A single point cutting tool is a essential tool withinside the machining process, in most cases used to form and end substances with precision. Unlike multi-factor gear, that have numerous reducing edges, a unmarried factor reducing device capabilities simply one most important reducing edge, which makes it best for operations consisting of turning, boring, and shaping. These gear are vital in diverse industries, which include automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, because of their cappotential to supply remarkable finishes and complicated shapes. By expertise the design, substances, and packages of single point cutting tool, specialists can optimize machining processes, decorate device life, and reap advanced consequences of their operations.
- Components of a Single Point Cutting Tool
- Types of Single Point Cutting Tools
- Materials Used for Single Point Cutting Tools
- Tool Geometry and Angles
- Tool Wear and Its Types
- Factors Affecting of Single Point Cutting Tools
- Tool Coatings of Single Point Cutting Tools
- Cutting Fluids and Their Role of Single Point Cutting Tools
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
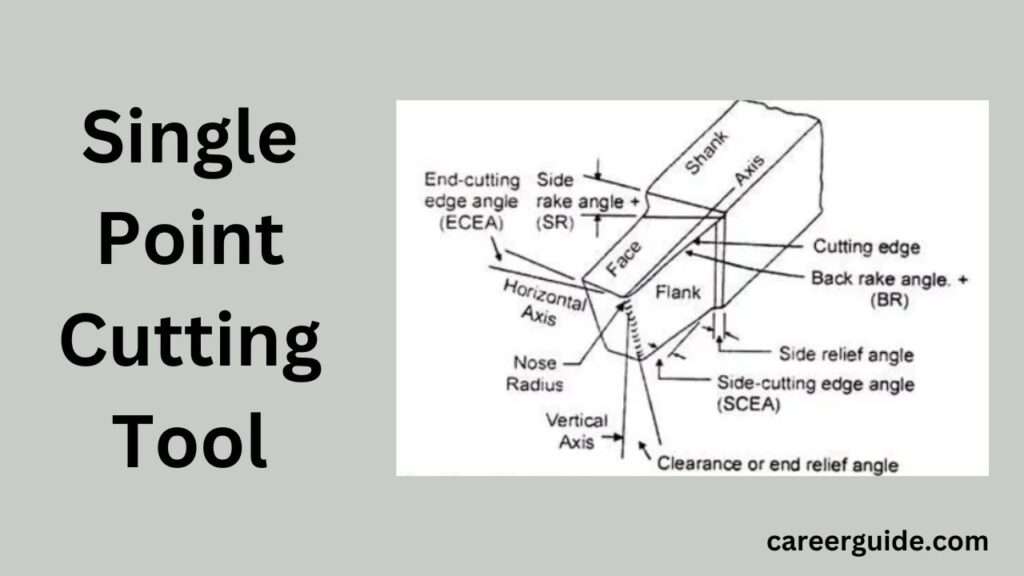
Components of a Single Point Cutting Tool
Tool Shank
Function: The tool shank is the part of the cutting tool this is clamped or secured withinside the device holder or gadget. It gives the vital guide and balance throughout the slicing process.
Design Variations: Tool shanks are available in numerous shapes and sizes, which includes cylindrical, square, or rectangular, relying at the gadget device and alertness requirements.
Tool Face
Function: The device face is the floor of the slicing device that without delay engages with the workpiece to eliminate material. It performs a vital position in chip formation and removal.
Surface Finish: The fine and end of the device face can effect the floor end of the machined element and the general performance of the slicing process.
Tool Flank
Function: The device flank is the floor adjoining to the slicing side that offers clearance among the device and the workpiece. This clearance prevents rubbing and allows in green chip removal.
Angle Considerations: The attitude of the flank, called the clearance attitude, is crucial for minimizing friction and put on throughout machining.
Tool Nose
Function: The device nostril is the pointed stop of the slicing device in which the slicing movement takes place. It determines the form and end of the workpiece.
