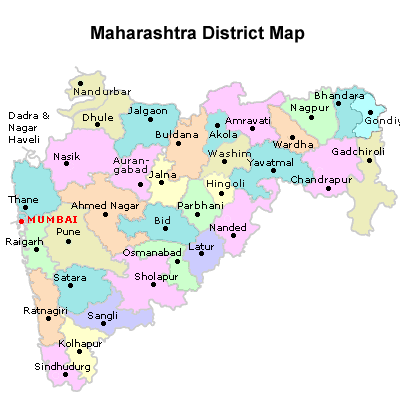
How many District in Maharashtra , one of India’s most populous and economically significant states, is divided into a total of 36 districts. Each district serves as an administrative unit responsible for local governance and the implementation of government policies and programs at the grassroots level. These districts vary in size, population, and geographical features, ranging from urban centers like Mumbai, Pune, and Nagpur to rural areas and tribal regions. The distribution of districts across Maharashtra ensures effective administration and governance, allowing for the efficient delivery of public services and the representation of diverse communities and interests within the state. The establishment of districts facilitates decentralized decision-making and local development initiatives, fostering inclusive growth and enhancing the overall functioning of the state’s administrative machinery.
How many District in Maharashtra
- Maharashtra is divided into a total of 36 districts.
- These districts serve as administrative units responsible for local governance and the implementation of government policies and programs.
- Each district varies in size, population, and geographical features, catering to the diverse needs of the state’s inhabitants.
- The districts include urban centers such as Mumbai, Pune, Nagpur, and Thane, as well as rural and tribal regions.
- The distribution of districts across Maharashtra ensures effective administration and governance, facilitating the efficient delivery of public services.
- The establishment of districts allows for decentralized decision-making and local development initiatives.
- Each district has its own administrative headquarters and is headed by a District Collector or Deputy Commissioner, who oversees various administrative functions.
- The division of Maharashtra into districts helps in better representation and governance, ensuring that the state’s diverse communities and interests are adequately addressed.
- District boundaries are periodically reviewed and adjusted to accommodate changes in population density, geographic factors, and administrative requirements.
- Overall, the presence of 36 districts in Maharashtra contributes to the efficient functioning of the state’s administrative machinery and promotes inclusive development across its regions.
Breakdown of Districts
Breakdown of Districts in Maharashtra:
- Mumbai: The capital city of Maharashtra and one of the most populous urban districts in India, known for its economic significance, cultural diversity, and historic landmarks.
- Pune: A major industrial, educational, and cultural hub, Pune district is renowned for its manufacturing, IT, and automotive industries, as well as its esteemed educational institutions.
- Thane: Located adjacent to Mumbai, Thane district is a bustling urban center with a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial areas, known for its rapid urbanization and infrastructural development.
- Nagpur: The largest city in central India and the winter capital of Maharashtra, Nagpur district is a prominent commercial and political center, known for its oranges, textile industry, and historical monuments.
- Nashik: Situated on the banks of the Godavari River, Nashik district is known for its religious significance, as well as its thriving agricultural, industrial, and wine-producing sectors.
- Aurangabad: Home to UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Ajanta and Ellora Caves, Aurangabad district is a major tourist destination and industrial center, known for its historical and cultural heritage.
- Kolhapur: Located in the western region of Maharashtra, Kolhapur district is known for its rich cultural heritage, traditional arts and crafts, and agricultural produce, including sugarcane and jaggery.
- Solapur: A prominent industrial and commercial center in Maharashtra, Solapur district is known for its textile and garment industries, as well as its historical monuments and religious sites.
- Amravati: Located in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra, Amravati district is known for its agricultural produce, including cotton, pulses, and oranges, as well as its educational institutions and cultural heritage.
- Latur: Known for its sugarcane cultivation, Latur district is an important agricultural center in Maharashtra, also known for its historical sites and educational institutions.
District Administration
- District Collector or Deputy Commissioner: Each district is headed by a District Collector or Deputy Commissioner, who serves as the chief administrative officer responsible for overseeing the district’s affairs.
- Administrative Functions: The district administration is responsible for carrying out various administrative functions, including maintaining law and order, implementing government policies and programs, and providing essential services to the population.
- Law Enforcement: District administration works closely with law enforcement agencies such as the police to ensure public safety and maintain law and order within the district.
- Service Delivery: It is responsible for providing essential services such as healthcare, education, sanitation, and infrastructure development to the residents of the district.
- Economic Development: District administration plays a role in promoting economic development and welfare initiatives within the district, including employment generation programs and support for local industries and businesses.
- Coordination: District administrative officials work closely with various government departments, local elected representatives, civil society organizations, and other stakeholders to address the needs and concerns of the local population.
- Disaster Management: In times of natural disasters or emergencies, the district administration plays a crucial role in coordinating relief and rescue operations and providing assistance to affected communities.
- Revenue Administration: It oversees revenue administration, including land records, land acquisition, and collection of various taxes and fees within the district.
- Implementation of Government Schemes: District administration implements various government schemes and programs aimed at poverty alleviation, social welfare, rural development, and infrastructure improvement.
- Promotion of Participatory Governance: District administration promotes participatory governance by encouraging citizen engagement, transparency, and accountability in decision-making processes at the local level.
Conclusion
In conclusion, district administration serves as the backbone of governance at the grassroots level, playing a pivotal role in ensuring the effective implementation of government policies and programs and the delivery of essential services to the local population. Led by the District Collector or Deputy Commissioner, the district administration carries out diverse administrative functions, including maintaining law and order, providing public services, promoting economic development, and coordinating disaster management efforts. By working closely with various stakeholders, including government agencies, elected representatives, and civil society organizations, district administration fosters participatory governance and facilitates citizen engagement in decision-making processes. Overall, daistrict administration plays a crucial role in promoting inclusive development, ensuring public welfare, and enhancing the quality of life for residents within the district.
FAQs
Q: 1.How many districts are there in Maharashtra?
Ans: Maharashtra is divided into a total of 36 districts.
Q: 2 What are the names of some key districts in Maharashtra?
Ans: Some key districts in Maharashtra include Mumbai, Pune, Thane, Nagpur, Nashik, Aurangabad, Kolhapur, Solapur, Amravati, and Latur, among others.
Q:3. How are these districts distributed across the state?
Ans:The districts in Maharashtra are spread across different regions of the state, including urban centers, rural areas, and tribal regions, ensuring equitable representation and governance.
Q: 4.Who heads the administration of each district in Maharashtra?
Ans: Each district in Maharashtra is headed by a District Collector or Deputy Commissioner, who serves as the chief administrative officer responsible for overseeing the district’s affairs.






