Winding types are fundamental components in the design and operation of electrical machines. These windings, typically made from conductive wire, play a crucial role in generating electromagnetic fields, which enable the functioning of machines such as transformers, motors, and generators. The most common winding types include lap winding and wave winding. Lap winding features a series of coils that overlap, creating a more distributed winding pattern, while wave winding involves coils arranged in a way that they form a wave-like pattern. Understanding these winding types is essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of electrical machines.
Lap Winding and Wave Winding serve different purposes based on their structural and operational characteristics. Lap winding is primarily used to provide better current distribution and mechanical strength, making it ideal for motors and generators with low voltage and high current demands. Wave winding, with its distinctive wave-like configuration, is chosen for applications requiring higher voltage and smoother performance.
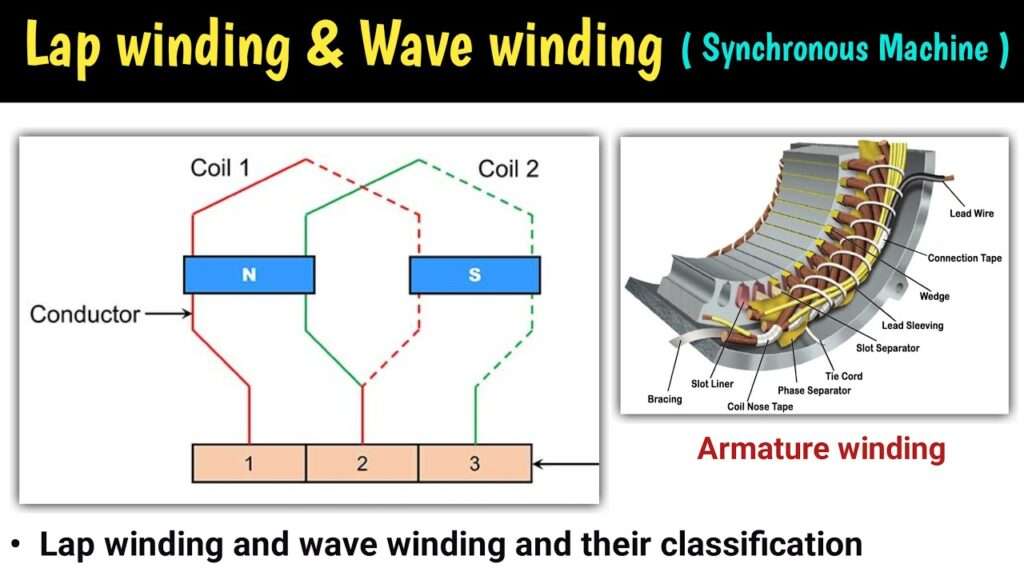
- Basics of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
- Lap Winding
- Wave Winding
- Comparative Analysis of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
- Lap Winding and Wave Winding Pattern and Insulation
- Manufacturing Techniques of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
- Troubleshooting Common Issues of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
- Practical Applications of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
Basics of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
Role in Electrical Machines
Windings play a vital position in electric machines via way of means of serving numerous key functions:
- Electromagnetic Induction: Windings are liable for producing the magnetic fields vital for electromagnetic induction. This precept is utilized in transformers to switch electric strength among circuits and in cars and turbines to transform strength forms.
- Voltage and Current Distribution: The layout and association of windings impact the distribution of voltage and present day in the course of the system. Proper winding layout guarantees most reliable overall performance and efficiency, minimizing losses and improving reliability.
- Mechanical Strength: Windings make a contribution to the structural integrity of the electric system. The bodily association and insulation of the windings make certain that the system can face up to operational stresses and thermal conditions.
Types of Windings
There Lap Winding and Wave Winding are numerous styles of windings utilized in electric machines, every with its personal precise traits and packages:
- Lap Winding: In lap winding, the coils overlap every other, growing a chain of overlapping coils. This form of winding is usually utilized in low-voltage, high-present day packages and presents higher mechanical electricity and present day distribution.
- Wave Winding: Wave winding includes arranging the coils in a wave-like pattern, which enables in attaining a smoother voltage distribution. It is usually utilized in high-voltage packages and presents a extra uniform electromagnetic field.
- Star (or Wye) Winding: In supermegacelebrity winding, the coils are related in a celebrity formation, with one cease of every coil related to a not unusualplace point (the neutral). This form of winding is utilized in three-section structures and is thought for its balanced voltage and present day distribution.
