INTRODUCTION
Entering the 11th grade is a crucial step in a student’s academic journey. For many, it marks the transition from secondary to higher secondary education, often determining future career paths. To secure a place in prestigious institutions or specialized programs, students are required to pass entrance exams that assess their knowledge and aptitude. This introduction provides an overview of 11th entrance exam papers, their structure, and how students can effectively prepare for them.
Importance of 11th Entrance Exams
11th entrance exams serve as a gateway to elite schools and colleges that offer advanced curricula tailored to various streams like Science, Commerce, and Arts. These exams are designed to evaluate a student’s understanding of fundamental concepts, analytical abilities, and problem-solving skills. Performing well in these exams can open doors to exceptional educational opportunities and set the stage for future academic and professional success.
TYPES OF PAPER
11th entrance exam papers vary in structure and format depending on the institution and the stream of study. Here are the common types of papers students might encounter:
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs):
These papers consist of questions with multiple answer choices, typically four or five, where only one is correct.
MCQs test a wide range of knowledge and require quick thinking and precision.
Short Answer Questions:
These questions require brief, concise answers, usually a few sentences or a short paragraph.
They test a student’s understanding and ability to express key concepts clearly.
Long Answer Questions:
These questions require more detailed responses, often several paragraphs.
They assess a student’s depth of knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to articulate thoughts comprehensively.
Subjective/Descriptive Papers:
These papers include a mix of short and long answer questions.
They evaluate a student’s ability to provide in-depth explanations and insights into various topics.
Objective Papers:
Similar to MCQs, these papers may also include true/false questions, fill-in-the-blanks, and matching type questions.
They focus on factual knowledge and quick recall abilities.
Practical/Skill-Based Tests:
These are more common in streams like Science and Arts, where practical skills are essential.
They assess a student’s ability to perform experiments, draw, or execute technical tasks accurately.
Aptitude Tests:
These papers evaluate logical reasoning, quantitative ability, verbal ability, and sometimes general knowledge.
They are designed to test a student’s overall aptitude and readiness for higher-level academic challenges.
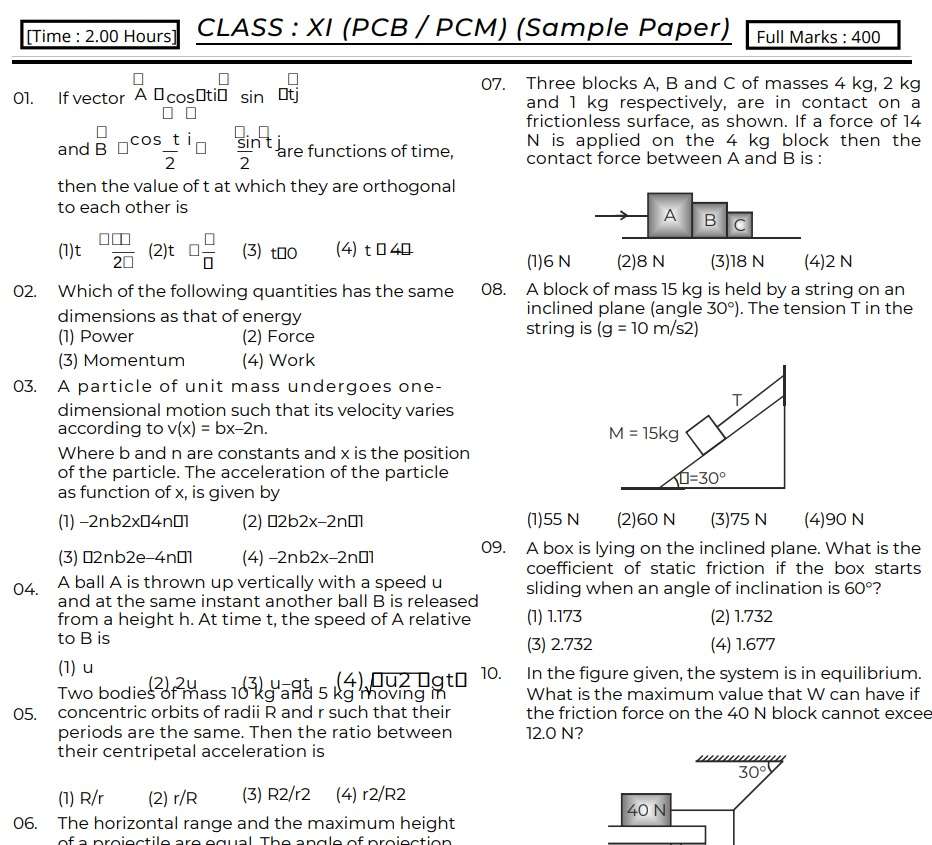
Download Paper
Download From Here
| YEAR | Links |
|---|---|
| Download Paper | Click Here |
Detail Structure of Paper
The structure of 11th entrance exam papers varies across institutions and streams but generally includes a combination of different question types to evaluate a range of skills and knowledge. Below is a detailed breakdown of the typical structure:
1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Format: Each question is followed by four or five options, with only one correct answer.
