How lenticels are different from typical stomata Lenticels and traditional stomata are wonderful structures worried in gas trade in plant life. Lenticels are specialized pores or openings discovered within the bark of woody stems and roots. They facilitate the exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide among internal tissues and the atmosphere. Lenticels are large and extra seen as compared to stomata, regularly acting as raised, corky systems on the surface of older plant tissues. In evaluation, stomata are tiny pores frequently placed on the epidermis of leaves and young stems. They are surrounded by way of protect cells that regulate their opening and closing to manipulate the exchange of gases and water vapor. Stomata play a critical function in photosynthesis by way of allowing carbon dioxide uptake and oxygen release, even as also regulating water loss via transpiration. Overall, lenticels and stomata fluctuate in region, structure, and function, every serving critical roles in plant body structure and adaptation to environmental situations.
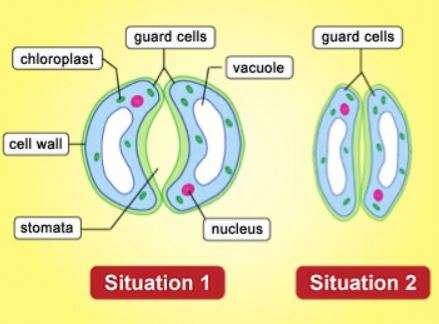
Introduction to Lenticels and Stomata
- Definition and Location:
- Lenticels: Lenticels are specialized pores or openings in the bark of woody stems and roots of vegetation. They facilitate fuel change between internal tissues and the ecosystem.
- Stomata: Stomata are microscopic pores inside the foremost determined at the epidermis of leaves and young stems. They alter fuel alternate, collectively with the uptake of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen and water vapor.
2. Structure: - Lenticels: Lenticels are massive and additional conspicuous compared to stomata. They are regularly raised, corky structures seen on the surface of older woody tissues.
- Stomata: Stomata encompass a pore surrounded with the aid of protect cells. These cells manage the outlet and closing of the pore to regulate gasoline exchange and water loss.
3. Function: - Lenticels: Lenticels facilitate the diffusion of gases at the side of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor into and out of the plant’s inner tissues, particularly in older, plenty much less energetic components of the plant.
- Stomata: Stomata play a crucial role How lenticels are different from typical stomata in photosynthesis thru allowing carbon dioxide uptake wanted for plant boom and improvement. They additionally alter water loss thru transpiration.
4. Distribution: - Lenticels: Lenticels are predominantly located at the bark of woody stems and roots, in which they offer a pathway for fuel alternate in tissues that lack active photosynthesis.
- Stomata: Stomata are densely dispensed on the surfaces of leaves and young stems, optimizing gas exchange for photosynthesis and responding to environmental factors which includes light depth and humidity.
5. Adaptations and Environmental Response: - Lenticels: Lenticels are diversifications of woody flora to facilitate How lenticels are different from typical stomata gas change in tissues where stomata are absent or lots less powerful.
How lenticels are different from typical stomata
- Location:
- Lenticels: Lenticels are positioned inside the bark of woody stems and roots of plant life.
- Stomata: Stomata are commonly positioned at the dermis of leaves and younger stems.
2. Structure: - Lenticels: Lenticels are huge, often raised, corky structures that allow fuel change via openings inside the bark.
- Stomata: Stomata are microscopic pores surrounded through guard cells, regulating gasoline alternate and water vapor.
3. Function: - Lenticels: Lenticels facilitate fuel change (oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor) among internal plant tissues and the surroundings, especially in older, a lot less lively additives of the plant.
- Stomata: Stomata specifically alter the uptake of carbon dioxide desired for photosynthesis How lenticels are different from typical stomata and the discharge of oxygen and water vapor via transpiration.
4. Distribution: - Lenticels: Lenticels are sporadically dispensed at the bark of woody stems and roots, supplying a pathway for fuel alternate in tissues lacking active photosynthesis.
- Stomata: Stomata are densely dispensed at the surfaces of leaves and young stems, optimizing gasoline exchange for green photosynthesis.
5. Regulation and Adaptation: - Lenticels: Lenticels offer a passive direction for gasoline trade and do now not actively adjust their starting and closing.