Lap Winding
Definition and Characteristics
Lap winding is a kind of armature winding utilized in electric machines, in which every coil overlaps with the adjoining coils. Key traits of lap winding include:
- Overlapping Coils: The coils in lap winding overlap every other, growing a layered structure.
- Parallel Paths: It presents a couple of parallel paths for the modern-day, which allows in dealing with excessive modern-day packages.
- High Current Handling: Due to the a couple of parallel paths, lap winding is specially powerful in coping with excessive currents and is generally utilized in low-voltage machines.
Construction and Design
The production of lap winding includes winding the coil activates the middle in one of these manner that every coil overlaps with the preceding one. The layout manner includes:
- Number of Coils: The range of coils and their association are decided primarily based totally at the device`s specs and operational requirements.
- Pole Pitch and Coil Span: The pole pitch (distance among poles) and coil span (duration of every coil) are crucial elements in designing lap winding.
- Insulation: Proper insulation is needed among the overlapping coils to save you electric quick circuits and make certain dependable operation.
- Design Example: In a lap-wound motor with a 4-pole configuration, if the device has 36 slots, every coil will span throughout a couple of slots to make certain that it overlaps with the adjoining coils.
Applications in Electrical Machines
Lap winding is broadly utilized in numerous electric machines because of its traits and benefits:
- DC Motors: Commonly utilized in DC motors, in particular for packages requiring excessive beginning torque and right modern-day dealing with capabilities.
- Generators: Employed in DC turbines in which excessive modern-day output is needed.
- Transformers: Used in transformers for low-voltage windings, in which excessive modern-day sporting ability is essential.
Wave Winding
Definition and Characteristics
Wave winding is a sort of armature winding utilized in electric machines, in which the coils are organized in a wave-like sample. Key traits of wave winding include:
- Wave-Like Pattern: Coils are organized in a sample that resembles a wave, with every coil spanning a couple of poles.
- High Voltage Capability: Designed to address excessive voltages efficaciously with the aid of using supplying a greater balanced voltage distribution.
- Reduced Harmonics: Wave winding has a tendency to lessen harmonic distortions withinside the generated voltage, main to smoother overall performance.
Construction and Design
The production of wave winding includes winding the coils in a sample that guarantees every coil overlaps with unique positions at the center to shape a wave-like structure. The layout procedure includes:
- Number of Coils: The overall wide variety of coils and their association rely on the device`s voltage and modern requirements.
- Pole Pitch and Coil Span: Unlike lap winding, wave winding usually spans multiple pole pitch, growing a wave-like structure. This allows in dispensing the voltage greater evenly.
- Insulation: Proper insulation is essential to save you electric brief circuits and make certain secure and dependable operation.
- Design Example: For a device with a 6-pole configuration and 36 slots, the wave winding would possibly contain spanning every coil throughout a couple of pole.
Applications in Electrical Machines
Wave winding is utilized in diverse electric machines in which excessive voltage and clean overall performance are required:
- AC Generators: Commonly utilized in AC mills in which a clean and solid voltage output is necessary.
- Transformers: Employed in transformers for excessive-voltage packages to acquire a uniform voltage distribution.
- High-Voltage Motors: Used in excessive-voltage automobiles in which a balanced voltage and decreased harmonic distortion are crucial for green operation.
Comparative Analysis of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
Design Differences
Lap Winding:
- Configuration: Coils in lap winding overlap every other. Each coil is wound in one of these manner that it overlaps with the adjoining coils, developing a chain of overlapping layers.
- Coil Arrangement: Typically includes fewer turns according to coil, main to a bigger wide variety of parallel paths for present day flow.
- Pole Pitch and Coil Span: The coil spans are normally identical to the pole pitch or a more than one of it, with overlapping coils offering mechanical strength.
Wave Winding:
- Configuration: Coils are organized in a wave-like sample, in which every coil spans more than one poles, developing a uniform and clean voltage distribution.
- Coil Arrangement: Generally includes extra turns according to coil and spans multiple pole pitch, ensuing in a wave-like sample that balances voltage throughout the armature.
- Pole Pitch and Coil Span: The coil span is generally a more than one of the pole pitch, with a focal point on dispensing voltage evenly.
Performance Comparison
Lap Winding:
- Current Handling: Excellent for excessive-present day programs because of more than one parallel paths for present day flow. This makes lap winding appropriate for low-voltage, excessive-present day programs.
- Voltage Distribution: Less powerful at dispensing voltage uniformly as compared to wave winding. This can result in much less clean overall performance and better harmonic distortion.