Nose Radius: The radius of the device nostril impacts the floor end and the slicing forces. A large nostril radius normally improves the floor end and device life.
Tool Base
Function: The device base is the a part of the slicing device that offers a basis for the slicing side and helps the general shape of the device.
Stability: The base guarantees that the device stays securely hooked up withinside the device holder, that’s crucial for preserving precision and balance throughout machining operations.
Types of Single Point Cutting Tools
Turning Tools
Purpose: Turning tools are used to system the outside surfaces of a rotating workpiece, ordinarily in a lathe. They are designed to provide cylindrical shapes and numerous outside contours.
Design Features: These equipment usually have a pointy reducing part with a particular geometry, along with rake and clearance angles, to correctly reduce the fabric and gain preferred floor finishes.
Applications: Commonly utilized in operations which include facing, turning, and profiling, turning equipment are flexible and crucial in production elements like shafts, pins, and different cylindrical additives.
Boring Tools
Purpose: Boring equipment are hired to amplify or end inner holes in a workpiece. They are used after drilling to gain particular dimensions and clean finishes at the internal surfaces.
Design Features: These equipment have a unmarried reducing part that may be adjusted to govern the scale of the hole. They frequently characteristic a long, narrow shank to attain deep into the workpiece.
Applications: Boring equipment are utilized in numerous applications, along with the machining of engine cylinders, bearings, and housings wherein excessive precision and floor end are required.
Grooving Tools
Purpose: Grooving equipment are designed to reduce slender grooves or channels right into a workpiece. They are used to create capabilities which include slots, recesses, or keyways.
Design Features: These equipment have a slender, immediately reducing part that lets in for particular reducing of grooves. The device geometry consists of unique angles to make certain easy and correct cuts.
Applications: Grooving equipment are utilized in production additives that require groove capabilities, which include gears, splines, and elements with locking grooves.
Parting Tools
Purpose: Parting equipment are used to reduce off or separate sections of a workpiece from the principle fabric. They are frequently hired to reduce completed elements from a bigger piece.
Design Features: These equipment have a thin, flat reducing part designed to slice thru the fabric with minimum force. They are frequently used with a excessive feed price to correctly reduce thru fabric.
Applications: Parting equipment are normally utilized in turning operations on a lathe to split completed additives, which include shafts and rings, from the workpiece. They also are utilized in developing particular cuts in metalworking and machining tasks.
Materials Used for Single Point Cutting Tools
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
Properties: High-Speed Steel is thought for its sturdiness and cappotential to preserve hardness at excessive temperatures. It is able to withstanding the acute warmth generated throughout slicing operations.
Applications: HSS is normally used for general-cause slicing gear, which includes drills, taps, and turning gear, making it flexible for diverse machining tasks.
Advantages: HSS gear are distinctly clean to sharpen, cost-effective, and offer a very good stability among hardness and sturdiness, appropriate for a huge variety of materials.
Carbides
Properties: Carbide slicing gear, commonly crafted from Tungsten Carbide, provide excessive hardness and put on resistance. They are able to retaining their slicing area at excessive temperatures and below heavy slicing conditions.
Applications: Carbide gear are used for excessive-pace and precision machining of difficult materials, which includes metals, alloys, and composites. They are best for turning, milling, and drilling applications.
Advantages: Carbide gear have an extended device lifestyles in comparison to HSS, decreased slicing forces, and offer advanced overall performance in tough machining environments.
Ceramics
Properties: Ceramic slicing gear are crafted from superior ceramic materials, including Aluminum Oxide or Silicon Nitride, which provide excessive hardness, chemical stability, and put on resistance.
Applications: Ceramics are used for machining difficult and brittle materials, which includes excessive-temperature alloys and superalloys, in addition to for excessive-pace slicing operations.
Advantages: Ceramic gear can perform at better speeds and temperatures than carbide or HSS gear, imparting awesome overall performance and floor end in particular applications.
