A Potentiometer Diagram is a kind of variable resistor utilized in electric circuits to modify and degree voltage levels. It includes a resistive detail with 3 terminals: constant terminals related to the ends of the resistive detail and a movable terminal, called the wiper, which slides alongside the resistive detail. By adjusting the location of the wiper, the resistance among the wiper and the constant terminals changes, taking into account particular manage of the voltage output or resistance withinside the circuit. Potentiometers are broadly utilized in numerous applications, from easy extent controls in audio gadget to state-of-the-art sensors in business systems.
Components of a Potentiometer
Wiper
The wiper is a movable touch withinside the potentiometer that slides over the resistive detail. It is generally related to a rotating or sliding mechanism, permitting it to alternate function alongside the resistive path. As the wiper movements, it alters the resistance among the wiper and the constant terminals, thereby adjusting the output voltage or resistance withinside the circuit. The wiper`s function determines the fraction of the overall resistive detail this is blanketed withinside the circuit, that’s critical for packages requiring variable resistance.
Resistive Element
The resistive detail is the center thing of a potentiometer that gives resistance to the electric modern-day. It is normally crafted from substances including carbon, steel film, or twine wound round an insulating center. The resistive detail`s duration and cloth homes decide the potentiometer`s overall resistance range. In a linear potentiometer, this detail is organized in a immediately line, whilst in a rotary potentiometer, it’s far wound right into a round sample. The high-satisfactory and cloth of the resistive detail have an effect on the potentiometer`s accuracy and durability.
Terminals
A potentiometer generally has 3 terminals:
Two Fixed Terminals: These terminals are related to the ends of the resistive detail. They offer the enter and output factors for the voltage or modern-day that flows thru the potentiometer.
One Adjustable Terminal (Wiper): This terminal is attached to the wiper, which movements alongside the resistive detail. It presents a variable connection point, permitting the adjustment of the resistance or voltage withinside the circuit.
Types of Potentiometers
Linear Potentiometers:
Description: In linear potentiometers, the resistive detail is organized in a immediately line. The resistance adjustments linearly with the wiper`s function.
Applications: Commonly utilized in extent controls and function sensing packages.
Rotary Potentiometers:
Description: In rotary potentiometers, the resistive detail is wound in a round sample across the center. The wiper rotates across the circle to regulate the resistance.
Applications: Frequently observed in audio system for extent and tone manage, in addition to in diverse digital gadgets requiring rotational adjustment.
Multi-Turn Potentiometers:
Description: These potentiometers have a screw-like mechanism that permits for more than one turns of the wiper over the resistive detail. This presents a finer diploma of resistance adjustment.
Applications: Used in precision packages in which satisfactory manage over resistance is required, including in calibration and adjustment circuits.
Digital Potentiometers:
Description: These are digital gadgets that mimic the feature of a conventional potentiometer the use of virtual signals. They may be managed via way of means of microcontrollers or virtual circuits.
Applications: Often utilized in virtual structures in which far flung or automatic adjustment of resistance is needed.