- Sections: Typically includes sections covering different subjects such as Mathematics, Science, English, etc.
- Scoring: Often includes negative marking for incorrect answers to discourage guessing.
2. Short Answer Questions
- Format: Requires brief responses, usually a few sentences or a short paragraph.
- Sections: Can cover a variety of topics within a subject, focusing on key concepts and definitions.
- Scoring: Points are awarded based on the accuracy and completeness of the answer.
3. Long Answer Questions
- Format: Requires detailed responses, often several paragraphs or a page.
- Sections: Typically included in subjects like English, Social Studies, and Science.
- Scoring: Evaluates depth of knowledge, clarity of explanation, and coherence of arguments.
4. Subjective/Descriptive Papers
- Format: Mix of short and long answer questions.
- Sections: Comprehensive coverage of a subject, testing both breadth and depth of understanding.
- Scoring: Based on content quality, logical flow, and ability to effectively communicate ideas.
5. Objective Papers
- Format: Includes MCQs, true/false questions, fill-in-the-blanks, and matching questions.
- Sections: Often organized by topic within a subject.
- Scoring: Focuses on factual recall and quick decision-making.
6. Practical/Skill-Based Tests
- Format: Hands-on tasks or practical problems to solve.
- Sections: Specific to the subject, such as laboratory experiments for Science or technical drawings for Arts.
- Scoring: Based on accuracy, methodology, and skill proficiency.
7. Aptitude Tests
- Format: Varied question types including MCQs, puzzles, and logical reasoning problems.
- Sections: Logical Reasoning, Quantitative Ability, Verbal Ability, and sometimes General Knowledge.
- Scoring: Evaluates overall aptitude and problem-solving skills.
Example Structure for a Science Stream Entrance Exam
Section A: Physics
- MCQs: 20 questions, 1 mark each.
- Short Answer Questions: 5 questions, 2 marks each.
- Long Answer Questions: 2 questions, 5 marks each.
Section B: Chemistry
- MCQs: 20 questions, 1 mark each.
- Short Answer Questions: 5 questions, 2 marks each.
- Long Answer Questions: 2 questions, 5 marks each.
Section C: Mathematics
- MCQs: 20 questions, 1 mark each.
- Short Answer Questions: 5 questions, 2 marks each.
- Long Answer Questions: 2 questions, 5 marks each.
Section D: English
- MCQs: 10 questions, 1 mark each.
- Short Answer Questions: 5 questions, 2 marks each.
- Long Answer Questions: 1 question, 5 marks.
Section E: Aptitude Test
- Logical Reasoning: 10 questions, 1 mark each.
- Quantitative Ability: 10 questions, 1 mark each.
- Verbal Ability: 10 questions, 1 mark each.
PREPARATION TIPS
Preparing for 11th entrance exams requires a strategic and disciplined approach. Here are some detailed tips to help students prepare effectively:
1. Understand the Syllabus and Exam Pattern
- Thorough Review: Obtain the detailed syllabus and exam pattern from the institution’s official website or other reliable sources.
- Breakdown: Divide the syllabus into manageable sections and create a study plan that covers all topics systematically.
2. Create a Study Schedule
- Daily Routine: Allocate specific time slots for each subject, ensuring a balanced approach.
- Prioritize: Focus more on subjects or topics that are challenging.
- Consistency: Stick to the schedule consistently to build a routine.
3. Use Quality Study Materials
- Textbooks: Rely on standard textbooks recommended by the institution.
- Guides and Reference Books: Use additional guides and reference books for deeper understanding and practice.
- Online Resources: Utilize educational websites, online courses, and video tutorials for varied learning methods.
4. Practice with Sample Papers and Previous Years’ Papers
- Regular Practice: Solve sample papers and previous years’ question papers regularly.
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Practice under timed conditions to get accustomed to the exam environment.
- Analyze Performance: Review your answers, identify mistakes, and learn from them.
5. Focus on Conceptual Understanding
- Clear Basics: Ensure a strong grasp of fundamental concepts before moving to advanced topics.
- Application: Practice applying concepts to different types of questions to enhance problem-solving skills.
6. Enhance Time Management Skills
- Timed Practice: Regularly practice completing sections within a set time to improve speed.
- Prioritize Questions: Learn to prioritize easier questions first to secure quick marks and then move to more challenging ones.
7. Take Regular Breaks and Stay Healthy
- Breaks: Take short, regular breaks during study sessions to avoid burnout.
- Physical Health: Maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and ensure adequate sleep.
8. Join Study Groups or Coaching Classes
- Group Study: Study with peers to exchange knowledge, solve doubts, and stay motivated.
- Coaching: Enroll in coaching classes if additional guidance is needed.
9. Utilize Technology Wisely
- Educational Apps: Use educational apps for interactive learning and quizzes.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums and discussion groups to clarify doubts and learn from others.
10. Stay Positive and Confident
- Positive Mindset: Maintain a positive attitude towards preparation and avoid stress.
- Self-Belief: Believe in your abilities and stay confident about your preparation.