- Efficiency: Generally much less green in excessive-voltage programs however well-appropriate for programs requiring excessive beginning torque.
Wave Winding:
- Current Handling: Not as powerful in coping with excessive currents as compared to lap winding. because it offers fewer parallel paths for present day flow.
- Voltage Distribution: Provides a extra balanced and clean voltage distribution, main to decreased harmonic distortion and higher overall performance.
- Efficiency: More green in excessive-voltage programs because of higher voltage distribution and decreased harmonics.
Lap Winding and Wave Winding Pattern and Insulation
Importance of Proper Insulation
Proper insulation in electric Lap Winding and Wave Winding is vital for numerous reasons:
- Preventing Short Circuits: Insulation prevents electric brief circuits among the coils and among the coils and the middle. Without right insulation Lap Winding and Wave Winding, electric shorts can cause device failure and protection hazards.
- Enhancing Performance: Effective insulation allows keep the overall performance of electrical machines through making sure that the windings perform successfully with out electric leakage or lack of current.
Types of Insulation Materials
Various insulation substances Lap Winding and Wave Winding are utilized in electric windings, every with particular houses proper for specific applications:
- Paper Insulation: Often utilized in transformers and generators, paper insulation is blended with oil (as in oil-paper insulation) to offer each electric insulation and cooling.
- Varnish Insulation: Electrical varnishes are carried out to windings to offer insulation and protection. Common sorts encompass epoxy, polyester, and polyurethane varnishes.
Insulation Techniques for Lap and Wave Winding
Lap Winding:
- Insulation Between Coils: In lap winding, the insulation among overlapping coils is crucial to save you electric shorts. Typically, a aggregate of paper or varnish insulation is used among coils to make certain powerful separation.
- Slot Insulation: Insulation is likewise carried out to the slots wherein the coils are placed. This insulation protects in opposition to electric discharge and allows in retaining the integrity of the winding.
Wave Winding:
- Insulation Between Coils: Wave winding entails a greater complicated coil arrangement. Insulation among the coils need to be particular to make certain that every coil stays electrically isolated. Varnish or tooth coating is regularly used for this purpose.
- Slot and Core Insulation: Similar to lap winding, insulation is carried out to the slots and the middle to save you electric discharge and to defend the winding from mechanical damage.
Manufacturing Techniques of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
Tools and Equipment for Winding:
- Winding Machines: Automated or guide winding machines are used to wind coils onto the armature. These machines may be custom designed for Lap Winding and Wave Winding configurations.
- Insulation Dispensers: Devices that observe insulation substances, including varnish or enamel, to the coils throughout or after winding.
- Core Formers: Tools that form and aid the middle onto which the Lap Winding and Wave Winding is done.
- Slot Insulation Equipment: Tools used to use insulation substances within the slots of the middle.
- Varnishing Stations: Stations for dipping or spraying the windings with insulating varnish to offer extra protection.
Steps in Manufacturing Lap Winding
Core Preparation:
- Prepare the middle through slicing and shaping it to the specified dimensions. Ensure that the middle is easy and loose from contaminants.
Slot Insulation:
- Apply insulation fabric to the slots of the middle. This step prevents electric discharge and guarantees that the windings do now no longer come into direct touch with the middle.
Winding the Coils:
- Set up the winding device consistent with the lap winding configuration.
- Monitor the winding system to make sure even and correct winding.
Insulation Between Coils:
- Apply insulation fabric among the overlapping coils to save you electric shorts. Use paper or varnish insulation as required.
End-Winding Insulation:
- Insulate the ends of the coils in which they transition from the middle. Ensure right insulation to keep away from electric touch with different components.
Varnishing and Curing:
- Dip or spray the wound coils with insulating varnish. Cure the varnish consistent with the manufacturer`s specs to make sure right insulation.
Testing:
- Conduct electric exams to test for insulation resistance and make sure that the winding meets overall performance and protection standards.
Final Assembly:
- Assemble the armature with the wound coils into the very last device structure. Perform any extra assessments and modifications as needed.
Troubleshooting Common Issues of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
Common Problems in Lap Winding
Overlapping Coils:
- Problem: Coils might also additionally overlap incorrectly or excessively, inflicting quick circuits or mechanical pressure.
- Symptoms: Irregular winding sample, sudden electric behavior.
- Solution: Regularly take a look at the winding procedure and alignment. Adjust system settings to make certain correct coil placement.
Insulation Failure:
- Problem: Insulation among coils or slots might also additionally become worse or be improperly applied.