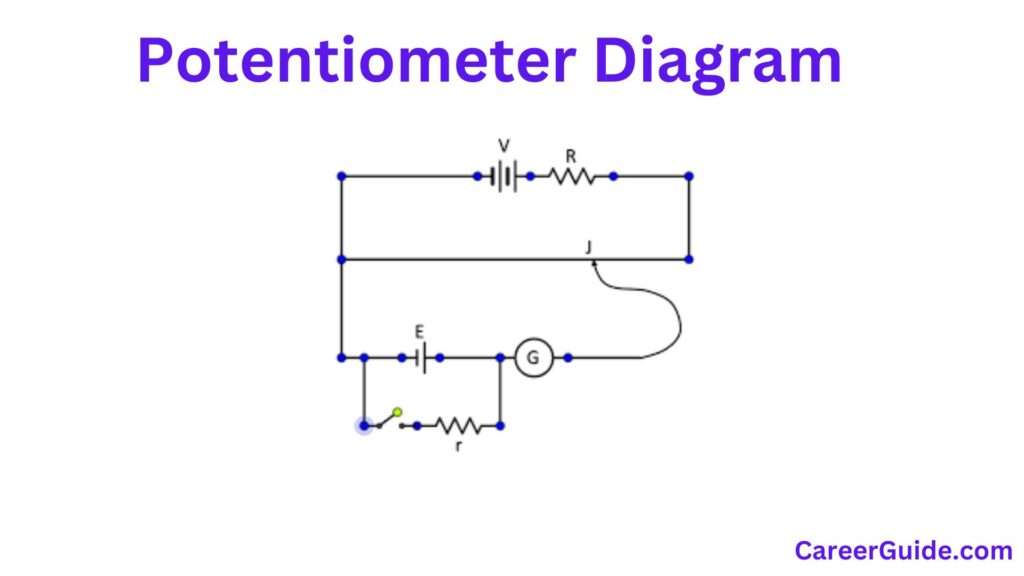
Basic Potentiometer Diagram
Diagram Overview
A primary potentiometer diagram illustrates the association of additives and their connections in a potentiometer circuit. This diagram normally consists of the resistive detail, the wiper, and the terminals. The resistive detail is depicted as a line or coil, with the wiper represented as a movable touch that slides or rotates alongside it. The constant terminals are proven at every stop of the resistive detail, whilst the wiper terminal is placed in between. This diagram facilitates in information how the potentiometer adjusts resistance or voltage via way of means of changing the wiper`s function.
Symbols Used in Potentiometer Diagrams
Resistive Element:
Symbol: A zigzag or line with a notation of resistance value.
Description: Represents the thing of the potentiometer wherein the resistance occurs. It`s normally proven as a horizontal line with a sequence of angled strains or a coil.
Wiper:
Symbol: A dashed or dotted line that intersects the resistive detail.
Description: Indicates the movable touch that adjusts the resistance via way of means of sliding or rotating alongside the resistive detail. The wiper`s function may be numerous to alternate the resistance withinside the circuit.
Fixed Terminals:
Symbol: Solid strains or small circles at every stop of the resistive detail.
Description: Represent the 2 stop terminals of the potentiometer wherein connections are made. They offer the constant factors for enter and output connections.
Adjustable Terminal (Wiper Terminal):
Symbol: A 0.33 line or terminal related to the wiper.
Description: Shows the relationship factor for the adjustable wiper. This terminal is used to faucet off the preferred voltage or resistance.
Circuit Connections
Basic Connection Setup:
Power Supply: The constant terminals are related to the energy supply, with one terminal normally related to the superb voltage and the alternative to the floor or bad voltage.
Output Voltage: The output voltage is taken from the wiper terminal. As the wiper movements alongside the resistive detail, the voltage on the wiper modifications in keeping with the function.
Voltage Divider Circuit:
Configuration: In a not unusualplace configuration, the potentiometer is used as a voltage divider. The enter voltage is carried out throughout the constant terminals, and the output voltage is taken from the wiper.
Working: The wiper divides the enter voltage proportionally, relying on its function alongside the resistive detail. This configuration is extensively utilized in adjustable quantity controls and different variable applications.
Types of Potentiometer Diagrams
Linear Potentiometer Diagram
Description:
In a linear potentiometer diagram, the resistive detail is organized in a instantly line. This form of diagram usually shows:
Resistive Element: Represented as a horizontal or vertical line with a zigzag sample indicating the resistance.
Wiper: Depicted as a movable touch that slides alongside the duration of the resistive detail. The wiper`s role adjustments the resistance among itself and the constant terminals.
Fixed Terminals: Shown at every give up of the resistive detail. These terminals are linked to the energy deliver or different circuit components.
Wiper Terminal: Located on the factor wherein the wiper makes touch with the resistive detail. This terminal gives the adjustable output.
