures to perform specialized functions. They include tissues like xylem and phloem, which facilitate the transport of water, nutrients, and organic compounds.
Q:3 What is the primary function of simple tissues?
Ans Simple tissues primarily provide basic functions such as storage of nutrients (parenchyma), support for young plant parts (collenchyma), and rigidity in mature tissues (sclerenchyma).
Q: 4 How do complex tissues differ from simple tissues in terms of organization?
Ans: Complex tissues are organized into distinct structures with multiple cell types. For example, xylem tissues include vessel elements, tracheids, fibers, and parenchyma cells arranged to efficiently transport water and minerals.