- Stomata: Stomata actively reply to environmental cues which include moderate depth, humidity, and How lenticels are different from typical stomata carbon dioxide ranges, adjusting their aperture to balance photosynthesis and water loss.
Function of Stomata in Plant Physiology
Stomata play a essential position in plant body structure, often facilitating gasoline exchange among the plant and its environment. Here are the key functions of stomata:
- Gas Exchange: Stomata adjust the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the ecosystem, that’s essential for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through open stomata and is used at some point of photosynthesis to produce sugars and other organic compounds.
- Oxygen Release: During photosynthesis, oxygen (O2) is launched as a byproduct through open stomata. This process is essential for aerobic respiration in vegetation and different organisms.
- Water Regulation: Stomata manage the loss of water vapor from the plant thru a procedure called transpiration. When stomata open to permit fuel exchange, water vapor escapes from the plant. This lack of water facilitates to chill the plant and creates a negative stress gradient that aids in the motion of water and minerals from roots to shoots (referred to as transpiration circulate).
- Regulation of Plant Temperature: Stomatal opening and closing additionally have an impact on the inner temperature of the plant. Opening stomata allows for cooling via transpiration, supporting to alter plant temperature and save you overheating, mainly in hot environments.
- Control of Gas Diffusion: Stomata alter the diffusion of gases (CO2, O2, and water vapor) via commencing and final in response to environmental factors which includes light depth, humidity, and carbon How lenticels are different from typical stomata dioxide stages. This law ensures gold standard situations for photosynthesis at the same time as minimizing water loss.
Role in Water and Gas Exchange
Stomata play a critical role in facilitating each water and fuel change in vegetation, critical for his or her growth, survival, and edition to changing environmental conditions. Here’s a top level view of their function:
- Gas Exchange:
- Carbon Dioxide Uptake: Stomata are the number one access points for carbon dioxide (CO2) into plant leaves. CO2 is a vital raw fabric used in photosynthesis, where it is transformed into sugars and different natural compounds.
- Oxygen Release: During photosynthesis, oxygen (O2) is launched as a byproduct through open stomata. This system is crucial for cardio respiratory in plant life and other organisms.
2. Water Regulation: - Transpiration: Stomata manipulate How lenticels are different from typical stomata the discharge of water vapor from the plant through a procedure referred to as transpiration. When stomata open to allow gas trade, water vapor escapes into the surroundings. This loss of water helps alter the internal pressure (turgor strain) of plant cells and creates a suction pressure (transpiration pull) that draws water and dissolved nutrients from the roots up through the plant’s vascular gadget.
- Water Conservation: Stomatal regulation additionally facilitates vegetation preserve water at some point of instances of drought or high temperatures by using adjusting their establishing and final in reaction to environmental cues such as mild intensity, humidity, and water availability.
3. Temperature Regulation: - Cooling Mechanism: Stomatal starting helps the cooling of plant tissues through transpiration. As water evaporates from the leaf floor, it absorbs warmth, thereby cooling the plant and preventing overheating, in particular in warm environments.
4. Gas Diffusion Control:
Regulation of Gas Diffusion: Stomata actively How lenticels are different from typical stomata adjust the diffusion of gases (CO2, O2, and water vapor) via starting and final in reaction to environmental stimuli.
Conclusion
FAQs
Q: 1What are lenticels, and where are they found on plants?
Ans: Lenticels are specialized pores found on the bark of woody plants, allowing for gas exchange. They are often visible as small raised structures.
Q:2 How do lenticels differ in function from stomata?
Ans: Lenticels primarily facilitate gas exchange for woody tissues, while stomata regulate gas exchange and water loss primarily in leaves.
Q:3 What is the structure of lenticels compared to stomata?
Ans Lenticels are often larger and less regulated than stomata, lacking guard cells and opening and closing mechanisms.
Q:4Are lenticels involved in photosynthesis like stomata?
Ans Challenges include external pressures like land encroachment, climate change impacts, inadequate funding, and conflicting interests between conservation goals and economic development. Addressing these challenges requires community engagement, policy support, and sustainable resource management strategies.