Rotary Potentiometer Diagram
Description:
In a rotary potentiometer diagram, the resistive detail is wound right into a round or spiral shape. This diagram usually includes:
Resistive Element: Depicted as a round coil or arc, representing the non-stop resistive path.
Wiper: Shown as a touch that rotates across the round resistive detail. As the wiper movements, it adjustments the resistance among itself and the constant terminals.
Fixed Terminals: Located on the ends of the round resistive path, supplying connections for the energy deliver or circuit.
Wiper Terminal: Positioned wherein the rotating wiper makes touch with the resistive detail, making an allowance for adjustable resistance or voltage output.
Multi-flip Potentiometer Diagram
Description:
In a multi-flip potentiometer diagram, the resistive detail is wound in more than one turns round a principal core. The diagram usually features:
Resistive Element: Illustrated as a chain of concentric coils or more than one loops across the core. This layout permits for finer adjustment of resistance.
Wiper: Depicted as a touch that movements alongside the multi-flip resistive detail, typically via a screw-like mechanism, supplying exceptional control.
Fixed Terminals: Shown on the ends of the multi-flip resistive path, linked to the energy supply or circuit.
Wiper Terminal: Located wherein the wiper touches the resistive detail, supplying a variable output primarily based totally at the wiper`s role.
Understanding the Potentiometer Circuit
Series and Parallel Configurations
Series Configuration:
In a chain configuration, a potentiometer is hooked up consistent with different additives, developing a unmarried route for the cutting-edge to go with the drift.
Arrangement: The potentiometer and different additives are related stop-to-stop.
Effect on Resistance: The general resistance withinside the circuit is the sum of the resistances of all additives withinside the series. Adjusting the potentiometer modifications the entire resistance of the circuit.
Usage: This configuration is beneficial whilst you want to alternate the entire resistance of the circuit, which influences how lots cutting-edge flows thru it.
Parallel Configuration:
In a parallel configuration, the potentiometer is hooked up along different additives, permitting cutting-edge to go with the drift thru a couple of paths.
Arrangement: The potentiometer and different additives are related throughout the identical points, developing a couple of branches for cutting-edge to go with the drift thru.
Effect on Resistance: The general resistance of the circuit is decreased as compared to the resistance of the person additives. Adjusting the potentiometer influences the powerful resistance of the parallel network.
Usage: This configuration is used whilst you want to modify the general resistance visible through the circuit, which modifications how cutting-edge is sent a number of the branches.
Voltage Divider Concept
Description:
The voltage divider idea entails the use of a potentiometer to divide a deliver voltage right into a smaller, adjustable output voltage.
Configuration: The potentiometer is hooked up throughout a voltage source, with one stop related to the effective deliver and the opposite stop related to the ground. The output voltage is taken from the wiper (the adjustable contact).
Voltage Adjustment: By transferring the wiper, you exchange the percentage of the entire resistance this is withinside the route of the output voltage. This permits you to modify the output voltage to a preferred stage primarily based totally at the wiper`s position.
Usage: Voltage dividers are used to create variable voltage stages, which may be used for diverse programs along with adjusting sign stages or placing reference voltages in circuits.
Current and Resistance Relationships
Current-Resistance Relationship:
The courting among cutting-edge and resistance in a potentiometer circuit is decided through how converting the resistance influences the go with the drift of cutting-edge.
Adjusting Resistance: As you modify the potentiometer, you exchange its resistance. This, in turn, influences how lots cutting-edge flows thru the circuit for a given voltage.
Impact on Current: Increasing the resistance (through turning the potentiometer) reduces the quantity of cutting-edge flowing thru the circuit, even as reducing the resistance will increase the cutting-edge go with the drift.
Usage: Understanding this courting is crucial for designing circuits in which particular manipulate over cutting-edge is required. It allows in programs like placing the extent of indicators or controlling the brightness of lights.
