There are 1000 grams in 1 kilogram. The prefix “kilo-” in the metric system denotes a factor of 1000, so when converting from kilograms (kg) to grams (g), you multiply by 1000. This relationship is fundamental in everyday measurements and scientific contexts where weights and masses are expressed in metric units. For example, if you have 2 kilograms of flour, it would be equivalent to 2000 grams. Understanding this conversion is important for accurately measuring and comparing weights across different metric units.
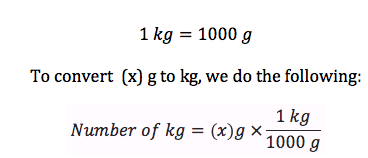
How many grams are in 1 kg
- Basic Conversion: 1 kilogram (kg) equals 1000 grams (g).
- Metric Prefix: The prefix “kilo-” denotes a factor of 1000 in the metric system, so 1 kg = 1000 g.
- Fundamental Unit: Grams (g) are smaller units used to measure mass within the metric system
- Multiplicative Factor: To convert kilograms to grams, multiply the kilogram value by 1000.
- Examples:
- 2 kg = 2000 g
- 0.5 kg = 500 g
- 3.5 kg = 3500 g
6. Common Usage: Used globally for measuring weights in everyday life, science, industry, and commerce.
7. Precision: Provides a precise measurement for smaller quantities compared to kilograms.
8. Convenience: Allows for easier handling of smaller quantities and more precise calculations.
9. Educational Importance: Taught in schools as part of basic math and science curricula.
10. Practical Application: Essential for accurate measurement and conversion of mass in various fields and industries.
Comparison with Other Measurement Systems
Comparing grams (g) and kilograms (kg) with other measurement systems highlights their unique characteristics and advantages within the metric system:
- Metric System vs. Imperial System: In the Imperial system, weight is measured in ounces, pounds, and tons. Grams are more precise for smaller weights compared to ounces, while kilograms are roughly equivalent to 2.2 pounds.
- Precision: Grams offer finer granularity for smaller weights, which is advantageous in scientific and culinary contexts where precise measurements are crucial. In contrast, ounces and pounds in the Imperial system are larger units and may require decimal fractions for accuracy.
- Ease of Conversion: The metric system’s base-10 structure simplifies conversions between units. For instance, 1 kilogram equals 1000 grams, whereas conversions in the Imperial system involve varied conversion factors between ounces and pounds.
- Global Standard: The metric system, including grams and kilograms, is widely adopted globally, facilitating uniformity in measurements across borders and industries. This consistency is particularly valuable in international trade and scientific research.
- Applications: Grams and kilograms are extensively used in fields like pharmaceuticals, food production, and engineering due to their precise measurement capabilities and straightforward conversions. In contrast, the Imperial system’s units may vary by region and industry.
Teaching and Learning Metric Conversion
Teaching and learning metric conversion involves several key strategies to help students understand and apply the principles effectively:
- Understanding Metric Units: Begin by introducing the basic units of the metric system: meter (length), gram (mass), and liter (volume). Explain their relationships and how prefixes such as kilo-, centi-, and milli- modify these units.
- Multiplicative Relationships: Teach students that metric conversions are based on powers of 10. For example, 1 kilogram = 1000 grams, and 1 meter = 100 centimeters. Use visual aids and real-life examples to illustrate these relationships.
- Practice with Conversion Tables: Provide conversion tables for common metric units (length, mass, volume) and encourage students to practice converting between units. Emphasize the importance of unit cancellation and maintaining consistent units throughout calculations.
- Hands-On Activities: Engage students in hands-on activities where they measure and convert objects using metric units. For instance, have them measure lengths in meters and centimeters, or weigh objects in grams and kilograms.
- Real-World Applications: Relate metric conversion to everyday scenarios and professions where it is used, such as cooking (measuring ingredients), science experiments (calculating volumes), and international trade (converting currencies).
- Interactive Tools: Use interactive tools and educational apps that simulate metric conversions, allowing students to practice in a digital environment. These tools often provide instant feedback and reinforce learning through repetition.
- Problem-Solving Exercises: Present students with word problems and practical exercises that require them to apply metric conversion skills. Encourage them to explain their reasoning and steps taken to arrive at the solution.
- Assessment and Feedback: Assess students’ understanding through quizzes, tests, and assignments that include metric conversion tasks. Provide constructive feedback to address any misconceptions and reinforce learning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, learning metric conversion is essential for understanding and applying measurements in various fields, from science and engineering to everyday tasks like cooking and shopping. By mastering the relationships between metric units and practicing conversions through hands-on activities and real-world examples, students develop valuable skills in accuracy, problem-solving, and numerical fluency. Educators play a crucial role in facilitating this learning process by providing structured lessons, interactive tools, and opportunities for practical application. Ultimately, proficiency in metric conversion enhances students’ ability to navigate a globalized world where standardized measurements are fundamental to communication and collaboration across borders.
FAQs
Q: 1What is the relationship between kilograms (kg) and grams (g)?
Ans: 1 kilogram (kg) is equivalent to 1000 grams (g). This conversion is based on the metric system, where the prefix “kilo-” denotes a factor of 1000.
Q:2. Why are grams and kilograms used for measuring weight?
Ans: Grams and kilograms are part of the metric system, which is widely used globally for its simplicity and consistency. They provide a standardized way to measure weights across various applications, from scientific experiments to everyday use.
Q:3 How do you convert kilograms to grams and vice versa?
Ans : To convert kilograms to grams, multiply the kilogram value by 1000. For example, 2 kilograms = 2000 grams. To convert grams to kilograms, divide the gram value by 1000. For instance, 3000 grams = 3 kilograms.
Q:4. In what contexts are grams and kilograms typically used?
Ans: Grams are commonly used for measuring smaller weights, such as food ingredients in recipes, while kilograms are used for larger weights like human body weight, packages, and industrial materials.