Subject-Specific Tips
Mathematics
- Practice Daily: Solve mathematical problems every day to improve accuracy and speed.
- Formulas: Memorize important formulas and practice their applications.
Science (Physics, Chemistry, Biology)
- Conceptual Clarity: Focus on understanding concepts rather than rote learning.
- Diagrams and Experiments: Practice drawing diagrams and understand experiments thoroughly.
English
- Reading: Read books, newspapers, and articles to improve vocabulary and comprehension.
- Grammar: Practice grammar exercises and write essays to enhance language skills.
Aptitude Tests
- Logical Puzzles: Solve logical puzzles and reasoning questions regularly.
- Mock Tests: Take mock tests to gauge your aptitude skills and improve accordingly.
DIFFICULTY LEVEL
High-difficulty level (Level 3) questions are designed to challenge a student’s deep understanding, analytical skills, and problem-solving abilities. Here are some tailored preparation strategies for tackling these challenging questions:
1. Master the Fundamentals
- Deep Understanding: Ensure a thorough grasp of basic concepts, as Level 3 questions often build on foundational knowledge.
- Connections: Understand how different concepts interrelate and apply this knowledge to complex problems.
2. Practice Advanced Problems
- Challenging Questions: Regularly solve high-difficulty problems from advanced textbooks and specialized guides.
- Variety: Expose yourself to a wide variety of problems to build versatility in tackling different types of questions.
3. Develop Analytical Skills
- Critical Thinking: Engage in activities that enhance critical thinking, such as puzzles, logic games, and brainteasers.
- Reasoning: Practice logical reasoning and analytical questions to improve your ability to think through complex problems.
4. Focus on Application
- Real-World Problems: Practice applying concepts to real-world scenarios and problems.
- Case Studies: Analyze case studies and examples that require applying multiple concepts simultaneously.
5. Strengthen Problem-Solving Techniques
- Step-by-Step Approach: Break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps.
- Alternative Methods: Learn and practice different methods to solve the same problem, enhancing flexibility in thinking.
6. Time Management
- Timed Practice: Regularly practice solving high-difficulty questions within a set time to improve speed and efficiency.
- Prioritization: Learn to quickly assess and prioritize questions based on your strengths and the time required.
7. Review and Reflect
- Error Analysis: Review your solutions to high-difficulty problems and analyze any mistakes to understand where you went wrong.
- Feedback: Seek feedback from teachers or peers on your approach and solutions to complex problems.
8. Advanced Study Materials
- Reference Books: Use advanced-level reference books and materials that cater specifically to high-difficulty questions.
- Online Resources: Utilize online platforms and courses that offer advanced problem sets and detailed solutions.
Subject-Specific Tips for High-Difficulty Level Questions
Mathematics
- Higher-Order Problems: Practice problems from Olympiad books, advanced mathematical competitions, and higher-level textbooks.
- Theorems and Proofs: Study and understand advanced theorems, their proofs, and applications.
Physics
- Complex Scenarios: Solve problems involving multiple physical principles and complex scenarios.
- Derivations: Practice deriving formulas and understanding their applications in various contexts.
Chemistry
- In-Depth Reactions: Study complex chemical reactions, mechanisms, and their applications.
- Advanced Topics: Focus on advanced topics like organic synthesis, physical chemistry, and thermodynamics.
Biology
- Detailed Processes: Understand detailed biological processes at the molecular and cellular levels.
- Research Papers: Read and analyze research papers and advanced articles on various biological topics.
English
- Advanced Comprehension: Practice reading and analyzing advanced literary texts, including classic literature and scholarly articles.
- Essay Writing: Write essays on complex topics, focusing on coherence, argumentation, and depth of analysis.
CONCLUSION
Class 11th entrance exams play a pivotal role in shaping a student’s academic journey, serving as a gateway to prestigious institutions and specialized programs. The structure of these exams—comprising multiple-choice questions, short and long answer questions, objective tests, practical exams, and aptitude assessments—demands a well-rounded preparation strategy.
Understanding the detailed structure of the exam papers, mastering the fundamentals, and practicing with sample and previous years’ papers are essential for success. Focusing on conceptual clarity, enhancing problem-solving skills, and managing time effectively during preparation and the exam are crucial.
Preparation should also include the use of quality study materials, regular practice under timed conditions, and leveraging resources such as online courses, educational apps, and study groups. Maintaining a positive mindset, taking regular breaks, and staying healthy contribute significantly to sustained, effective study habits.
By adhering to these preparation strategies and tips, students can confidently approach their 11th entrance exams, perform to the best of their abilities, and secure their desired academic opportunities, setting a strong foundation for future success.
FAQ's
The exam usually includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs), short answer questions, long answer questions, objective tests, and sometimes practical or skill-based tests.
Practicing previous years’ papers is crucial as it helps you understand the exam pattern, identify important topics, and improve time management. It also gives you an idea of the difficulty level and types of questions asked.
Time management can be improved by practicing under timed conditions, prioritizing easier questions first, and allocating specific time slots for each section during the exam. Regular timed practice sessions can help build this skill.