- Symptoms: Electrical shorts, decreased insulation resistance.
- Solution: Inspect insulation substances for best earlier than use. Ensure right software and curing of insulation substances.
Winding Irregularities:
- Problem: Inconsistent winding, together with choppy turns or gaps, can cause overall performance issues.
- Symptoms: Uneven voltage distribution, inefficient operation.
- Solution: Use calibrated winding machines and intently display the winding procedure to make certain uniformity.
Mechanical Stress:
- Problem: Mechanical pressure at the winding because of incorrect coping with or layout can reason harm.
- Symptoms: Physical harm to the coils, bizarre noise throughout operation.
- Solution: Implement right coping with techniques and take a look at for mechanical pressure factors throughout assembly.
Poor Varnishing:
- Problem: Inadequate varnish software or curing can cause bad insulation.
- Symptoms: Insulation breakdown, decreased overall performance.
- Solution: Ensure accurate varnish software strategies and curing times. Regularly check out varnishing best.
Common Problems in Wave Winding
Coil Span Issues:
- Problem: Coils might not span the proper range of pole pitches, main to choppy voltage distribution.
- Symptoms: Irregular voltage output, overall performance issues.
- Solution: Verify coil span calculations and system settings to make certain right coil arrangement.
Insulation Defects:
- Problem: Defects in insulation substances or software can reason electric shorts or decreased overall performance.
- Symptoms: Reduced insulation resistance, electric shorts.
- Solution: Inspect insulation substances and alertness processes. Use superb insulation and make certain right curing.
Practical Applications of Lap Winding and Wave Winding
Lap Winding in DC Machines
Overview:
- Lap Winding is typically utilized in DC machines because of its cappotential to address excessive currents and offer excessive beginning torque. This winding technique is specially powerful for programs wherein excessive cutting-edge and coffee voltage are required.
Applications:
- DC Motors: Used in programs inclusive of electric powered vehicles, commercial drives, and traction vehicles wherein excessive beginning torque and dependable overall performance are critical.
- Generators: Employed in low-voltage DC mills for battery charging, small electricity supplies, and coffee-electricity programs.
- Transformers: Lap winding is used withinside the low-voltage windings of transformers to address excessive cutting-edge tiers efficiently.
Advantages:
- High Current Handling: Provides more than one parallel paths for cutting-edge flow, making it appropriate for excessive-cutting-edge programs.
- High Starting Torque: Offers outstanding beginning torque because of its configuration, that is useful for programs requiring robust preliminary overall performance.
Example:
- Electric Vehicles: In electric powered vehicles, DC vehicles with lap winding are used to offer the important beginning torque and green electricity delivery.
Wave Winding in AC Machines
Overview:
- Wave Winding is regularly utilized in AC machines because of its cappotential to supply a easy and balanced voltage output. It is specifically powerful in programs wherein uniform voltage distribution and excessive-voltage operation are critical.
Applications:
- AC Generators: Used in AC mills for electricity generation, wherein easy and solid voltage output is vital for constant electricity supply.
- Transformers: Employed in excessive-voltage transformers wherein wave winding allows in lowering harmonic distortion and attaining uniform voltage distribution.
- High-Voltage Motors: Applied in excessive-voltage AC vehicles wherein balanced voltage and decreased electric noise are vital for green operation.
Advantages:
- Balanced Voltage Distribution: Provides a uniform and easy voltage output, that is critical for excessive-voltage programs.
- Reduced Harmonics: Minimizes harmonic distortion, ensuing in stepped forward performance and overall performance Lap Winding and Wave Winding.
Freqently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is lap winding?
Ans. Lap winding is a type of winding used in electrical machines where the coils overlap each other. It is typically used in DC machines and low-voltage transformers, providing high current handling and strong starting torque.
Q2: What is wave winding?
Ans.Wave winding is a winding method used in AC machines where the coils are arranged in a wave-like pattern. It is commonly used in high-voltage AC generators and transformers to achieve balanced voltage distribution and reduce harmonic distortion.
Q3:Where is lap winding commonly used?
Ans. Lap winding is commonly used in DC motors, low-voltage generators, and transformers where high current and starting torque are required.
Q4: Where is wave winding typically used?
Ans. Wave winding is used in high-voltage AC generators, transformers, and high-voltage motors where smooth voltage output and reduced harmonics are important.
Q5: What are the main advantages of lap winding?
Ans. Advantages of lap winding include high current handling capability, strong starting torque, and suitability for low-voltage applications.