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
Properties: CBN is one of the toughest recognised materials, 2d simplest to diamond, and is used for slicing difficult and excessive-energy materials. It keeps its slicing area below excessive conditions.
Applications: CBN gear are best for machining hardened steels, forged iron, and superalloys, wherein they offer advanced put on resistance and device lifestyles.
Advantages: CBN gear provide excellent hardness, durability, and warmth resistance, making them appropriate for excessive-precision and excessive-manufacturing machining tasks.
Diamond
Properties: Diamond slicing gear are crafted from artificial diamonds, which give the best hardness and put on resistance available. They are used for precision slicing of very difficult materials.
Applications: Diamond gear are used for machining abrasive materials, including glass, ceramics, and positive metals, wherein they provide unequalled slicing overall performance and floor end.
Advantages: Diamond gear offer the longest device lifestyles, excellent slicing overall performance, and the pleasant floor pleasant for ultra-difficult materials, despite the fact that they’re commonly greater high-priced than different materials.
Tool Geometry and Angles
Rake Angle
Definition: The rake attitude is the attitude among the slicing area and a aircraft perpendicular to the slicing floor. It affects how the slicing area engages with the workpiece.
Impact on Cutting: A wonderful rake attitude reduces slicing forces and improves floor end, at the same time as a bad rake attitude will increase device electricity however calls for better slicing forces. The desire of rake attitude relies upon at the fabric being machined and the preferred reduce quality.
Clearance Angle
Definition: The clearance attitude is the attitude among the device flank and the floor of the workpiece. It offers essential area to save you the slicing device from rubbing towards the workpiece.
Impact on Tool Life: Adequate clearance reduces friction and heat, thereby minimizing device put on and enhancing device lifestyles. It is critical for accomplishing correct cuts and stopping device damage.
Cutting Edge Angle
Definition: The slicing area attitude is the attitude fashioned among the slicing area and the floor of the workpiece. It affects the slicing forces and the performance of fabric removal.
Impact on Cutting Performance: A smaller slicing area attitude can decorate the sharpness and precision of the reduce, at the same time as a bigger attitude offers higher device electricity and stability. The greatest attitude relies upon at the slicing situations and fabric characteristics.
Nose Radius
Definition: The nostril radius is the rounded area on the tip of the slicing device. It performs a important function withinside the geometry of the slicing device and impacts the completed floor of the workpiece.
Impact on Machining: A large nostril radius improves floor end and device lifestyles via way of means of dispensing slicing forces greater evenly. It additionally reduces the prevalence of device marks and extends the device`s durability. However, it is able to additionally growth slicing forces and decrease precision for best or designated work.
Tool Wear and Its Types
Crater Wear
Definition: Crater put on refers back to the formation of a hole or crater-like melancholy at the device face because of the excessive temperatures and friction generated in the course of slicing.
Causes and Effects: This sort of put on is in general because of the abrasive movement of the chips and the warmth generated in the course of slicing. It can cause decreased slicing performance and device life, because the crater will increase the touch vicinity among the device and the workpiece, main to in addition put on.
Flank Wear
Definition: Flank put on happens at the device flank, that’s the floor of the slicing device adjoining to the workpiece. It effects from non-stop rubbing among the device flank and the workpiece cloth.
Causes and Effects: This sort of put on is because of abrasive movement and friction from the workpiece cloth. It results in a sluggish discount withinside the device`s slicing cappotential and floor end excellent. Increased flank put on can bring about dimensional inaccuracies and bad floor finishes at the workpiece.
Notch Wear
Definition: Notch put on develops as a localized put on sample on the intensity of cut, developing a notch or groove at the slicing device’s side.
Causes and Effects: It is frequently because of the cyclic strain and effect forces exerted in the course of the slicing process, in particular while machining difficult substances or interrupted cuts. Notch put on can cause decreased device power and accuracy, affecting the excellent of the machined floor and device life.
