The title of a bachelor’s degree program in the age-old Indian medical system of Ayurveda is “Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine and Surgery,” or BAMS. By maintaining the equilibrium between the body, mind, and spirit while applying natural treatments and therapies, ayurveda promotes total wellbeing. The BAMS course provides interns with practical clinical experience and covers topics including anatomy, herbal medicine, yoga, and Panchakarma. After completing the program, alumni can practice Ayurveda legally and help promote and preserve traditional medicine both in India and around the world. In order to provide a complementary and all-encompassing approach to healthcare, BAMS is essential.
- Understanding BAMS
- BAMS Education and Training
- BAMS vs. Other Medical Systems
- Role of a BAMS Doctor
- Ayurvedic Treatments and Therapies
- Ayurvedic Diagnosis and Assessment
- Integrative Medicine and BAMS
- Legal and Ethical Aspects of BAMS
- Global Acceptance and Future Prospects
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Understanding BAMS
Exploring the fundamentals of BAMS (Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine and Surgery), a bachelor’s degree program centered on the traditional Indian medical system of Ayurveda, is necessary to comprehend this undergraduate degree program. In order to achieve balance and comprehensive well-being, BAMS includes the study of Ayurvedic concepts like Tridosha (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and Panchamahabhutas (Five Elements). The relevance of BAMS in conserving conventional medical procedures is shown by its rich historical development, which is founded in Ayurveda. The BAMS ideology places a strong emphasis on lifestyle management, natural treatments, and preventive healthcare. BAMS practitioners are essential in promoting holistic approaches to health and wellness and enhancing modern healthcare as the world undergoes a renaissance of interest in Ayurveda.
2. BAMS Education and Training
The “BAMS Education and Training” part of the textbook focuses on how students enrolled in the Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine and Surgery (BAMS) program have progressed academically and in real-world settings. It describes the requirements for admission, such as the entrance examinations and selection processes. Examining the BAMS curriculum and syllabus, with a focus on key subjects and clinical training. Discussed are the program’s length and structure as well as the importance of the internship time. For BAMS students, the section also discusses evaluation and assessment techniques. It also notes the possibilities for BAMS practitioners to pursue research, specialization, and ongoing medical education. Overall, this part offers a thorough grasp of the training possibilities and educational components offered by the BAMS program.
3. BAMS vs. Other Medical Systems

This section contrasts BAMS with other medical systems such as allopathy, homeopathy, and unani while stressing their unique characteristics, advantages, and potential for integration. It explores the potential for complementarity in patient care, evidence-based practices, holistic vs. reductionist methods, worldwide acceptability, and evidence-based practices.
4. Role of a BAMS Doctor
BAMS physicians are essential to healthcare because they offer clinical services, individualized care, and health promotion. They make a priority of preventive care while diagnosing and prescribing Ayurvedic medicines. The collaboration of BAMS doctors with other medical specialists supports integrative healthcare approaches.
5. Ayurvedic Treatments and Therapies

Ayurvedic treatments and therapies are covered in the “Ayurvedic Treatments and Therapies” section, which also includes information on Panchakarma, herbal remedies, yoga, meditation, abhyanga, Ayurvedic nutrition, Marma therapy, and skincare. The goal is to regain equilibrium and wellbeing through organic and specialized treatments.
6. Ayurvedic Diagnosis and Assessment
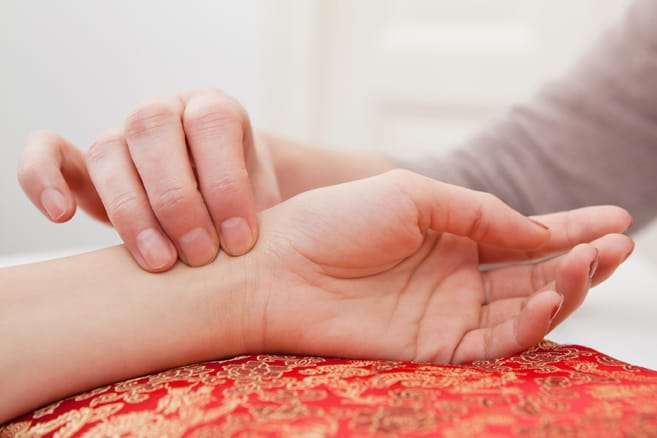

Ayurvedic diagnostic concepts such as Tridosha (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and Agni (digestive fire) are explained in this section. Additionally, it presents Nadi Pariksha, an essential Ayurvedic pulse diagnosing technique.
7. Integrative Medicine and BAMS
This section examines integrative medicine while highlighting how BAMS is compatible with it. By showing case stories and outlining potential paths for BAMS in integrative healthcare, it emphasizes the advantages of integrating conventional and Ayurvedic treatments.
8. Legal and Ethical Aspects of BAMS
The legal and ethical implications of BAMS are covered in this part, along with the regulatory agencies, requirements for licenses, and the code of ethics that applies to BAMS practitioners.
9.Global Acceptance and Future Prospects

The focus of the “Global Acceptance and Future Prospects” section is on the BAMS (Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine and Surgery)’s prospects in the future. With a focus on international partnerships and projects promoting its practice, it emphasizes the increasing acceptability of Ayurveda on a global scale. The part also looks at current Ayurvedic medical research and potential topics for future development. It explores how technology might expand Ayurveda’s influence and facilitate its incorporation into international healthcare systems. The section’s overall message emphasizes the growing importance and bright future of BAMS in the field of global healthcare.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
BAMS stands for “Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine and Surgery.” It is an undergraduate degree program in the field of traditional Indian medicine known as Ayurveda.
The duration of the BAMS course is typically five and a half years, including a one-year internship.
The eligibility criteria for BAMS admission may vary depending on the country or institution. Generally, candidates should have completed their higher secondary education (12th grade) in science with biology, chemistry, and physics as main subjects. Entrance exams may also be required in some cases.
The BAMS curriculum includes subjects like anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, herbal medicine, Panchakarma (detoxification), yoga, and meditation, among others.