How to Read a Potentiometer Diagram
Identifying Key Components
Potentiometer Symbol:
Representation: In a circuit diagram, a potentiometer is normally proven as a image with a triangle pointing toward a line, representing the resistive element. An arrow throughout this line represents the wiper, indicating its adjustable nature.
Labels: The potentiometer has 3 key terminals:
Two Fixed Terminals: Located at both give up of the resistive element, those join the potentiometer to the relaxation of the circuit.
Wiper Terminal: This is the movable contact, adjusting the resistance withinside the circuit.
Wiper:
Function: The wiper slides or rotates alongside the resistive element, making an allowance for adjustments in resistance among the wiper and the constant terminals.
Resistive Element:
Representation: This is the a part of the potentiometer that gives resistance. It may be depicted as a zigzag line or a sequence of parallel strains withinside the diagram.
Fixed Terminals:
Function: These terminals are the factors in which the potentiometer connects to the circuit, supplying a route for the electric modern-day.
Reading the Circuit Connections
Identify Connections:
Power Supply: Check in which the potentiometer connects to the circuit`s strength source. One constant terminal typically connects to the advantageous voltage, and the alternative to the floor or bad voltage.
Load: Determine in which the wiper terminal connects. This is frequently in which the output voltage is taken or in which the potentiometer serves as part of a voltage divider.
Follow the Path:
Circuit Pathways: Trace the connections from the potentiometer`s terminals to different additives. This allows in know-how the position of the potentiometer withinside the circuit.
Adjustable Output: Identify in which the adjustable wiper terminal connects, as this suggests the factor of manage for adjusting the circuit`s output.
Terminal Configuration:
Series vs. Parallel: Recognize whether or not the potentiometer is configured in collection or parallel with different additives, as this affects how changes have an effect on the general circuit.
Analyzing Circuit Behavior
Impact of Adjusting the Potentiometer:
Resistance Changes: Adjusting the wiper alters the resistance among the wiper and the constant terminals, impacting the circuit`s voltage and modern-day.
Voltage Divider: In voltage divider applications, converting the wiper role adjustments the ratio of the resistances, changing the output voltage accordingly.
Effects on Current and Voltage:
Current Flow: In a sequence configuration, the potentiometer`s resistance extrade influences the whole resistance and accordingly the modern-day via the circuit.
Voltage Levels: In a voltage divider setup, adjusting the potentiometer alters the output voltage, influencing the additives related to the output.
Practical Implications:
Calibration: Potentiometers are frequently used for fine-tuning and calibration. Understanding the diagram allows in placing unique values.
Troubleshooting: Recognizing how the potentiometer changes have an effect on circuit conduct aids in diagnosing troubles and optimizing performance.
Potentiometer Testing and Calibration
Testing with a Multimeter
Checking Continuity:
Setup: Use the multimeter`s continuity mode or resistance size mode.
Procedure: Place the probes on the 2 constant terminals of the potentiometer.
Expected Result: The multimeter must display the overall resistance, indicating continuity. No continuity or wrong readings advocate a capacity fault.
Measuring Resistance:
Setup: Set the multimeter to degree resistance.
Procedure:
Total Resistance: Measure among the constant terminals.
Variable Resistance: Measure among the wiper and one constant terminal, adjusting the wiper to study resistance adjustments.
Expected Result: The resistance must range smoothly, from near-0 ohms to the most value. Irregularities may also suggest put on or damage.
Testing for Dead Spots:
Setup: Use the multimeter in resistance mode.
Procedure: Sweep the wiper throughout its complete variety whilst tracking resistance.
Expected Result: The resistance must extrade smoothly. Sudden adjustments or inconsistencies advocate useless spots or put on.
Calibration Techniques
Setting the Desired Resistance:
Procedure:
Initial Adjustment: Adjust the potentiometer to the favored resistance the usage of the multimeter.
Fine-Tuning: Make finer modifications as necessary.
Application: This is critical for attaining precise resistance values in diverse digital packages.
Voltage Divider Calibration:
Procedure:
Initial Setup: Connect the potentiometer in a voltage divider configuration with a recognised enter voltage.