Built-Up Edge (BUE)
Definition: Built-Up Edge (BUE) happens while cloth from the workpiece adheres to the slicing fringe of the device, forming a layer of labor cloth at the device floor.
Causes and Effects: BUE is commonly because of excessive slicing temperatures and chemical reactions among the device and the workpiece cloth. It can cause bad floor end, accelerated slicing forces, and untimely device put on, because the built-up side disrupts the slicing movement and impacts device performance.
Factors Affecting of Single Point Cutting Tools
Cutting Speed
Definition: Cutting pace refers back to the fee at which the slicing fringe of the device passes via the fabric being machined. It is commonly measured in meters consistent with minute (m/min) or ft consistent with minute (ft/min).
Impact on Tool Life: Higher slicing speeds typically cause multiplied temperatures on the slicing side, that could boost up device put on because of thermal strain and abrasion. However, immoderate slicing pace also can motive untimely device failure. Optimal slicing speeds stability green fabric elimination with device longevity.
Feed Rate
Definition: Feed fee is the space the slicing device advances into the workpiece consistent with revolution of the workpiece or consistent with byskip of the device. It is generally measured in millimeters consistent with minute (mm/min) or inches consistent with minute (in/min).
Impact on Tool Life: Higher feed quotes boom the burden at the slicing side and may motive speedy put on or maybe device breakage. Conversely, a completely low feed fee can cause inefficient slicing and overheating. Maintaining the correct feed fee enables make sure powerful slicing even as prolonging device existence.
Depth of Cut
Definition: Depth of reduce is the thickness of fabric eliminated in a unmarried byskip of the slicing device. It is measured perpendicular to the slicing surface.
Impact on Tool Life: A large intensity of reduce will increase the slicing forces and temperature, that could boost up device put on. On the alternative hand, a smaller intensity of reduce reduces slicing forces however can also additionally require a couple of passes, probably affecting productivity. Optimizing the intensity of reduce is essential for balancing device existence and machining efficiency.
Work Material
Definition: Work fabric refers back to the sort of fabric being machined, consisting of metals, alloys, ceramics, or composites.
Impact on Tool Life: Different substances have various hardness, abrasiveness, and thermal properties, all of which have an effect on device put on. Harder substances typically motive greater speedy device put on because of multiplied friction and abrasion, even as softer substances can also additionally bring about quicker device deterioration because of better slicing forces and deformation.
Tool Material
Definition: Tool fabric is the fabric from which the slicing device is made, consisting of High-Speed Steel (HSS), carbide, ceramics, Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN), or diamond.
Impact on Tool Life: The hardness, toughness, and thermal resistance of the device fabric appreciably have an effect on its overall performance and longevity. Tool substances with better hardness and put on resistance, like carbide or CBN, typically provide longer device existence and higher overall performance below harsh slicing conditions.
Tool Coatings of Single Point Cutting Tools
Titanium Nitride (TiN)
Properties: Titanium Nitride is a tough, metal ceramic coating recognized for its gold-coloured appearance. It complements the floor hardness and put on resistance of slicing equipment.
Benefits: TiN coatings lessen friction among the device and the workpiece, which allows in extending device lifestyles and enhancing slicing overall performance. It additionally affords true oxidation resistance and allows in retaining sharpness over extended usage.
Applications: Commonly used on drills, stop mills, and turning equipment, TiN is appropriate for standard machining applications, especially wherein excessive put on resistance is needed.
Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN)
Properties: Titanium Carbonitride is a ceramic coating that mixes titanium nitride with carbon. It is more difficult than TiN and gives higher put on resistance and advanced slicing overall performance.
Benefits: TiCN coatings offer decreased friction, better hardness, and higher resistance to abrasion and chipping. They are especially powerful in machining tough and abrasive substances.
Applications: TiCN is used on equipment that require excessive slicing speeds and toughness, along with inserts and stop mills, making it appropriate for a extensive variety of machining tasks.