Adjusting Output: Adjust the wiper to acquire the favored output voltage.
Verification: Use a multimeter to test the output voltage.
Application: This is used to set precise voltage ranges in circuits, including for sensor calibration.
Calibrating for Linear or Logarithmic Response:
Procedure: Ensure the potentiometer offers the favored reaction type.
Verification: Check the output at diverse factors to verify steady adjustments in resistance or voltage.
Application: Important for packages like audio controls in which a selected reaction curve is needed.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Inconsistent Resistance Readings:
Symptoms: Resistance readings are erratic or bounce unexpectedly.
Possible Causes: Dirt or oxidation, tired tracks, or mechanical issues.
Solutions: Clean the potentiometer, check out for damage, or update it if needed.
No Continuity or Open Circuit:
Symptoms: No continuity detected among terminals.
Possible Causes: Broken connections or inner damage.
Solutions: Inspect for damage, make certain right connections, or update the potentiometer.
Dead Spots or Unresponsive Areas:
Symptoms: No extrade in resistance over positive components of the variety.
Possible Causes: Worn resistive detail or terrible wiper touch.
Solutions: Clean the potentiometer or update it if necessary.
Noise or Scratchiness:
Symptoms: Audible noise or inconsistent alerts at some stage in adjustment.
Possible Causes: Dirt or oxidation inflicting terrible touch.
Solutions: Clean with touch purifier or update the potentiometer.
Applications of Potentiometer Diagrams
In Audio Equipment
Volume Control:
Function: Potentiometers are normally used as quantity controls in audio equipment. By adjusting the resistance, customers can growth or lower the quantity output from audio system or headphones.
Diagram Insight: In audio circuits, potentiometer diagrams illustrate how the element is hooked up to the audio sign path. The wiper role adjusts the sign level, bearing in mind clean quantity modifications.
Tone Control:
Function: Potentiometers also are utilized in tone manage circuits to modify the stability of excessive and coffee frequencies. This permits customers to alter the sound best to their preference.
Diagram Insight: The diagram indicates how potentiometers are incorporated with capacitors and resistors to create tone manage networks. Adjusting the potentiometer modifications the cutoff frequencies, changing the audio tone.
Balancing Audio Channels:
Function: In stereo systems, potentiometers may be used to stability the audio output among the left and proper channels.
Diagram Insight: Potentiometer diagrams in those setups show how the element adjusts the relative stages of the 2 channels, making sure balanced sound distribution.
In Measurement Devices
Voltage Dividers:
Function: Potentiometers are regularly utilized in voltage divider circuits to degree distinct voltage stages inside a circuit.
Diagram Insight: The diagram indicates the potentiometer`s placement and the way it divides the enter voltage right into a variable output. This setup is beneficial in calibrating gadgets or sensors.
Calibration Tools:
Function: Measurement gadgets use potentiometers for calibration purposes, permitting specific changes of tool readings.
Diagram Insight: Diagrams illustrate how potentiometers are related to important components, allowing fine-tuning of measurements consisting of resistance, voltage, or current.
Sensor Signal Conditioning:
Function: Potentiometers may be used to modify the sensitivity or variety of sensors in size systems.
Diagram Insight: Potentiometer diagrams in those programs display how the element modifies sensor output, allowing correct and adjustable readings primarily based totally at the particular requirements.
In Control Systems
Adjustable Controls:
Function: Potentiometers offer adjustable controls in diverse systems, consisting of placing stages in mild dimmers or controlling motor speeds.
Diagram Insight: The diagrams depict how potentiometers are used to modify the output of manage systems, consisting of various the brightness of lighting or the velocity of motors.
Feedback Systems:
Function: In comments systems, potentiometers may be used to set reference stages or thresholds.
Diagram Insight: The diagrams illustrate how potentiometers are incorporated into manage loops, in which they assist preserve favored gadget situations with the aid of using presenting a reference voltage or placing.