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
Properties: Aluminum Oxide, additionally referred to as alumina, is a ceramic coating that gives top notch hardness and put on resistance. It is commonly implemented the use of strategies along with bodily vapor deposition (PVD).
Benefits: Al2O3 coatings offer excessive resistance to oxidation and thermal put on, making them appropriate for excessive-temperature slicing applications. They additionally enhance the device`s slicing overall performance and longevity.
Applications: Al2O3 coatings are used on equipment that function below excessive temperatures and stresses, along with the ones in aerospace and automobile industries. They are powerful for machining hardened substances and enhancing device lifestyles.
Diamond Coatings
Properties: Diamond coatings are the toughest recognized coatings and are implemented to equipment the use of strategies like chemical vapor deposition (CVD). They provide unequalled hardness and put on resistance.
Benefits: Diamond coatings notably beautify the slicing device’s overall performance via way of means of imparting incredible hardness, thermal conductivity, and abrasion resistance. They are best for machining extraordinarily tough or abrasive substances.
Applications: Diamond coatings are used on equipment for precision machining of substances along with ceramics, glass, and composites, wherein advanced slicing overall performance and floor end are required.
Cutting Fluids and Their Role of Single Point Cutting Tools
Types of Cutting Fluids
Coolants: These fluids in the main lessen the temperature generated all through machining via way of means of soaking up and dissipating warmness. Examples encompass water-primarily based totally answers and oil-water emulsions.
Lubricants: Lubricants lessen friction among the slicing device and the workpiece, which facilitates in extending device lifestyles and enhancing floor end. Common examples encompass neat oils and artificial oils.
Combination Fluids: These are blends of coolants and lubricants designed to offer each cooling and lubrication effects. They are formulated to fit diverse machining situations and materials.
Benefits of Using Cutting Fluids
Heat Dissipation: Cutting fluids assist in casting off warmness from the slicing area, which prevents overheating of the device and workpiece, thereby lowering device put on and enhancing performance.
Friction Reduction: They limit friction among the slicing device and the workpiece, which lowers slicing forces and complements the floor end of the machined part.
Chip Removal: Cutting fluids help in flushing away chips and particles from the slicing zone, which facilitates in keeping device sharpness and forestalls chip recutting, main to higher machining accuracy.
Application Methods
Flood Application: This approach entails making use of a big quantity of slicing fluid immediately to the slicing zone. It presents powerful cooling and chip elimination for high-velocity machining.
Mist Application: Cutting fluid is atomized right into a pleasant mist and directed in the direction of the slicing area. This approach is beneficial for lowering fluid intake even as nonetheless imparting ok lubrication and cooling.
Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL): This approach makes use of a minimum quantity of slicing fluid, generally withinside the shape of a pleasant spray, to offer focused lubrication. It is powerful in lowering fluid utilization and environmental effect even as keeping device performance.
Freqently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a single point cutting tool?
A single point cutting tool has one main cutting edge used for machining operations like turning and shaping. It is ideal for creating external surfaces and complex shapes on a rotating workpiece.
Q2. What are the main components of a single point cutting tool?
The main components are the tool shank (for mounting), tool face (where cutting occurs), tool flank (provides clearance), tool nose (the pointed end), and tool base (foundation of the tool).
Q3. What materials are commonly used for single point cutting tools?
Common materials include High-Speed Steel (HSS) for general use, Carbides for high-speed machining, Ceramics for hard materials, Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) for very hard materials, and Diamond for precision cutting of extremely hard materials.
Q4. How does cutting speed affect tool life?
Higher cutting speeds increase the temperature at the cutting edge, which can accelerate tool wear. Optimal cutting speed balances performance with tool longevity.
Q5. What is the purpose of tool coatings?
Tool coatings, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Diamond coatings, enhance hardness, wear resistance, and reduce friction, improving tool performance and extending tool life.