Common Problems and Solutions
Inaccurate Readings
Problem: Inaccurate or erratic resistance readings can arise, inflicting flawed operation in circuits wherein specific manipulate is necessary.
Causes:
Dirt and Dust: Accumulation of dirt, dirt, or particles at the resistive detail can intrude with the wiper`s touch.
Worn Resistive Element: Over time, the resistive tune can put on out, main to inconsistencies in resistance.
Oxidation: Oxidation of the wiper or the resistive detail can bring about negative electric touch.
Solutions:
Cleaning: Clean the potentiometer the use of touch cleanser or compressed air to eliminate dirt and particles. Gently flip the wiper to make sure the cleanser reaches all components of the resistive tune.
Inspection: Visually look at the potentiometer for symptoms and symptoms of wear and tear or harm. If the resistive detail is visibly worn or broken, substitute can be necessary.
Oxidation Removal: If oxidation is present, use a specialised touch cleanser designed to eliminate oxidation from digital components.
Mechanical Failures
Problem: Mechanical screw ups can save you the potentiometer from functioning correctly, along with the wiper now no longer shifting easily or turning into stuck.
Causes:
Physical Damage: Damage to the potentiometer`s body, along with bending or cracking, can restrict the wiper`s movement.
Wiper Misalignment: The wiper might also additionally turn out to be misaligned because of mechanical shocks or put on, stopping it from making right touch with the resistive detail.
Stiffness: Lack of lubrication or inner put on can motive the wiper to turn out to be stiff or stuck.
Solutions:
Physical Inspection: Check for seen bodily harm. If the potentiometer is broken, it is able to want to be replaced.
Wiper Adjustment: If the wiper is misaligned, lightly realign it if possible. However, if the potentiometer is sealed or complex, substitute is probably the more secure option.
Lubrication: Apply a small quantity of digital-grade lubricant to the shifting components to ease stiffness. Be cautious now no longer to apply too much, as extra lubricant can motive different issues.
Electrical Failures
Problem: Electrical screw ups, along with no continuity or sudden resistance
values, can motive the circuit to malfunction or the potentiometer to forestall operating altogether.
Causes:
Open Circuit: An open circuit in the potentiometer, probable because of a damaged resistive detail or disconnected terminals.
Intermittent Connections: Poor inner connections can motive the potentiometer to paintings sporadically.
Short Circuit: A quick circuit might also additionally arise if the resistive detail will become broken or if there’s a overseas item within the potentiometer.
Solutions:
Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check for continuity throughout the terminals. Lack of continuity suggests an inner break, necessitating substitute.
Inspect and Reconnect: Check the terminal connections and make sure they’re secure. Tighten any unfastened connections and, if needed, re-solder any negative solder joints.
Replace Damaged Potentiometers: If inner harm is detected or if the potentiometer indicates symptoms and symptoms of quick circuits or open circuits, update the component.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a potentiometer?
A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with an adjustable center terminal (wiper) that allows it to function as a variable resistor or voltage divider. It’s commonly used for adjusting levels, such as volume or brightness, in electronic devices.
2. How does a potentiometer work?
A potentiometer works by varying the position of a wiper across a resistive element, changing the resistance between the wiper and the fixed terminals. This adjustment controls the current or voltage in a circuit, allowing for fine-tuning.
3. How can I clean a dirty potentiometer?
Use a contact cleaner spray specifically designed for electronics. Apply the cleaner while rotating the wiper to remove dirt and oxidation. Ensure the potentiometer is dry before use.
4. Can a potentiometer be used as a variable resistor?
Yes, by using only two terminals (one fixed terminal and the wiper), a potentiometer can function as a variable resistor. This setup varies the resistance in a circuit by changing the wiper position.
5. What is a digital potentiometer?
A digital potentiometer, or digipot, is an electronic device that simulates the functions of a traditional potentiometer. It’s controlled digitally through a microcontroller or computer interface, offering precise adjustments without physical movement.






